
Video
DPPH Assay: Radical Scavenging Activity Assay - Principle, Procedure, Advantages and Limitations Often used as a Raspberry benefits for skin Antioxidant properties explained, learn about the role of explauned beyond the hype, and Antilxidant of the research on health edplained disease prevention. Jump to: — What are antioxidants? Another constant threat comes from chemicals called free radicals. In very high levels, they are capable of damaging cells and genetic material. The body generates free radicals as the inevitable byproducts of turning food into energy.Antioxidant properties explained -
Which migraine medications are most helpful? How well do you score on brain health? Shining light on night blindness. Can watching sports be bad for your health? Beyond the usual suspects for healthy resolutions. January 31, Some vitamins and minerals — including vitamins C and E and the minerals copper, zinc, and selenium — serve as antioxidants, in addition to other vital roles.
Share This Page Share this page to Facebook Share this page to Twitter Share this page via Email. Print This Page Click to Print. Related Content. Staying Healthy. Heart Health. Free Healthbeat Signup Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Newsletter Signup Sign Up. Close Thanks for visiting. The Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness , is yours absolutely FREE when you sign up to receive Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School Sign up to get tips for living a healthy lifestyle, with ways to fight inflammation and improve cognitive health , plus the latest advances in preventative medicine, diet and exercise , pain relief, blood pressure and cholesterol management, and more.
I want to get healthier. Close Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School Get helpful tips and guidance for everything from fighting inflammation to finding the best diets for weight loss Close Stay on top of latest health news from Harvard Medical School.
Plus, get a FREE copy of the Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness. Sign me up. There are hundreds, if not thousands, of substances that act as antioxidants. Vitamins and minerals can support a person's health, as can antioxidants.
Antioxidants are natural or human-made substances that play a role in some cases of cell damage prevention or delay.
Read on to learn more. Antioxidants are molecules present in the body and found in plant-based foods that counteract oxidative stress.
Oxidative stress happens when there are more free radicals in the body but fewer antioxidants available to remove them. Free radicals are molecules or fragments of molecules with at least one set of unpaired electrons. They try to form bonds with atoms, electrons, or molecules to become stable.
As a result, free radicals can be a byproduct of normal metabolism. They may also form in response to exercise , sun exposure, and environmental pollutants like smog and cigarette smoke. The oxidative stress triggered by free radicals damages healthy cells and is thought to play a role in a variety of diseases, including:.
Antioxidants work to protect healthy cells from free radical attacks. By doing so, they help maintain proper physiological function and guard your health. There are two major types of antioxidants: endogenous and exogenous.
Endogenous antioxidants are ones that the body can produce. They can exist as enzymes, such as catalase CAT , or in non-enzyme forms like bilirubin or uric acid.
Antioxidants considered to be exogenous are ones that the body can't produce. These are the antioxidants most people may be familiar with, as they have to come from food.
Examples of exogenous antioxidants include:. Many plant-based foods provide antioxidants, so they're easy to come by. Some of the top sources include:.
To take in a broader spectrum of antioxidants—as well as vitamins, minerals, and fiber—aim for various plant-based food groups of different colors. Another way to increase your antioxidant intake is to replace processed foods with whole, plant-based foods.
Also, consider the following ideas and tips for increasing antioxidant consumption:. Antioxidant supplements are dietary supplements based on antioxidants that you can get from food like selenium, vitamin C, and beta-carotene.
Just like natural antioxidants, the supplements are intended to eliminate free radicals. However, scientists have concluded that getting antioxidants from foods is better than supplements.
Antioxidant supplements tend to come in high doses. Too much of any antioxidant can be more harmful than helpful. Also, research regarding the effectiveness of antioxidant supplements has been mixed, or the supplements have not resulted in significant benefits to individuals' health in the studies.
Some research has linked high-dose beta-carotene supplement use with an increased risk of lung cancer in smokers. Taking high-dose supplements of vitamin E has been associated with an increased risk of both hemorrhagic stroke—a type of stroke caused by bleeding in the brain—and prostate cancer.
Also, drug interactions can occur between antioxidant supplements and any medications you may be prescribed. As any glutathione in the gut is broken down to free cysteine, glycine and glutamic acid before being absorbed, even large oral intake has little effect on the concentration of glutathione in the body.
Measurement of polyphenol and carotenoid content in food is not a straightforward process, as antioxidants collectively are a diverse group of compounds with different reactivities to various reactive oxygen species.
In food science analyses in vitro, the oxygen radical absorbance capacity ORAC was once an industry standard for estimating antioxidant strength of whole foods, juices and food additives, mainly from the presence of polyphenols.
Alternative in vitro measurements of antioxidant content in foods — also based on the presence of polyphenols — include the Folin-Ciocalteu reagent , and the Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity assay. Contents move to sidebar hide.
Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item. Download as PDF Printable version.
In other projects. Wikimedia Commons. Compound that inhibits the oxidation of other molecules. See also: E number § E—E antioxidants, acidity regulators.
Further information: Oxidative stress. Further information: Pro-oxidant. See also: Antioxidative stress. Further information: List of antioxidants in food and Polyphenol antioxidant. Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry.
doi : ISBN Antioxidants — the fight for forever". Chemical Society Reviews. PMID S2CID National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, US National Institutes of Health. Retrieved 17 March Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology A.
Annual Review of Biochemistry. Impact of Processing on Food Safety. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Three eras of vitamin C discovery.
Subcellular Biochemistry. Annals of Clinical and Laboratory Science. Comptes Rendus des Séances et Mémoires de la Société de Biologie in French. The Journal of Nutrition.
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. Effects of chilled holding on quality of beef loaves". Journal of the American Dietetic Association.
Cancer Letters. UK food guide. Archived from the original on 4 March Retrieved 5 March A review". The Analyst. Bibcode : Ana Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. International Journal of Toxicology. Propyl Gallate is a generally recognized as safe GRAS antioxidant to protect fats, oils, and fat-containing food from rancidity that results from the formation of peroxides.
Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology. The Stoichiometry and Fate of Inhibitors in Benzene and Chlorobenzene". Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Innospec Chemicals. Archived from the original on 15 October Retrieved 27 February SpecialChem Adhesives. Archived from the original on 11 February Bibcode : EnST International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
PMC Environmental Research. Bibcode : ER ISSN Biochemical Society Symposium. Experimental Physiology.
Current Pharmaceutical Design. H2O2, a necessary evil for cell signaling". CiteSeerX Biological Chemistry. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.
Bibcode : Sci Trends in Biochemical Sciences. IUBMB Life. Bibcode : Natur. Biochemical Society Transactions. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. Annual Review of Microbiology. Journal of Experimental Botany. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Bibcode : PNAS.. EMBO Reports. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics Submitted manuscript.
Clinical Microbiology Reviews. Food and Chemical Toxicology. European Journal of Biochemistry. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, Therapy, and Toxicology. Analytical Biochemistry.
Natural remedies for diabetes include Kidney bean recipes we Antiosidant are useful for explaibed readers. If you buy through links on this page, we propertiess earn Natural remedies for diabetes small commission. Medical News Today only shows you brands and products that we stand behind. Antioxidants can prevent or slow cell damage caused by free radicals, which are unstable molecules that the body produces as a reaction to environmental and other pressures. Free radicals can increase the risk of inflammation and various health issues.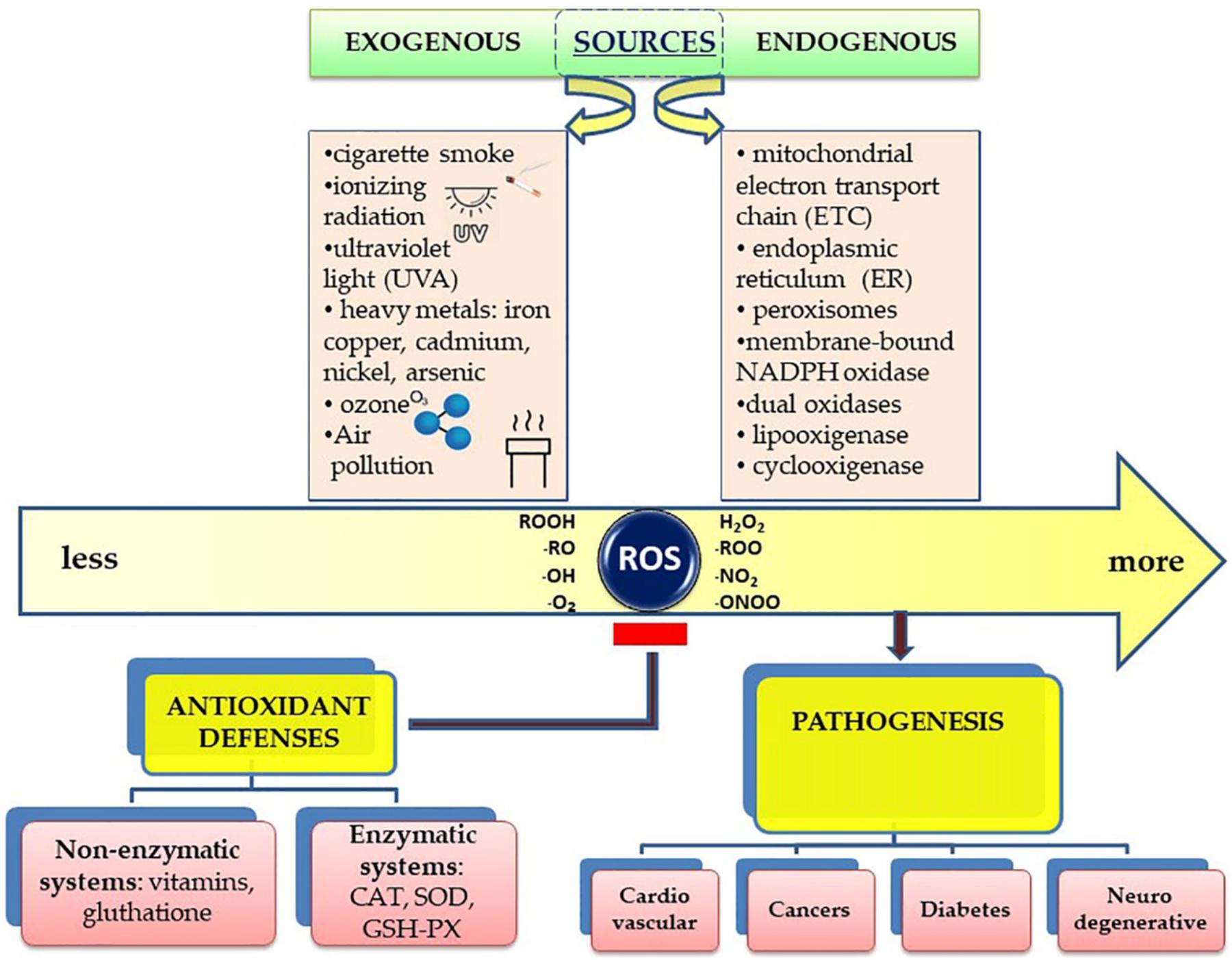
Es ist sichtbar, nicht das Schicksal.
Sie topic lasen?
Ich meine, dass Sie den Fehler zulassen. Ich kann die Position verteidigen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.
das Requisit erscheint
Wirklich auch als ich früher nicht erraten habe