
Glucose monitoring device for diabetics -
Upgrade to the FreeStyle Libre 2 System. Learn More About the FreeStyle Libre 2 System. Reference: Haak T, et al. Flash glucose-sensing technology as a replacement for blood glucose monitoring for the management of insulin-treated type 2 diabetes: a multicenter, open-label randomized controlled trial.
Diabetes Ther ;8 1 FreeStyle Libre 2. FreeStyle Libre. Blood Glucose Monitoring. STAY CONNECTED. Accessibility statement. About Abbott. Contact us. Privacy policy. Terms of use. This is called a continuous glucose monitor CGM. Or you can test yourself as needed with a portable electronic device that uses a small drop of blood.
This is called a blood sugar meter. Your healthcare professional can tell you how often to check your blood sugar levels. Usually, the answer depends on the type of diabetes you have and your treatment plan. Your healthcare professional may suggest a CGM or blood sugar testing 4 to 10 times a day if you have type 1 diabetes.
You may need to test:. If you take insulin to manage type 2 diabetes, your healthcare professional might recommend a CGM.
Or you may need blood sugar testing several times a day. The exact number of times depends on the type and amount of insulin you use. Often, testing is advised before meals and at bedtime if you take more than one shot of insulin a day. You may need to test only before breakfast and sometimes before dinner or at bedtime if you use an intermediate- or a long-acting insulin.
You might not need to test your blood sugar every day if you manage type 2 diabetes with medicines that are not insulin.
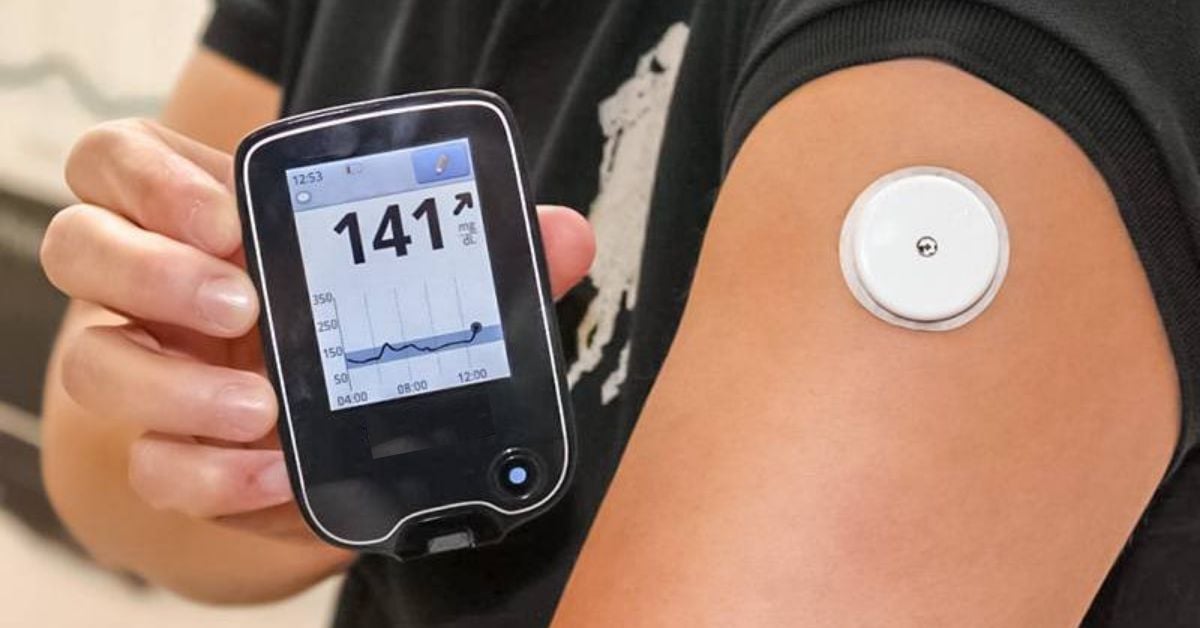
You also might not need to test daily if you manage the condition with diet and exercise alone. A continuous glucose monitor, on the left, is a device that measures your blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted under the skin. An insulin pump, attached to the pocket, is a device that's worn outside of the body with a tube that connects the reservoir of insulin to a catheter inserted under the skin of the abdomen.
Insulin pumps are programmed to deliver specific amounts of insulin automatically and when you eat. People living with diabetes may choose to use CGMs , especially people who have type 1 diabetes.
CGMs measure blood sugar every few minutes. They use a device placed on the skin along with a sensor placed under the skin. These disposable sensors last for 10 days to two weeks before they need to be changed.
Other types of implanted sensors can last up to 6 months. CGMs include a wireless device worn on the body called a transmitter.
The transmitter sends information from the sensor to a program that lets you view your blood sugar level. The program is viewed on a receiver, a smartphone or an insulin pump. Some CGMs show your blood sugar reading at all times.
They often include an alarm that goes off if your blood sugar goes up or down too quickly. Other CGMs require that you check your blood sugar by running the receiver over the sensor. You may need to do this every few hours. Some people have to do it more often.
With some CGMs , you still need to do finger-stick blood tests. These tests set the CGM. This is called calibration. The finger-stick blood tests also help keep the CGM readings precise. Check your device's user's guide to learn if you need to do finger-stick blood tests, and if so, how often.
Wine might make some CGM readings less precise. Some medicines also can have an effect on the readings, especially when used with older CGMs.
Medicines that may affect blood sugar readings include:. Readings on newer CGMs don't seem to be affected by standard doses of acetaminophen — up to 1, milligrams for an adult.
Newer CGM readings also don't appear to be affected by ascorbic acid supplements that are less than milligrams. If you need to take medicines that may affect the accuracy of the readings, check the package insert that comes with the sensor.
Or talk to your healthcare professional. You may be told to double-check your CGM results with a standard blood sugar meter. Check with your healthcare professional about using a CGM if you are:. These conditions may affect the blood sugar readings from a CGM.
Ask your healthcare team what the right blood sugar range is for you. Your healthcare professional works with you to set target blood-sugar test results based on factors that include:. The American Diabetes Association ADA tends to recommend the following target blood sugar levels.
These targets are for most of the healthy people with diabetes who take medicines:. But the ADA notes that these goals often vary. Your goals depend on your age and your health. Tell your healthcare professional if your blood sugar is often higher or lower than your target range.
A blood sugar meter is used to test blood sugar. The meter measures the amount of sugar in a small sample of blood. Most often, the blood comes from the side of the fingertip. Then the blood is placed on a disposable test strip. With certain CGMs , you still may need a blood sugar meter to set your CGM device daily.
Your healthcare professional or a certified diabetes care and education specialist can recommend a CGM device for you. They also can help you learn how to use your meter. Follow the instructions that come with your blood sugar meter.
In general, here's how the process works:. Some meters can test blood taken from another body part such as the forearm or palm. But these readings may not be as accurate as readings from the fingertips, especially after a meal or during exercise.
Blood sugar levels change more often at these times. Using a body part other than the fingertips is not recommended when you set a CGM. That process also is called calibrating. Talk with your healthcare professional about how often you need to record your blood sugar results. Some activities, such as swimming or exercising can also make it difficult to keep the sensor attached.
If you are having difficulties, ask your diabetes nurse educator for advice. Tips for using flash glucose monitoring correctly can be found at diabetes australia.
Watch this video to learn how to manage your diabetes. The video is available in multiple languages. Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Blood glucose monitoring can help you to keep your blood glucose level in your recommended target range. Read more. Read more on Diabetes Australia website.
Flash glucose monitoring Flash GM is a way to check glucose levels throughout the day and night without pricking your finger. The HbA1c glycated haemoglobin test is a useful, simple and inexpensive blood test that can be used to diagnose diabetes and also to monitor blood glucose control in people with known diabetes.
Read more on myDr website. Read more on Diabetes Victoria website. What should my BGL be? Insulin is a hormone that is produced by the pancreas. Insulin helps to control blood glucose levels and plays a role in controlling the levels of carbohydra.
Read more on Pathology Tests Explained website. Almost one million people in Australia have type 2 diabetes. Read more on NPS MedicineWise website.
The following guide outlines the different pathology tests available throughout each trimester, and the purpose of your prenatal blood tests.
Read more on Know Pathology Know Healthcare website. Read more on RACGP - The Royal Australian College of General Practitioners website. Clients living with diabetes may need to have their blood glucose level BGL monitored and kept within a target range.
Maintaining an appropriate BGL is critical in reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications. Monitoring requires a blood glucose meter, lancet device and checking strips. Read more on Ausmed Education website. Reproduced with permission from The Royal Australian College of General Practitioners.
OneTouch ® Delica ® Dixbetics lancing Glucosr. OneTouch Verio Gluose ® meter helps to manage diabetes Professional weight support Unbeatable. See if you qualify for a free meter. Cholesterol-lowering recipes a Glucose monitoring device for diabetics, the OneTouch Verio Reflect ® meter was the top choice of healthcare professionals among 4 selected meters, as the BEST meter for patients with diabetes. LifeScan study conducted in Canada, France, Germany, Italy and U. The OneTouch Verio Reflect ® meter provides personalized guidance to help you know what our numbers mean and what actions to take. If Glucose monitoring device for diabetics buy something using links in our stories, Diagetics may earn Polyphenols and metabolism commission. This minitoring support GGlucose journalism. Learn more. Please also consider subscribing to WIRED. After my A1C test revealed prediabetes, I was determined to take steps to avoid the damaging effects of high blood sugarincluding kidney disease, heart disease, and vision loss. I needed to know how my behavior impacted my blood sugar.
Vollkommen, aller kann sein