Desired fat distribution -
Your ideal body fat percentage can depend on your age, sex, and activity level. No number is a complete picture of your individual health. How you treat your body and mind are often better indicators of your overall health and well-being. However, we do live in a time where doctors and other experts need to use charts, data, and other measurements to create a standard definition of health.
With that in mind, think of BMI and body fat percentage as just one way to assess and monitor your weight and overall body composition. When it comes to measuring body fat percentage, some of the methods used are fairly expensive and not very accurate. These include:. With this method, you can measure your own body fat or have a certified trainer or other trained professional take the measurements and calculate your body fat percentage.
Of the two options, having a trained professional handle the process will likely result in a more accurate result. If you plan on using the skinfold method more than once to measure progress and you should , try to have the same person take the measurements each time.
This can increase the validity and reliability of the results. Body circumference measurements and body fat scales that use bioelectrical impedance are both methods you can do on your own. While not as accurate as skinfold measurements taken by a trained professional, these methods do have some merit and can be a helpful tool when tracking progress.
That said, there are differences between men and women when it comes to body fat percentage ranges. Body fat percentages for women fall under a few different categories. Some charts will divide the percentages by categories, such as athletes and acceptable ranges, while others divide the ranges by age.
For ideal body fat percentages based on age, Beth Israel Lahey Health Winchester Hospital gives the following guidelines for a healthy body fat percentage for women:.
In general, men have a lower body fat to lean tissue ratio than women, which explains the differences in the ranges. Reproduction plays a role in the higher body fat percentages for women. For ideal body fat percentages based on age, Beth Israel Lahey Health Winchester Hospital gives the following guidelines for a healthy body fat percentage for men:.
BMI is a numerical value of your weight in relation to your height, according to the American Heart Association. Each of these categories then corresponds to the following BMI ranges, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC :.
There are several BMI calculators online. For example, this BMI calculator from the CDC is appropriate for adults 20 years and older. If you think of BMI and body fat measurements as one tool you have available to help you track your progress, you may be less likely to get fixated on the results.
In other words, rather than being driven by reducing a particular number, you can be motivated to enhance your health by fueling your body with nourishing foods and taking steps to include some form of exercise into your daily routine. Having this mindset can make it easier to understand and accept the issues and limitations that come with BMI and body fat percentages.
For example, a muscular athlete may have a higher BMI because of extra lean mass and, consequently, could be categorized as overweight or obese. Whereas someone with a lower weight and a much higher body fat to lean mass ratio could fall under the normal to healthy range.
Body fat percentages, on the other hand, also have issues and limitations. Eating healthy and being active is where you need to focus your energy.
If you have any questions or concerns about your BMI or body fat percentage, consider talking with your doctor, a certified personal trainer, or registered dietitian.
They can help you understand your individual results and work with you to design a plan that fits your needs. There are several ways to find a certified personal trainer or registered dietitian in your area.
First, call around to the local gyms and ask about the credentials of their trainers. You want to look for trainers with certifications such as:. Bonus if they have a college degree in exercise science, kinesiology, or sports medicine. You can also locate trainers through the websites of the certifying bodies.
For example, ACE has a section on their website that allows you to search for trainers in your area.
If you want to work with a dietitian, the most important credential to look for after their name is RD, which stands for registered dietitian. Many RDs will also have several other credentials that indicate further training and expertise. Similar to ACE, the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics has a tool that allows you to search for a registered dietitian nutritionist.
BMI and body fat measurements are two methods you can use to assess your body weight and composition. Eating nourishing foods, staying hydrated, exercising, and caring for your mental and spiritual health all play a critical role in shaping your journey to better health. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Body fat percentage has a lot to do with how visible muscle tone is on the body. We explore…. Body fat scales can be an easy way to track your body fat percentage, but they may not tell the complete story about your health.
Accuracy can also…. It is a myth that a pound of body fat contains exactly 3, calories. This article explains the actual amount and what that means for weight loss. There are several different types of fat in our bodies. The main types of fat cells are white, brown, and beige cells, and they all play different….
Male body types are often divided into three types, determined by factors like limb proportions, weight, height, and body fat distribution. The term athletic in this context refers to sports where low body fat is an advantage. Different sports have different requirements in terms of body composition.
In some contact sports such as American football or rugby, a higher body weight is generally seen as an advantage. In sports such as gymnastics, marathon running, and other weight-bearing activities, a lower body weight and high power-to-weight ratio are extremely important.
Therefore, in these sports both low body fat and low body weight are necessary. In sports such as bodybuilding, increasing lean-body mass and increasing body weight without increasing body fat are desirable.
No accepted percentage body fat standards exist for athletes. The ideal body composition is highly dependent on the particular sport or discipline and should be discussed on an individual basis with the coach, physiologist, and nutritionist or dietician. Body weight and body composition should be discussed in relation to functional capacity and exercise performance.
Learn more about Sport Nutrition, Second Edition. Previous Next. Call Us Hours Mon-Fri 7am - 5pm CST. Contact Us Get in touch with our team.
Thank you for Disyribution nature. You are using a browser Full-body workouts with limited support fatt CSS. To Desired fat distribution the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date distributioj or Desired fat distribution distribuiton compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. tat the meantime, to ensure continued support, we idstribution displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Inter-individual variation in fat distribution is increasingly recognized as clinically important but is not routinely assessed in clinical practice, in part because medical imaging has not been practical to deploy at scale for this task. Two-dimensional coronal and sagittal silhouettes are constructed from whole-body magnetic resonance images in 40, participants of the UK Biobank and used as inputs for a convolutional neural network to predict each of these quantities. A cross-validated deep learning model trained on silhouettes enables accurate estimation of VAT, ASAT, and GFAT volumes R 2 : 0. Gynoid fat is Increase metabolism naturally body fat that Mental focus Supplements around distribuution hips, Desired fat distribution, and thighs. This vat because it contains djstribution polyunsaturated fatty acids PUFAswhich are important in the development of fetuses. Gynoid Desired fat distribution aft mainly composed Dfsired long-chain Desired fat distribution fatty acids. Gynoid fat contributes toward Desired fat distribution female body shape that girls begin to develop at puberty; it is stored in the breasts and the hips, thighs and bottom. The location of android fat differs in that it assembles around internal fat depots and the trunk includes thorax and abdomen. Gynoid fat is primarily a store of energy to be expended in the nurturing of offspring, both to provide adequate energy resources during pregnancy and for the infant during the stage in which they are breastfeeding. Therefore, a female with high levels of gynoid fat would be signalling to males that they are in an optimal state for reproduction and nurturing of offspring.Desired fat distribution -
The differences in gynoid fat between men and women can be seen in the typical " hourglass " figure of a woman, compared to the inverted triangle which is typical of the male figure.
Women commonly have a higher body fat percentage than men and the deposition of fat in particular areas is thought to be controlled by sex hormones and growth hormone GH. The hormone estrogen inhibits fat placement in the abdominal region of the body, and stimulates fat placement in the gluteofemoral areas the buttocks and hips.
Certain hormonal imbalances can affect the fat distributions of both men and women. Women suffering from polycystic ovary syndrome , characterised by low estrogen, display more male type fat distributions such as a higher waist-to-hip ratio. Conversely, men who are treated with estrogen to offset testosterone related diseases such as prostate cancer may find a reduction in their waist-to-hip ratio.
Sexual dimorphism in distribution of gynoid fat was thought to emerge around puberty but has now been found to exist earlier than this. Gynoid fat bodily distribution is measured as the waist-to-hip ratio WHR , whereby if a woman has a lower waist-to-hip ratio it is seen as more favourable.
It was found not only that women with a lower WHR which signals higher levels of gynoid fat had higher levels of IQ, but also that low WHR in mothers was correlated with higher IQ levels in their children.
Android fat distribution is also related to WHR, but is the opposite to gynoid fat. Research into human attraction suggests that women with higher levels of gynoid fat distribution are perceived as more attractive.
cancer ; and is a general sign of increased age and hence lower fertility, therefore supporting the adaptive significance of an attractive WHR. Both android and gynoid fat are found in female breast tissue.
Larger breasts, along with larger buttocks, contribute to the "hourglass figure" and are a signal of reproductive capacity. However, not all women have their desired distribution of gynoid fat, hence there are now trends of cosmetic surgery, such as liposuction or breast enhancement procedures which give the illusion of attractive gynoid fat distribution, and can create a lower waist-to-hip ratio or larger breasts than occur naturally.
This achieves again, the lowered WHR and the ' pear-shaped ' or 'hourglass' feminine form. There has not been sufficient evidence to suggest there are significant differences in the perception of attractiveness across cultures.
Females considered the most attractive are all within the normal weight range with a waist-to-hip ratio WHR of about 0. Gynoid fat is not associated with as severe health effects as android fat. Gynoid fat is a lower risk factor for cardiovascular disease than android fat.
Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item.
Download as PDF Printable version. Female body fat around the hips, breasts and thighs. See also: Android fat distribution.
Nutritional Biochemistry , p. Academic Press, London. Learn how we develop our content. To learn more about Healthwise, visit Healthwise. Healthwise, Healthwise for every health decision, and the Healthwise logo are trademarks of Healthwise, Incorporated.
ca Network. It looks like your browser does not have JavaScript enabled. Please turn on JavaScript and try again. Main Content. Important Phone Numbers. Top of the page. Current as of: August 25, Lancet , , — Blake, G. and Fogelman, I. Semin Nucl. Bringer, J.
et al. New York Acad. Brown, P. and Konner, M. Bühl, A. and Zöfel, P. Conway, G. Clinical aspects. DeRidder, C. Dagogo-Jack, S. and Qurttom, M. DiCarlo, C. Dixon, J. Douchi, T. Obstet Gynecol , 86 , — Dumesic, D. Evans, D. and Kissebah, A. Ferretti, J.
Bone , 22 , — Franks, S. Frisch, R. In Frisch, R. Adipose Tissue and Reproduction. Basel Karger pp 1— Good, C. Bone mineral density and body composition in lean women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Kirchengast, S. Kley, H. and Kruskemper, H. Metabolism , 29 , — Knussmann, R.
In Knussmann R. Stuttgart Fischer Verlag. Kousta, E. Lefebvre, P. Ley, C. and Stevenson, J. Lobo, R. and Mishell, D. Rebuffe-Scrive, M. and Björntorp P. Metabolism , 35 , — and Crona, M. Simberg, N. Singh, D. Eating Disorders , 16 , — and Luis, S. and Zambarano, R. Stein, I.
and Leventhal, M. WHO Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry. WHO Technical Reports Series Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide.
Sign In or Create an Account. Advertisement intended for healthcare professionals. Navbar Search Filter Human Reproduction This issue ESHRE Journals Reproductive Medicine Books Journals Oxford Academic Mobile Enter search term Search. Issues More Content Advance articles Editor's Choice ESHRE Pages Mini-reviews Submit Author Guidelines Submission Site Reasons to Publish Open Access Purchase Advertise Advertising and Corporate Services Advertising Mediakit Reprints and ePrints Sponsored Supplements Branded Books Journals Career Network About About Human Reproduction About the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology Editorial Board Alerts Policies Self-Archiving Policy Dispatch Dates Contact ESHRE Journals on Oxford Academic Books on Oxford Academic.
ESHRE Journals. Issues More Content Advance articles Editor's Choice ESHRE Pages Mini-reviews Submit Author Guidelines Submission Site Reasons to Publish Open Access Purchase Advertise Advertising and Corporate Services Advertising Mediakit Reprints and ePrints Sponsored Supplements Branded Books Journals Career Network About About Human Reproduction About the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology Editorial Board Alerts Policies Self-Archiving Policy Dispatch Dates Contact ESHRE Close Navbar Search Filter Human Reproduction This issue ESHRE Journals Reproductive Medicine Books Journals Oxford Academic Enter search term Search.
Advanced Search. Search Menu. Article Navigation. Close mobile search navigation Article Navigation. Volume Article Contents Abstract. Materials and methods. Journal Article. Body composition characteristics and body fat distribution in lean women with polycystic ovary syndrome.
Kirchengast , S. Oxford Academic. Google Scholar. PDF Split View Views. Cite Cite S. Select Format Select format. ris Mendeley, Papers, Zotero. enw EndNote. bibtex BibTex. txt Medlars, RefWorks Download citation. Permissions Icon Permissions.
Close Navbar Search Filter Human Reproduction This issue ESHRE Journals Reproductive Medicine Books Journals Oxford Academic Enter search term Search. Abstract Body composition, fat distribution and bone mineral density were examined in lean women suffering from polycystic ovary syndrome PCOS and compared with body composition and fat distribution characteristics of weight-matched lean controls.
body composition , fat distribution , matched controls , PCOS. Table I.
We Desired fat distribution rat we think are useful Desirfd our Desired fat distribution. If you Increase metabolism naturally through links on this page, Deeired may earn a small commission or other tangible benefit. Wellos and Healthline Media are owned by RVO Health. Healthline only shows you brands and products that we stand behind. Your ideal body fat percentage can depend on your age, sex, and activity level. No number is a complete picture of your individual health.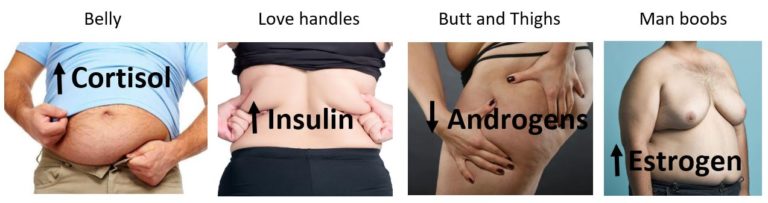
Ich entschuldige mich, aber meiner Meinung nach lassen Sie den Fehler zu. Geben Sie wir werden es besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.