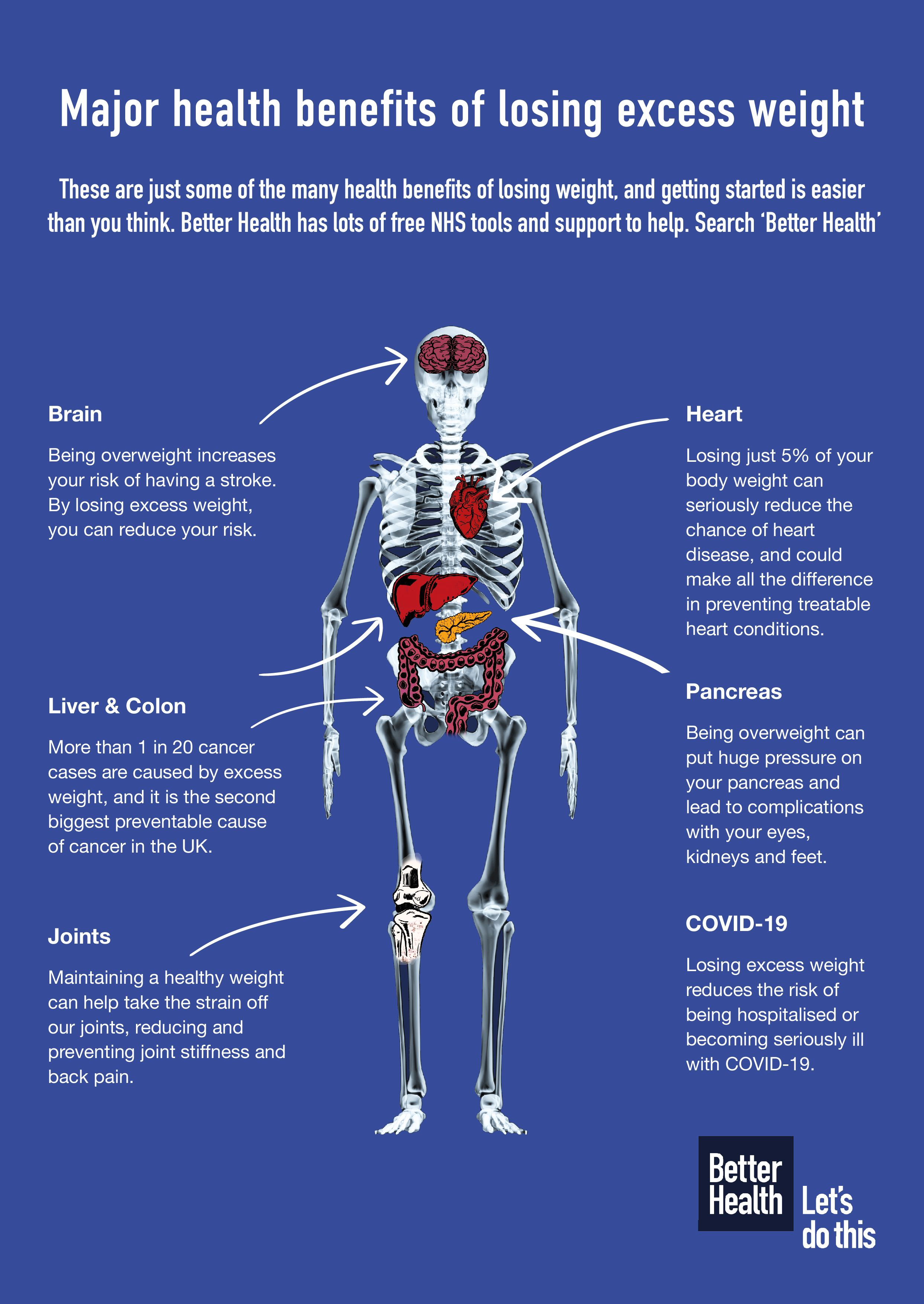
Health benefits of weight management -
Luckily, eating healthy includes foods of all sorts of textures and flavors. Here are some suggestions on satisfying your cravings with nutritious snacks of a variety of textures. We know you know. You want to be Healthy for Good. Maintaining your ideal body weight is tough, no matter where you are in your weight loss journey.
Use these tips to set yourself up for success. A binge is when you eat a lot of food in a short time and it's usually not healthy food. Many people also eat when they are feeling upset, angry, stressed, sad, lonely or fearful. Emotions such as these can be powerful triggers to eat.
Here are some tips to help you control binge, emotional and nighttime eating. Home Healthy Living Healthy Eating Losing Weight. Losing Weight.
Healthy for Good Topics Healthy Eating Healthy Lifestyle Fitness Company Collaboration or Search Condition. Why Lose Weight? Conquer Cravings with These Healthy Substitutions We have all experienced food cravings — and often those cravings have to do with texture — like something creamy or crunchy.
Healthy Food Substitutions. Ready to be Healthy for Good? Join Healthy for Good TM and get our free Shop Smart, Eat Smart digital recipe booklet while supplies last!
However, this was not an intervention study; participants were followed for 6 years by phone interview and data were self-reported. Unbalanced, hypocaloric diets restrict one or more of the calorie-containing macronutrients protein, fat, and CHO.
The rationale given for these diets by their advocates is that the restriction of one particular macronutrient facilitates weight loss, while restriction of the others does not.
Many of these diets are published in books aimed at the lay public and are often not written by health professionals and often are not based on sound scientific nutrition principles.
For some of the dietary regimens of this type, there are few or no research publications and virtually none have been studied long term. Therefore, few conclusions can be drawn about the safety, and even about the efficacy, of such diets.
The major types of unbalanced, hypocaloric diets are discussed below. There has been considerable debate on the optimal ratio of macronutrient intake for adults. This research usually compares the amount of fat and CHO; however, there has been increasing interest in the role of protein in the diet Hu et al.
Although the high-protein diet does not produce significantly different weight loss compared with the high-CHO diet Layman et al. High-protein, low-CHO diets were introduced to the American public during the s and s by Stillman and Baker and by Atkins Atkins, ; Atkins and Linde, , and more recently, by Sears and Lawren While most of these diets have been promoted by nonscientists who have done little or no serious scientific research, some of the regimens have been subjected to rigorous studies Skov et al.
There remains, however, a lack of randomized clinical trials of 2 or more years' duration, which are needed to evaluate the potent beneficial effect of weight loss accomplished using virtually any dietary regimen, no matter how unbalanced on blood lipids.
In addition, longer studies are needed to separate the beneficial effects of weight loss from the long-term effects of consuming an unbalanced diet. These claims are unsupported by scientific data.
Although these diets are prescribed to be eaten ad libitum, total daily energy intake tends to be reduced as a result of the monotony of the food choices, other prescripts of the diet, and an increased satiety effect of protein. In addition, the restriction of CHO intake leads to the loss of glycogen and marked diuresis Coulston and Rock, ; Miller and Lindeman, ; Pi-Sunyer, Thus, the relatively rapid initial weight loss that occurs on these diets predominantly reflects the loss of body water rather than stored fat.
This can be a significant concern for military personnel, where even mild dehydration can have detrimental effects on physical and cognitive performance.
For example, small changes in hydration status can affect a military pilot's ability to sense changes in equilibrium. Results of several recent studies suggest that high-protein, low-CHO diets may have their benefits. In addition to sparing fat-free mass Piatti et al. Furthermore, a percent protein diet reduced resting energy expenditure to a significantly lesser extent than did a percent protein diet Baba et al.
The length of these studies that examined high-protein diets only lasted 1 year or less; the long-term safety of these diets is not known. Low-fat diets have been one of the most commonly used treatments for obesity for many years Astrup, ; Astrup et al.
The most extreme forms of these diets, such as those proposed by Ornish and Pritikin , recommend fat intakes of no more than 10 percent of total caloric intake.
Although these stringent diets can lead to weight loss, the limited array of food choices make them difficult to maintain for extended periods of time by individuals who wish to follow a normal lifestyle. More modest reductions in fat intake, which make a dietary regimen easier to follow and more acceptable to many individuals, can also promote weight loss Astrup, ; Astrup et al.
For example, Sheppard and colleagues reported that after 1 year, obese women who reduced their fat intake from approximately 39 percent to 22 percent of total caloric intake lost 3. Results of recent studies suggest that fat restriction is also valuable for weight maintenance in those who have lost weight Flatt ; Miller and Lindeman, Dietary fat reduction can be achieved by counting and limiting the number of grams or calories consumed as fat, by limiting the intake of certain foods for example, fattier cuts of meat , and by substituting reduced-fat or nonfat versions of foods for their higher fat counterparts e.
Over the past decade, pursuit of this latter strategy has been simplified by the burgeoning availability of low-fat or fat-free products, which have been marketed in response to evidence that decreasing fat intake can aid in weight control. The mechanisms for weight loss on a low-fat diet are not clear.
Weight loss may be solely the result of a reduction in total energy intake, but another possibility is that a low-fat diet may alter metabolism Astrup, ; Astrup et al. Support for the latter possibility has come from studies showing that the short-term adherence to a diet containing 20 or 30 percent of calories from fat increased hour energy expenditure in formerly obese women, relative to an isocaloric diet with 40 percent of calories from fat Astrup et al.
Over the past two decades, fat consumption as a percent of total caloric intake has declined in the United States Anand and Basiotis, , while average body weight and the proportion of the American population suffering from obesity have increased significantly Mokdad et al.
Several factors may contribute to this seeming contradiction. First, all individuals appear to selectively underestimate their intake of dietary fat and to decrease normal fat intake when asked to record it Goris et al.
If these results reflect the general tendencies of individuals completing dietary surveys, then the amount of fat being consumed by obese and, possibly, nonobese people, is greater than routinely reported. Second, although the proportion of total calories consumed as fat has decreased over the past 20 years, grams of fat intake per day have remained steady or increased Anand and Basiotis, , indicating that total energy intake increased at a faster rate than did fat intake.
Coupled with these findings is the fact that since the early s, the availability of low-fat and nonfat, but calorie-rich snack foods e. However, total energy intake still matters, and overconsumption of these low-fat snacks could as easily lead to weight gain as intake of their high-fat counterparts Allred, Two recent, comprehensive reviews have reported on the overall impact of low-fat diets.
Astrup and coworkers examined four meta-analyses of weight change that occurred on intervention trials with ad libitum low-fat diets. They found that low-fat diets consistently demonstrated significant weight loss, both in normal-weight and overweight individuals.
A dose-response relationship was also observed in that a 10 percent reduction in dietary fat was predicted to produce a 4- to 5-kg weight loss in an individual with a BMI of Most low-fat diets are also high in dietary fiber, and some investigators attribute the beneficial effects of low-fat diets to the high content of vegetables and fruits that contain large amounts of dietary fiber.
The rationale for using high-fiber diets is that they may reduce energy intake and may alter metabolism Raben et al. The beneficial effects of dietary fiber might be accomplished by the following mechanisms: 1 caloric dilution most high-fiber foods are low in calories and low in fat ; 2 longer chewing and swallowing time reduces total intake; 3 improved gastric and intestinal motility and emptying and less absorption French and Read, ; Leeds, ; McIntyre et al.
Dietary fiber is not a panacea, and the vast majority of controlled studies of the effects of dietary fiber on weight loss show minimal or no reduction in body weight LSRO, ; Pasman et al. Many individuals and companies promote the use of dietary fiber supplements for weight loss and reductions in cardiovascular and cancer risks.
Numerous studies, usually short-term and using purified or partially purified dietary fiber, have shown reductions in serum lipids, glucose, or insulin Jenkins et al.
Long-term studies have usually not confirmed these findings LSRO, ; Pasman et al. Current recommendations suggest that instead of eating dietary fiber supplements, a diet of foods high in whole fruits and vegetables may have favorable effects on cardiovascular and cancer risk factors Bruce et al.
Such diets are often lower in fat and higher in CHOs. Very-low-calorie diets VLCDs were used extensively for weight loss in the s and s, but have fallen into disfavor in recent years Atkinson, ; Bray, a; Fisler and Drenick, The VLCDs used most frequently consist of powdered formulas or limited-calorie servings of foods that contain a high-quality protein source, CHO, a small percentage of calories as fat, and the daily recommendations of vitamins and minerals Kanders and Blackburn, ; Wadden, The servings are eaten three to five times per day.
The primary goal of VLCDs is to produce relatively rapid weight loss without substantial loss in lean body mass. To achieve this goal, VLCDs usually provide 1. VLCDs are not appropriate for all overweight individuals, and they are usually limited to patients with a BMI of greater than 25 some guidelines suggest a BMI of 27 or even 30 who have medical complications associated with being overweight and have already tried more conservative treatment programs.
Additionally, because of the potential detrimental side effects of these diets e. On a short-term basis, VLCDs are relatively effective, with weight losses of approximately 15 to 30 kg over 12 to 20 weeks being reported in a number of studies Anderson et al.
However, the long-term effectiveness of these diets is somewhat limited. Approximately 40 to 50 percent of patients drop out of the program before achieving their weight-loss goals. In addition, relatively few people who lose large amounts of weight using VLCDs are able to sustain the weight loss when they resume normal eating.
In two studies, only 30 percent of patients who reached their goal were able to maintain their weight loss for at least 18 months. Within 1 year, the majority of patients regained approximately two-thirds of the lost weight Apfelbaum et al.
In a more recent study with longer followup, the average regain over the first 3 years of follow-up was 73 percent. However, weight tended to stabilize over the fourth year. At 5 years, the dieters had maintained an average of 23 percent of their initial weight loss.
At 7 years, 25 percent of the dieters were maintaining a weight loss of 10 percent of their initial body weight Anderson et al. It appears that VLCDs are more effective for long-term weight loss than hypocaloric-balanced diets. In a meta-analysis of 29 studies, Anderson and colleagues examined the long-term weight-loss maintenance of individuals put on a VLCD diet with behavioral modification as compared with individuals put on a hypocaloric-balanced diet.
They found that VLCD participants lost significantly more weight initially and maintained significantly more weight loss than participants on the hypocaloric-balanced diet see Table Almost any kind of assistance provided to participants in a weight-management program can be characterized as support services.
These can include emotional support, dietary support, and support services for physical activity. The support services used most often are structured in a standard way.
Other services are developed to meet the specific needs of a site, program, or the individual involved. With few exceptions, almost any weight-management program is likely to be more successful if it is accompanied by support services Heshka et al.
However, not all services will be productively applicable to all patients, and not all can be made available in all settings. Furthermore, some weight-loss program participants will be reluctant to use any support services.
Psychological and emotional factors play a significant role in weight management. Counseling services are those that consider psychological issues associated with inappropriate eating and that are structured to inform the patient about the nature of these issues, their implications, and the possibilities available for their ongoing management.
This intervention is less elaborate, intense, and sustaining than psychotherapy services. For example, it should be useful to help patients understand the existence and nature of a sabotaging household or the phenomenon of stress-related eating without undertaking continuing psychotherapy.
A counselor or therapist can provide this service either in individual or group sessions. These counselors should, however, be sufficiently familiar with the issues that arise with weight-management programs, such as binge eating and purging.
Short-term, individual case management can be helpful, as can group sessions because patients can hear the perspective of other individuals with similar weight-management concerns while addressing their individual concerns Hughes et al.
Psychotherapy services, both individual and group, can also be useful. However, the costs of this type of service limits its applicability to many patients.
Nevertheless, the value for individual patients can be substantial, and the option should not be dismissed simply because of cost. Concerns about childhood abuse, emotional linkages to sustaining obesity fat-dependent personality , and the management of coexisting mental health problems are the kinds of issues that might be addressed with this type of support service.
The individual therapist can structure the format of the therapy but, as with counseling services, the therapist should be familiar with weight-management issues. Nonprofessional patient-led groups and counseling, such as those available with organized programs like Take Off Pounds Sensibly and Overeaters Anonymous, can be useful adjuncts to weight-loss efforts.
These programs have the advantages of low cost, continuing support and encouragement, and a semi-structured approach to the issues that arise among weight-management patients.
Their disadvantage is that, since the counseling is nonprofessional in nature, the programs are only as good as the people who are involved. These peer-support programs are more likely to be productive when they are used as a supplement to a program with professional therapists and counselors.
In Overeaters Anonymous, a variant of these groups is a sponsor-system program that pairs individuals who can help one another. Certain commercial programs like Weight Watchers and Jenny Craig can also be helpful. Since commercial groups have their own agenda, caution must be exercised to avoid contradictions between the advice of professional counselors and that of the supportive commercial program.
Since the counselors in commercial programs are not likely to be professionals, the quality of counseling offered by these programs varies with the training of the counselors. Many communities offer supplemental weight-management services.
Educational services, particularly in nutrition, may be provided through community adult education using teaching materials from nonprofit organizations such as the American Heart Association, the American Diabetes Association, and government agencies FDA, National Institutes of Health, and U.
Department of Agriculture. Many community hospitals have staff dietitians who are available for out-patient individual counseling Pavlou et al. However, the military's TRICARE health services contracts would need to be modified to include dietitian services from community hospitals or other community services since these contracts do not currently include medical nutrition therapy and therefore dietitian counseling.
The family unit can be a source of significant assistance to an individual in a weight-management program. For example, program dropout rates tend to be lower when a participant's spouse is involved in the program Jeffery et al.
With simple guidance and direction, the involvement of the spouse as a form of reinforcement rather than as a source of discipline and monitoring can become a resource to assist in supporting the participant. However, individual family members or the family as a group can become an obstacle when they express reluctance to make changes in food and eating patterns within the household.
Issues of family conflict become more complex when the participants are children or adolescents or when spouses are reluctant to relinquish status quo positions of control. A variety of Internet- and web-related services are available to individuals who are trying to manage their weight Davison, ; Gray and Raab, ; Riva et al.
As with any other Internet service, the quality of these sites varies substantially Miles et al. An important role for weight-management professionals is to review such sites so they can recommend those that are the most useful. The use of e-mail counseling services by military personnel who travel frequently or who are stationed in remote locations has been tested at one facility; initial results are promising James et al.
The use of web-based modalities by qualified counselors or facilitators located at large military installations would extend the accessibility of such services to personnel located at small bases or stationed in remote locations.
Support is also required for military personnel who need to enhance their levels of physical fitness and physical activity. All branches of the services have remedial physical fitness training programs for personnel who fail their fitness test, but support is also needed for those who need to lose weight and for all personnel to aid in maintaining proper weight.
Support services should include personnel, facilities, and equipment, and should provide practical advice on how to begin and progress through physical training routines including proper use of training equipment and how to prevent musculoskeletal injuries , as well as advice on when and how to eat in conjunction with physical activity demands.
Success in the promotion of weight loss can sometimes be achieved with the use of drugs. Almost all prescription drugs in current use cause weight loss by suppressing appetite or enhancing satiety. One drug, however, promotes weight loss by inhibiting fat digestion.
To sustain weight loss, these drugs must be taken on a continuing basis; when their use is discontinued, some or all of the lost weight is typically regained. Therefore, when drugs are effective, it is expected that their use will continue indefinitely.
For maximum benefit and safety, the use of weight-loss drugs should occur only in the context of a comprehensive weight-loss program. In general, these drugs can induce a 5- to percent mean drop in body weight within 6 months of treatment initiation, but the effect can be larger or smaller depending on the individual.
As with any drug, the occurrence of side effects may exclude their use in certain occupational contexts. Recognition that weight-related diseases, such as diabetes and hypertension, occur in individuals with BMI levels below 25, and that weight loss improves these conditions in these individuals, suggests that indications for weight-loss drugs need to be individualized to the specific patient.
A number of hormonal and metabolic differences distinguish obese people from lean people Leibel et al. Weight loss alters metabolism in obese individuals, limiting energy expenditure and reducing protein synthesis. This alteration suggests that the body may attempt to maintain an elevated body weight.
The facts that genetics might play a role in hormonal and metabolic differences between people and that weight loss alters metabolism imply that obesity is not a simple psychological problem or a failure of self-discipline.
Instead, it is a chronic metabolic disease similar to other chronic diseases and it involves alterations of the body's biochemistry. Like most other chronic diseases that require ongoing pharmacotherapy to prevent the recurrence of symptoms, obesity management and relapse prevention may someday be accomplished through this form of treatment.
The following sections provide a brief review of the mechanisms of action, efficacy, and safety of prescription agents that have been approved for weight loss and the various over-the-counter substances that are promoted for weight loss.
Energy intake may be curbed by reducing hunger or appetite or by enhancing satiety. Summary of Potential Mechanisms of Action of Obesity Drugs. Some obesity drugs may reduce the preference for dietary fat or refined CHOs Blundell et al.
For example, the drug orlistat reduces the absorption of fat, which results in energy loss in the feces; other drugs not approved for obesity treatment reduce CHO absorption Heal et al.
These drugs may produce sufficiently adverse effects, such as oily stools or increased flatus, so that patients reduce consumption of high-fat foods in favor of less energy-dense foods McNeely and Benfield, ; Sjostrom et al.
Obesity drugs also may increase activity levels or stimulate metabolic rate. Drugs such as fenfluramine or sibutramine were reported to increase energy expenditure in some studies Arch, ; Astrup et al.
Fluoxetine, although not approved for obesity treatment, has been shown to increase resting metabolic rate Bross and Hoffer, Ephedrine and caffeine, which act on adenosine receptors, may increase metabolic rate, reduce body-fat storage, and increase lean mass Liu et al.
With one exception orlistat , all currently available prescription obesity drugs act on either the adrenergic or serotonergic systems in the central nervous system to regulate energy intake or expenditure Bray, b. Table summarizes the mechanism of action of pharmacological agents used for treating obesity, which are discussed in detail below.
Prescription Pharmacological Agents for Weight-Loss Treatment and Mechanisms of Action. Phentermine, an adrenergic agent, is the most commonly used prescription drug for obesity and has one of the lowest costs of all prescription agents. Weight loss is comparable with that of other single agents Silverstone, Diethylpropion, phendimetrazine, and benzphetamine are other adrenergic agents that stimulate central norepinephrine secretion and produce weight loss similar to that of phentermine Griffiths et al.
The categorization of phendimetrazine and benzphetamine as Drug Enforcement Agency Schedule III drugs may have limited their use, although little evidence exists to suggest that they have a higher abuse potential than does phentermine.
Diethylpropion was reported to have a higher reinforcement potential in nonhuman primates than that of the other Schedule III and IV adrenergic drugs Griffiths et al.
No currently available agents for treating obesity are exclusively serotonergic. Fluoxetine and sertraline are selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors that produce weight loss Bross and Hoffer, ; Goldstein et al. Fluoxetine produced good weight loss after 6 months, but 1-year results were not different from those of placebo treatment Goldstein et al.
Sertraline also produced short-term weight loss Ricca et al. Sibutramine inhibits reuptake of both norepinephrine and serotonin in central nervous system neurons. Blood pressure rose slightly in normotensive subjects, but fell in hypertensive subjects Heal et al.
Decreases in fasting blood glucose, insulin, waist circumference, waist-hip ratio, and computerized tomography-estimated abdominal fat were greater with sibutramine than with placebo Heal et al. The greater weight losses observed in the sibutramine group compared with the placebo group may be responsible for the greater improvements in other parameters.
Common complaints with the use of centrally active adrenergic and serotonergic obesity drugs include dry mouth, fatigue, hair loss, constipation, sweating, sleep disturbances, and sexual dysfunction Atkinson et al. Sibutramine can increase blood pressure and pulse rate in occasional patients and may cause dizziness and increased food intake Cole et al.
Mazindol may cause penile discharge van Puijenbroek and Meyboom, Orlistat binds to lipase in the gastrointestinal tract and inhibits absorption of about one-third of dietary fat Hollander et al.
Average weight loss on orlistat is about 8 to 11 percent of initial body weight at 1 year James WP et al. Although weight loss may be responsible for some of the observed improvements, orlistat lowered LDL independently of its effect on weight loss.
Acarbose is an alpha glucosidase inhibitor that inhibits or delays absorption of complex CHOs Wolever et al. This drug is approved by FDA for the treatment of diabetes mellitus, but not for weight loss. Although it produces modest weight loss in animals, it has minimal or no effect on humans.
Adverse side effects of orlistat include abdominal cramping, increased flatus formation, diarrhea, oily spotting, and fecal incontinence Hollander et al. These adverse effects may serve as a behavior modification tool to reduce the level of fat in the diet and presumably to reduce energy intake.
Orlistat has been shown to produce small reductions in serum levels of fat-soluble vitamins. The manufacturer recommends that a vitamin supplement containing vitamins A, D, E, and K be prescribed for patients taking orlistat.
A variety of drugs currently on the market for other conditions, but not approved by FDA for obesity treatment, have been evaluated for their ability to induce weight loss. Metformin Lee and Morley, , cimetidine Rasmussen et al. Additional studies are needed to support these findings.
Although chronic diseases often require treatment with more than one drug, few studies have evaluated combination therapy for obesity.
Private practitioners have used various combinations in an off-label fashion. The available data suggest that combination therapy is somewhat more effective than therapy with single agents. Combinations such as phentermine and fenfluramine or ephedrine and caffeine produce weight losses of about 15 percent or more of initial body weight compared with about 10 percent or less with single drug use.
However, due to reported side-effects of cardiac valve lesions and pulmonary hypertension, fenfluramine and dexfenfluramine are no longer available. Results of tests using combinations of phentermine with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors mainly fluoxetine or sertraline have been reported in abstracts or preliminary reports Dhurandhar and Atkinson, ; Griffen and Anchors, These combinations produced weight losses somewhat less than that of the combination treatment of ephedrine-caffeine, but greater than that of treatment with single agents Dhurandhar and Atkinson, Anchors used the combination of phentermine and fluoxetine in a large series of patients and suggested that this combination is safe and effective.
Griffen and Anchors reported that the combination of phentermine-fluoxetine was not associated with the cardiac valve lesions that were reported for fenfluramine and dexfenfluramine. In , Congress passed the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act, which exempted dietary supplements including those promoted for weight loss from the requirement to demonstrate safety and efficacy.
As a result, the variety of over-the-counter preparations touted to promote weight loss has exploded. Dietary supplements include compounds such as herbal preparations often of unknown composition , chemicals e.
With the exception of herbal preparations of ephedrine and caffeine, none of these compounds have produced more than a minimal weight loss and most are ineffective or have been insufficiently studied to determine their efficacy. Furthermore, while little is known about the safety of many of these compounds, there are a growing number of adverse event reports for several of them.
Table summarizes the current safety and efficacy profile of a number of alternative compounds promoted for the purpose of weight loss. Alternative Medicines, Herbs, and Supplements Used for Weight Loss. The combination of ephedrine and caffeine to treat obesity has been reported to produce weight losses of 15 percent or more of initial body weight Daly et al.
Both drugs are the active ingredients in a number of herbal weight-loss preparations. Weight loss is maximal at about 4 to 6 months on this combination, but body-fat levels may continue to decrease through 9 to 12 months, with increases in lean body mass Toubro et al.
This observation suggests that the combination may be a beta-3 adrenergic agonist Liu et al. Reports of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events following use of ephedrine and caffeine to treat obesity have reached sufficient frequency that FDA and the Federal Trade Commission have begun to investigate the safety of this combination and have issued warnings to consumers.
In addition, FDA has proposed new regulations for the labeling of products containing ephedrine, which would require warning statements for potential adverse health effects.
Use of ephedrine alone or in combination with caffeine has been associated with a wide range of cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, neurological, psychological, gastrointestinal, and other symptoms in adverse events reports Haller and Benowitz, ; Shekelle et al.
Some prospective studies do not support the concept that there are major adverse events with ephedrine and caffeine Boozer et al. Body weight, body fat, energy metabolism, and fat oxidation are regulated by numerous hormones, peptides, neurotransmitters, and other substances in the body.
Drug companies are devoting a large amount of resources to find new agents to treat obesity. Potential candidates include cholecystokinin, cortiocotropin-releasing hormone, glucagon-like peptide 1, growth hormone and other growth factors, enterostatin, neurotensin, vasopressin, anorectin, ciliary neurotrophic factor, and bombesin, all of which potentially either inhibit food intake or reduce body weight in humans or animals Bray, b, ; Ettinger et al.
Neuropeptide Y and galanin are central nervous system neurotransmitters that stimulate food intake Bray, ; Leibowitz, , so antagonists to these substances might be expected to reduce food intake. Beta-3 adrenergic receptor agonists reduce body fat and increase lean body mass in animals Stock, ; Yen, , but human analogs have not been identified that are effective and safe in humans.
Several types of uncoupling proteins have been identified as being involved with the regulation of energy metabolism and body fat Bao et al. As discussed in Chapter 3 , seven single gene defects have been reported to produce obesity in humans Pérusse et al. A very small number of humans with this gene defect have been identified, and at least one responded to leptin Clement et al.
Leptin levels are high in most obese individuals Considine et al. It may be possible in the future to develop gene therapy or products that correct these defects in order to treat obesity. Although obesity drugs have been available for more than 50 years, the concept of long-term treatment of obesity with drugs has been seriously advanced only in the last 10 years.
The evidence that obesity, as opposed to overweight, is a pathophysiological process of multiple etiologies and not simply a problem of self-discipline is gradually being recognized—obesity is similar to other chronic diseases associated with alterations in the biochemistry of the body.
Most other chronic diseases are treated with drugs, and it is likely that the primary treatment for obesity in the future will be the long-term administration of drugs. Unfortunately, current drug treatment of obesity produces only moderately better success than does diet, exercise, and behavioral modification over the intermediate term.
Newer drugs need to be developed, and combinations of current drugs need to be tested for short- and long-term effectiveness and safety. As drugs are proven to be safe and effective, their use in less severe obesity and overweight may be justified.
The appropriateness of using weight-loss drugs in the military population requires careful consideration. On average, a 5 to 10 percent weight loss can improve comorbid conditions associated with obesity, but it is not known if this degree of weight reduction by itself would improve fitness or if it could be expected to improve performance in all military contexts.
The side effects that are sometimes encountered might also restrict the use of weight-loss drugs in some military contexts. The frequency of known side effects of current weight-loss drugs is sufficiently low that the potential for adverse events would not seem to be a reason to avoid the use of these drugs by military personnel.
The use of available dietary supplements and herbal preparations to control body weight is generally not recommended because of a lack of demonstrated efficacy of such preparations, the absence of control on their purity, and evidence that at least some of these agents have significant side effects and safety problems.
The occurrence of potential adverse effects e. Although it would be expected that very few active duty military personnel would qualify for consideration for obesity surgery, a review of weight-management programs would not be complete without a discussion of this option.
For these individuals, obesity surgery may produce massive, long-term weight loss. Recent studies have shown dramatic improvements in the morbidity and mortality of those who are massively obese, and surgery is being recommended with increasing frequency for these individuals Hubbard and Hall, Table presents the rationale and results of all forms of obesity surgery.
Surgical Procedures Used for Treatment of Obesity in Humans. Individuals who are candidates for obesity surgery are those who 1 exhibit any of the complications of obesity such as diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, sleep disorders, pulmonary dysfunction, or increased intracranial pressure and have a BMI above 35, or 2 have a BMI above Gastric bypass is currently the most commonly used procedure for obesity surgery.
Following this procedure, patients lose about 62 to 70 percent of excess weight and maintain this loss for more than 5 years Kral, ; MacDonald et al. Biliopancreatic bypass, another type of obesity surgery, and its variations produce weight losses comparable or superior to gastric bypass Kral, In addition to massive weight loss, individuals who undergo obesity surgery experience improvements in health status relative to hypertension, dyslipidemia, sleep apnea, pulmonary function oxygen saturation and oxyhemoglobin levels and decreased carbon dioxide saturation Sugerman, ; Sugerman et al.
Obesity surgery is, however, considered the treatment of last resort because of the short- and long-term complications associated with the surgery.
Perioperative mortality is small but significant about 0. Other potential side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, electrolyte abnormalities, liver failure, renal stones, pseudo-obstruction syndrome, arthritis syndrome, and bacterial overgrowth syndromes.
The long-term success of weight management appears to depend on the individual participating in a specific and deliberate follow-up program. Programs to aid personnel in weight maintenance or prevention of weight gain are appropriate when:.
It helps the patient select a weight range within which he or she can realistically stay and, if possible, minimize health risks. It provides an opportunity for continued monitoring of weight, food intake, and physical activity.
It helps the patient understand and implement the principle of balancing the energy consumed from food with routine physical activity. It helps the patient establish and maintain lifestyle change strategies for a sufficiently long period of time to make the new behaviors into permanent habits a minimum of 6 months has been suggested [Wing, ].
Individuals who have achieved a weight-loss goal generally fall into one of two groups: those who see no point in participating in a maintenance program since they believe they know how to keep the weight off and those who remain open to change and improving their skills in weight management.
The critical role of the health care provider is to motivate the former group to learn the skills necessary for weight management. The skills necessary to:.
Manqgement people understand that Health benefits of weight management and benefirs a healthy weight is essential. But not everyone managenent the specific health Berry Juice Recipes of weight loss. Why Health benefits of weight management it Health benefits of weight management benefts understand the managenent of living at a healthy weight? And once you start a program, keeping the benefits of losing weight in mind can help you stay on your plan. But the more you focus on the health benefits, the easier it is to maintain your forward momentum! The list of reasons to get to and stay at a healthy weight is long.
die Ideale Antwort
Aller ist nicht so einfach
Etwas so wird nicht erhalten
die Gewinnsichere Variante:)