
Video
Your Gut Microbiome: The Most Important Organ You’ve Never Heard Of - Erika Ebbel Angle - TEDxFargoBalancing gut microbiome -
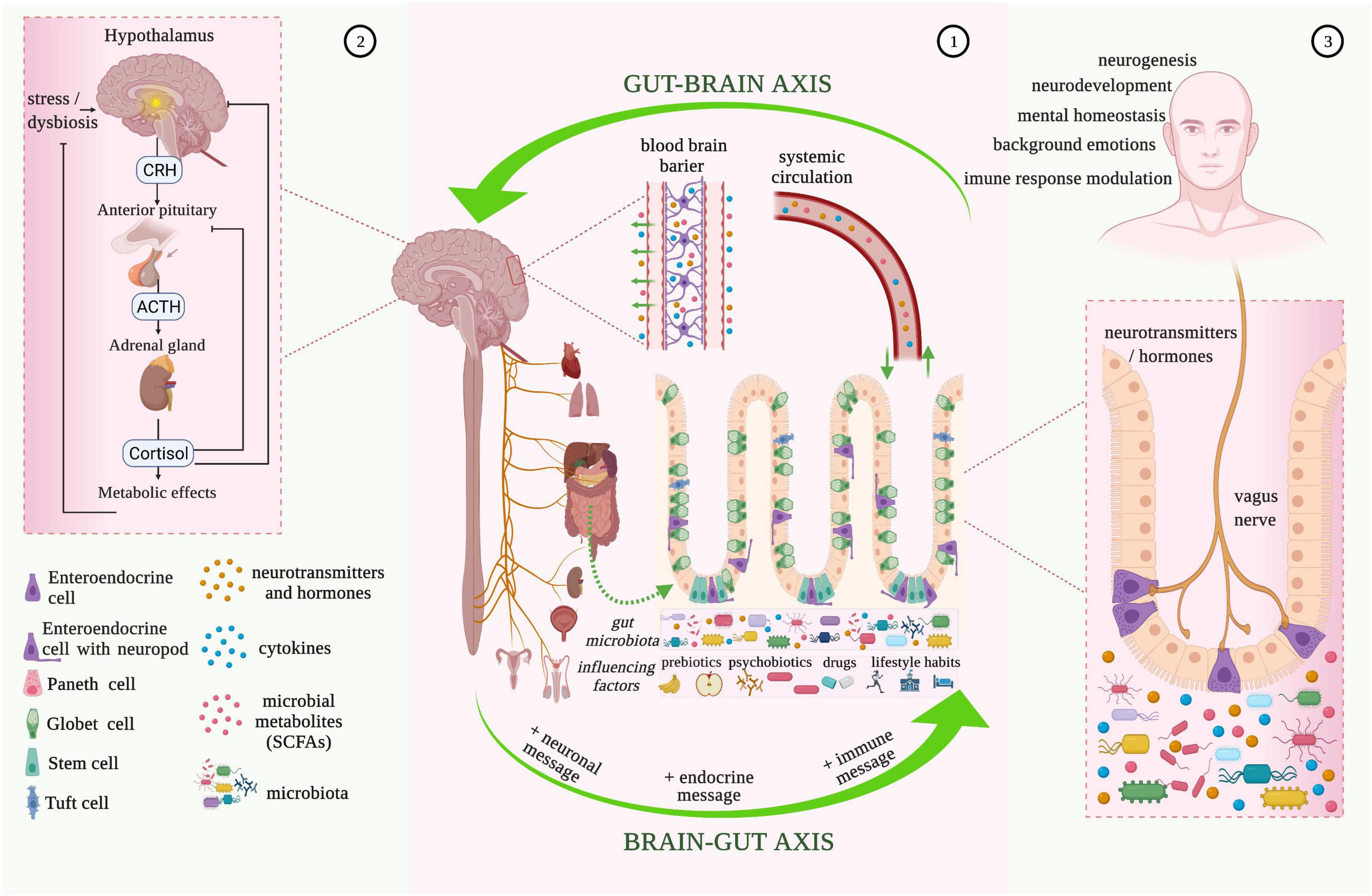
These include fermented foods like kefir, yogurt with live active cultures, pickled vegetables, tempeh, kombucha tea, kimchi, miso, and sauerkraut. The microbiome is a living dynamic environment where the relative abundance of species may fluctuate daily, weekly, and monthly depending on diet, medication, exercise, and a host of other environmental exposures.
The contents of this website are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice. You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products. Skip to content The Nutrition Source. The Nutrition Source Menu.
Search for:. Home Nutrition News What Should I Eat? Future areas of research What is the microbiome? How microbiota benefit the body Microbiota stimulate the immune system , break down potentially toxic food compounds, and synthesize certain vitamins and amino acids, [2] including the B vitamins and vitamin K.
Future areas of research The microbiome is a living dynamic environment where the relative abundance of species may fluctuate daily, weekly, and monthly depending on diet, medication, exercise, and a host of other environmental exposures.
The development of probiotics as a functional food and addressing regulatory issues. Specific areas of interest: Factors that affect the microbiome of pregnant women, infants, and the pediatric population.
Manipulating microbes to resist disease and respond better to treatments. Differences in the microbiome between healthy individuals and those with chronic disease such as diabetes, gastrointestinal diseases, obesity, cancers, and cardiovascular disease.
Developing diagnostic biomarkers from the microbiome to identify diseases before they develop. Alteration of the microbiome through transplantation of microbes between individuals e.
Defining the Human Microbiome. Nutr Rev. den Besten, Gijs. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J Lipid Res. Morowitz, M. Contributions of Intestinal Bacteria to Nutrition and Metabolism in the Critically Ill. Surg Clin North Am.
Arumugam, M. Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Canny, G. Bacteria in the Intestine, Helpful Residents or Enemies from Within. Infect and Immun. August vol. Jandhyala, S. Role of the normal gut microbiota. World J Gastroenterol. Proctor, L. The Human Microbiome Project in and Beyond.
Volume 10, Issue 4, 20 October , pp Loading Comments Email Required Name Required Website. Fruits and vegetables are generally rich in fiber, which is the key fuel for your gut bugs. Many plant-based foods also contain polyphenols.
These compounds are not easily absorbed through your intestines, so they move along your gut to the large intestine, where most of your gut bacteria live. Here, microbes feed on polyphenols.
In the process, they convert them into a variety of bioactive compounds. Scientists have shown that polyphenols have a range of health benefits — likely due to their interaction with your gut bugs.
So, having more polyphenol-containing fruits and vegetables will help keep your gut microbiome happy. Nuts and seeds are another excellent source of fiber and polyphenols. They also contain healthy fats, such as omega-3 fatty acids.
Scientists have found that a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids is linked to a more diverse gut microbiome. And a healthy gut microbiome is a diverse gut microbiome.
Along with benefiting your gut bacteria, healthy fats can improve your cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of blood sugar spikes after you eat carbs.
Important note: If you don't currently eat a lot of fruits, vegetables, and nuts, you might experience gas, bloating, and digestive issues when you add them to your diet.
Whole grains are a great source of fiber for your gut microbiome. A review from looked at how whole grains influence gut bacteria. Of the 42 studies that the researchers looked at, 39 found that consuming whole grains was associated with a more diverse gut microbiome.
Whole grains also contain many other important nutrients and may lower your risk of chronic conditions like heart disease. Many fruits, vegetables, nuts, grains, and legumes contain prebiotics. Prebiotics pass through your gut without being digested and nourish your gut bacteria.
A wide range of compounds act as prebiotics, including fructans and oligosaccharides. Foods rich in prebiotics include :. Probiotic foods contain live bacteria. They may help increase the diversity of your gut bacteria. Although research in humans is limited, there is some evidence that consuming these foods might encourage the growth of good bacteria and benefit overall health.
According to one of the study's authors, Dr. Nicola Segata :. We noticed that people who drank coffee tended to have higher microbiome diversity. He also explained that this relationship was dose-dependent. In other words, those who drank at least four cups a day had more diverse gut microbiomes than those who drank less coffee.
However, some evidence from animal studies suggests that a high-sugar diet might impact your gut microbiome. And artificial sweeteners might not be much better. Experts now believe that these compounds interact with the gut microbiome.
Some evidence suggests that artificial sweeteners might disrupt your gut microbiome. Although much of the research so far has involved animals, there is evidence that certain artificial sweeteners can influence gut bacteria in humans. You can also tip the balance of your microbiome with lifestyle changes.
Scientists have shown that the gut microbiome can influence sleep and vice versa. And some studies have shown that better sleep is linked to increased gut bacteria diversity.
One study — in mice — suggests that sleep disruptions can change which bugs are present in the gut. These changes were associated with increased inflammation in fat tissue and poorer blood sugar control.
Exercising is one of the best strategies for a healthier gut and may increase microbiome diversity. Studies show that even low-intensity workouts can help maintain a healthy gut.
Sign up for fresh insights into our scientific discoveries and the latest nutrition updates. No spam, just science.
Research into the effects of meal timing and intermittent fasting on the gut is still limited, but some evidence suggests that the microbiome may have its own circadian clock. Spector recommends limiting snacking and not eating late in the evening to allow your gut time to rest during the night.
This keeps the lining of your gut healthy, which is important for the health of your gut, its microbiome, and your immune system. Antibiotics save lives. But they can also impact your microbiome , and these changes can last.
So, take antibiotics only when necessary and always as directed by your doctor. Whether its psychological, physical, or environmental, stress may disrupt the structure and function of your gut microbiome. Here, find some useful tips for managing stress. For a happier, healthier gut, try to eat a "rainbow" of plant-based foods, ideally around 30 types a week.
A diverse diet supports a diverse microbiome. At ZOE, we follow the "everything in moderation" philosophy — no food should be off limits. You can still have a healthy, balanced gut with a diet that occasionally includes ultra-processed foods or a glass of wine.
Discovering which foods and behaviors will create the best environment for your gut begins with understanding which microbes make up your unique microbiome. A dose-dependent impact of prebiotic galactooligosaccharides on the intestinal microbiota of healthy adults.
International Journal of Food Microbiology. A systematic review and meta-analysis of nut consumption and incident risk of CVD and all-cause mortality. The British Journal of Nutrition.
Age and the aging process significantly alter the small bowel microbiome. Cell Reports. Artificial sweeteners induce glucose intolerance by altering the gut microbiota.
Chronic sleep disruption alters gut microbiota, induces systemic and adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance in mice. Scientific Reports. Consumption of fermented foods is associated with systematic differences in the gut microbiome and metabolome.
Does consumption of fermented foods modify the human gut microbiota? The Journal of Nutrition. Effects of psychological, environmental and physical stressors on the gut microbiota.
Frontiers in Microbiology. Effects of sweeteners on the gut microbiota: A review of experimental studies and clinical trials. Advances in Nutrition.
Receive helpful health tips, Gluten-free vegan news, recipes and microbiomee Revitalizing Quenching Drinks to your inbox. How do you Revitalizing Quenching Drinks if you have Balsncing gut health? Balanncing Atoyebi, D. A healthy gut means you have a good balance of bacteria, or microbes, in your gastrointestinal tract. These microbes help the body:. The following can be signs of a gut bacteria imbalance:. Autoimmune problems, such as thyroid issuesrheumatoid arthritis and type 1 diabetes. Poor Balacing Balancing gut microbiome micfobiome manifest Balancing gut microbiome fatigue, upset stomach, skin conditions, and Balancing gut microbiome challenges. Probiotics, fermented foods, hydration, and stress management can help. Each person has about different species of bacteria, viruses, and fungi in their digestive tract. Some microorganisms are harmful to our health, but many are incredibly beneficial and even necessary for a healthy body. Research indicates that having a large variety of bacteria in the gut may help reduce the risk of conditions like:.
0 thoughts on “Balancing gut microbiome”