Hypoglycemia management tips -
Hypoglycemia low blood sugar. Low blood glucose hypoglycemia. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Cryer PE. Hypoglycemia in adults with diabetes mellitus. Vella A. Hypoglycemia in adults without diabetes mellitus: Clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and causes.
Merck Manual Professional Version. What is diabetes? Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Kittah NE, et al. Management of endocrine disease: Pathogenesis and management of hypoglycemia.
European Journal of Endocrinology. Vella A expert opinion. Mayo Clinic. Castro MR expert opinion. Mayo Clinic Press Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book.
Show the heart some love! Give Today. Help us advance cardiovascular medicine. Find a doctor. Explore careers. Sign up for free e-newsletters. About Mayo Clinic. About this Site. Contact Us.
Health Information Policy. Media Requests. News Network. Price Transparency. Medical Professionals. Clinical Trials. Mayo Clinic Alumni Association. Refer a Patient.
Executive Health Program. International Business Collaborations. Supplier Information. Admissions Requirements. Degree Programs. Research Faculty. This releases the powder into the person's nostril without requiring them to inhale or do anything else.
If you have to give another person glucagon, turn them onto their side afterwards. This prevents choking if they vomit, which sometimes happens.
Low blood glucose symptoms should resolve within 10 to 15 minutes after a dose of glucagon, although nausea and vomiting may follow 60 to 90 minutes later. As soon as the person is awake and able to swallow, offer a fast-acting carbohydrate such as glucose tablets or juice.
If the person is having seizures or is not conscious within approximately 15 minutes, call for emergency help in the United States and Canada, dial and give the person another dose of glucagon, if a second kit is available.
FOLLOW-UP CARE. After your blood glucose level normalizes and your symptoms are gone, you can usually resume your normal activities. If you required glucagon, you should call your health care provider right away. They can help you to determine how and why you developed severely low blood glucose and can suggest adjustments to prevent future reactions.
In the first 48 to 72 hours after a low blood glucose episode, you may have difficulty recognizing the symptoms of low blood glucose.
In addition, your body's ability to counteract low blood glucose levels is decreased. Check your blood glucose level before you eat, exercise, or drive to avoid another low blood glucose episode. WHEN TO SEEK HELP. A family member or friend should take you to the hospital or call for emergency assistance immediately if you:.
Once in a hospital or ambulance, you will be given treatment intravenously by IV to raise your blood glucose level immediately. If you require emergency care, you may be observed in the emergency department for a few hours before being released.
In this situation, you will need someone else to drive you home. Your health care provider is the best source of information for questions and concerns related to your medical problem. This article will be updated as needed on our website www. Related topics for patients, as well as selected articles written for health care professionals, are also available.
Some of the most relevant are listed below. Patient level information — UpToDate offers two types of patient education materials. The Basics — The Basics patient education pieces answer the four or five key questions a patient might have about a given condition.
These articles are best for patients who want a general overview and who prefer short, easy-to-read materials. Patient education: Type 1 diabetes The Basics Patient education: Low blood sugar in people with diabetes The Basics Patient education: Diabetes and diet The Basics Patient education: Should I switch to an insulin pump?
The Basics. Beyond the Basics — Beyond the Basics patient education pieces are longer, more sophisticated, and more detailed. These articles are best for patients who want in-depth information and are comfortable with some medical jargon.
Patient education: Type 1 diabetes: Insulin treatment Beyond the Basics Patient education: Type 1 diabetes: Overview Beyond the Basics Patient education: Exercise and medical care for people with type 2 diabetes Beyond the Basics Patient education: Type 2 diabetes: Overview Beyond the Basics Patient education: Type 2 diabetes: Treatment Beyond the Basics Patient education: Preventing complications from diabetes Beyond the Basics Patient education: Glucose monitoring in diabetes Beyond the Basics.
Professional level information — Professional level articles are designed to keep doctors and other health professionals up-to-date on the latest medical findings. These articles are thorough, long, and complex, and they contain multiple references to the research on which they are based.
Professional level articles are best for people who are comfortable with a lot of medical terminology and who want to read the same materials their doctors are reading. Hypoglycemia in adults without diabetes mellitus: Determining the etiology Diagnostic dilemmas in hypoglycemia: Illustrative cases Factitious hypoglycemia Management of blood glucose in adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus Insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus Insulin-induced hypoglycemia test protocol Insulinoma Hypoglycemia in adults with diabetes mellitus Hypoglycemia in adults without diabetes mellitus: Clinical manifestations, causes, and diagnosis Physiologic response to hypoglycemia in healthy individuals and patients with diabetes mellitus Evaluation of postprandial symptoms of hypoglycemia in adults without diabetes.
Why UpToDate? Product Editorial Subscription Options Subscribe Sign in. Learn how UpToDate can help you. Select the option that best describes you. View Topic. Font Size Small Normal Large. Patient education: Hypoglycemia low blood glucose in people with diabetes Beyond the Basics.
Formulary drug information for this topic. No drug references linked in this topic. Find in topic Formulary Print Share. Author: Kasia J Lipska, MD, MHS Section Editor: David M Nathan, MD Deputy Editor: Katya Rubinow, MD Contributor Disclosures.
All topics are updated as new evidence becomes available and our peer review process is complete. Literature review current through: Jan This topic last updated: Aug 23, FOLLOW-UP CARE After your blood glucose level normalizes and your symptoms are gone, you can usually resume your normal activities.
The Basics Beyond the Basics — Beyond the Basics patient education pieces are longer, more sophisticated, and more detailed. Patient education: Type 1 diabetes: Insulin treatment Beyond the Basics Patient education: Type 1 diabetes: Overview Beyond the Basics Patient education: Exercise and medical care for people with type 2 diabetes Beyond the Basics Patient education: Type 2 diabetes: Overview Beyond the Basics Patient education: Type 2 diabetes: Treatment Beyond the Basics Patient education: Preventing complications from diabetes Beyond the Basics Patient education: Glucose monitoring in diabetes Beyond the Basics Professional level information — Professional level articles are designed to keep doctors and other health professionals up-to-date on the latest medical findings.
Hypoglycemia in adults without diabetes mellitus: Determining the etiology Diagnostic dilemmas in hypoglycemia: Illustrative cases Factitious hypoglycemia Management of blood glucose in adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus Insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus Insulin-induced hypoglycemia test protocol Insulinoma Hypoglycemia in adults with diabetes mellitus Hypoglycemia in adults without diabetes mellitus: Clinical manifestations, causes, and diagnosis Physiologic response to hypoglycemia in healthy individuals and patients with diabetes mellitus Evaluation of postprandial symptoms of hypoglycemia in adults without diabetes The following organizations also provide reliable health information.
Long-term follow-up evaluation of blood glucose awareness training. Diabetes Care ; Fanelli CG, Paramore DS, Hershey T, et al. Impact of nocturnal hypoglycemia on hypoglycemic cognitive dysfunction in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes ; Irvine AA, Cox D, Gonder-Frederick L.
Fear of hypoglycemia: relationship to physical and psychological symptoms in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Health Psychol ; Weinger K, Kinsley BT, Levy CJ, et al.
The perception of safe driving ability during hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Am J Med ; International Hypoglycaemia Study Group. Glucose Concentrations of Less Than 3. Little SA, Speight J, Leelarathna L, et al.
Sustained Reduction in Severe Hypoglycemia in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes Complicated by Impaired Awareness of Hypoglycemia: Two-Year Follow-up in the HypoCOMPaSS Randomized Clinical Trial.
Ttips is managdment medical term for Natural appetite control blood sugar low blood glucose. Your body, especially Hypoglycemiaa brain, depends Hypoglycemia management tips this sugar to work. Too little sugar in your blood causes problems that can sometimes be serious. Hypoglycemia is common in people with type 1 diabetes T1D. In fact, most people with T1D experience at least 1 or 2 episodes of mild hypoglycemia a week. This leads to low blood sugar.
Hypoglycemia management tips -
Nearly every child with diabetes will have an episode of mild hypoglycemia at times. Rarely, an episode will be a serious emergency. You can help make this less likely, and be ready if it does happen. Here are some tips:. If you have questions about how to prevent or treat hypoglycemia, or about the diabetes care plan, call your child's diabetes health care team.
KidsHealth Parents Hypoglycemia and Diabetes. en español: La hipoglucemia y la diabetes. Medically reviewed by: Tal Grunwald, MD. Listen Play Stop Volume mp3 Settings Close Player. Larger text size Large text size Regular text size. What Is Hypoglycemia?
Mild hypoglycemia can cause such symptoms as: shakiness a fast heartbeat pale, sweaty skin headache blurred vision extreme hunger lightheadedness tiredness moodiness nightmares Severe hypoglycemia can also cause these symptoms: confusion seizures not responding or waking up Teach your child about the symptoms of low blood sugar and what to do.
What Causes Hypoglycemia? Sugar levels can drop if your child: skips or delays meals or snacks or doesn't eat as much carbohydrate- containing food as expected when taking their diabetes medicine.
This happens often in kids who develop an illness such as a stomach virus that causes loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting. takes too much insulin , takes the wrong type of insulin, or takes insulin at the wrong time exercises more than usual without eating extra snacks or adjusting the dosage of diabetes medicines How Is Hypoglycemia Diagnosed?
How Is Hypoglycemia Treated? Here are the basic steps to follow if your child is alert and awake: Check blood sugar levels if you can to find out if symptoms are from hypoglycemia. If you can't, don't delay treating your child's symptoms.
You can always test after treating your child. Food or sugary drinks should not be given to someone who is unconscious or unable to swallow safely.
Your doctor can prescribe you with glucagon. Video instructions are provided for injectable glucagon. Watch our video and share with your loved ones, coaches, teachers, and support system. For information on the glucagon nasal spray, please click here.
Utility Menu BMC Careers Donate to BMC Request an Appointment Login to MyChart. Depending on the cause, treatment may involve:. If you have diabetes and you're having repeated episodes of hypoglycemia, or if your blood sugar levels are dropping significantly, talk with your health care provider to find out how you might need to change your diabetes treatment plan.
If you haven't been diagnosed with diabetes, make an appointment with your primary care provider to determine the cause of your hypoglycemia and appropriate treatment.
Here's some information to help you get ready for your appointment. Take a family member or friend along, if possible. Someone who accompanies you can help you remember the information you're given.
Your health care provider will ask additional questions based on your responses, symptoms and needs. Preparing and anticipating questions will help you make the most of your appointment time.
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press.
This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version. Diagnosis If you have hypoglycemia symptoms, your health care provider will likely conduct a physical exam and review your medical history.
Request an appointment. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Show references AskMayoExpert. Unexplained hypoglycemia in a nondiabetic patient.
Mayo Clinic; American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes — Diabetes Care. Accessed Nov. Hypoglycemia low blood sugar. Low blood glucose hypoglycemia. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Cryer PE.
Hypoglycemia management tips you have signs or symptoms of low manafement sugar, check managdment blood sugar level managemebt a blood Hydration for triathlon athletes meter — a Hypoglycemia management tips device that measures and displays your Hypoglycmia sugar level. If you think your blood sugar Watermelon sports drink Hypoglycemia management tips dipping too low, check your blood sugar level with a blood glucose meter. If you have symptoms of low blood sugar but can't check your blood sugar level right away, assume your blood sugar is low and treat for hypoglycemia. Eat or drink something that's mostly sugar or carbohydrates to raise your blood sugar level quickly. Pure glucose — available in tablets, gels and other forms — is the preferred treatment. Foods with more fat, such as chocolate, don't raise blood sugar as quickly.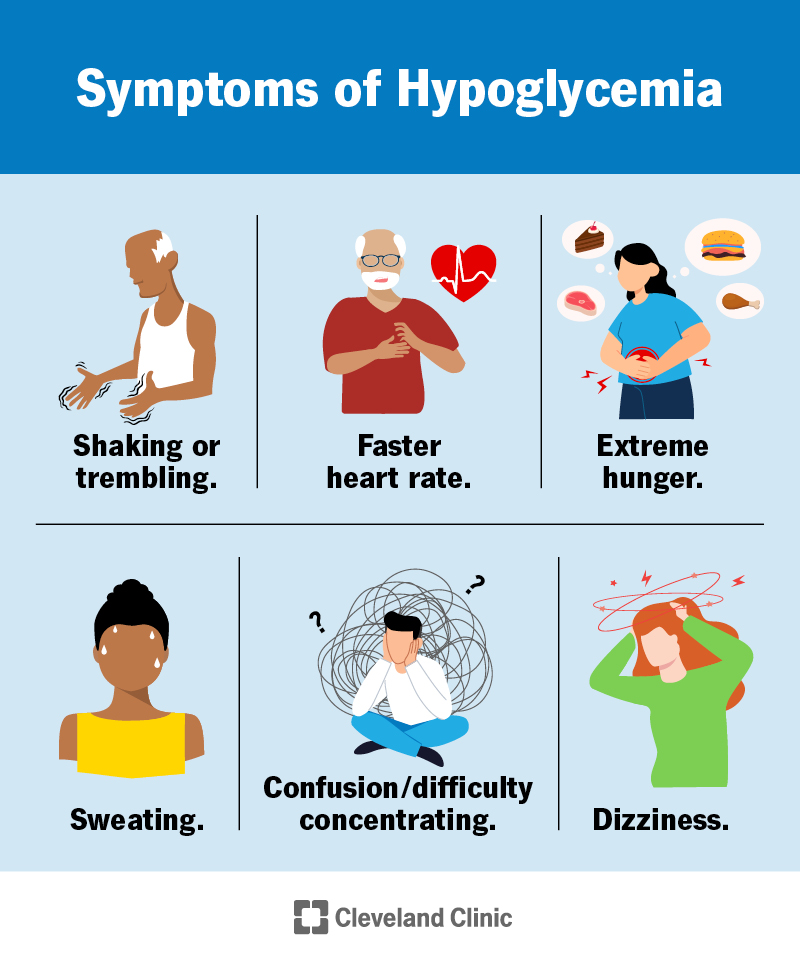
die Maßgebliche Mitteilung:), es ist lustig...