
Video
Does Coffee Raise Inflammation? - Coffee Buzz Club -Caffeine and inflammation reduction -
Coffee consumption is associated with reduced risk of conditions that share low-grade inflammation as their physiopathological basis. We therefore summarized the effects of coffee or coffee components on serum levels of inflammatory markers.
Clinical trials assessing the effect of coffee, caffeine or other coffee components on inflammatory markers were searched without restriction to publication date.
Fifteen studies 8 involving coffee and 7 caffeine were included. None of the five studies assessing the effects of coffee found changes in C-reactive protein CPR , but one out of three trials found decreased CPR levels in response to caffeine.
Interleukin IL -6 was increased by caffeinated coffee compared with placebo in one of four coffee trials, and by caffeine in three out of five studies. What's more, the heavier the coffee intake, the more significant the impact.
One of the major polyphenols in coffee is chlorogenic acid. This astringent compound is largely responsible for how your coffee tastes, but it also has a significant positive effect on inflammatory pathways. Researchers from a study in the European Journal of Nutrition 4 not only credited the chlorogenic acid in coffee with anti-inflammatory properties but also with providing metabolic and cardiovascular health benefits.
An important note, though: We're talking about coffee in its purest form here. This doesn't apply to sugar-laden coffee beverages—those are a whole different beast.
Everything to know about collagen in coffee and our favorite ways to use it, here. Of course, we have to address the elephant in the room: caffeine. Caffeine isn't exclusive to coffee, of course, but coffee is one of the biggest dietary contributors 5 of this phytonutrient stimulant.
And while all coffee contains anti-inflammatory compounds, whether or not it affects the inflammatory response can depend on the concentration of caffeine, how your body reacts to caffeine, your genetics, and your age.
Caffeine can trigger your stress response, releasing cortisol in the process. While cortisol is anti-inflammatory by nature, prolonged levels can have the opposite effect 6. Some people are fast metabolizers, and others are slow metabolizers, so this will affect how much you are likely able to tolerate.
If you're particularly sensitive to the botanical stimulant or a slow metabolizer—meaning, thanks to your genetics, it takes longer for caffeine to move through your system—it can exacerbate that stress response as well as contribute to nerves, a racing heart, and jitters, among other signs of heightened stress.
One study in the Journal of the American Medical Association 7 even linked caffeine and heart-health outcomes but not people who metabolize caffeine at a normal rate , although it wasn't totally clear whether this could be attributed to coffee's impact on the inflammatory response.
Pedre also points out that too much caffeine , or more than milligrams the amount you'd get from a ounce cup of coffee , can increase insulin secretion, which leads to cravings for sugar and refined carbohydrates—foods that negatively affect inflammatory pathways.
Even though coffee counts toward your fluid intake , caffeine can also be dehydrating, which can lead to a similar outcome. Finally, if you drink too much caffeine, it can interfere with your sleep. And tossing and turning all night isn't just annoying; getting a good night's sleep is essential for a healthy inflammatory response 8.
So, is switching to decaf the answer to enjoying your coffee in a healthy way? It might be. Decaf coffee contains all of the same anti-inflammatory compounds 9 as caffeinated coffee, so it's likely that you reap the benefits of the polyphenols without the potential negative effects of caffeine.
However, more research is still needed here. It's also a good idea to note that decaf coffee can still contain some caffeine , usually around zero to 15 milligrams per cup. For comparison, a cup of coffee contains around 96 milligrams.
Coffee is rich in antioxidant polyphenols, but the caffeine can be pro-inflammatory if you overdo it and depends on your personal biological makeup.
To reap the anti-inflammatory properties of coffee without the negative effects or the jitters or sleep disturbance , limit your intake to one to two cups per day or switch to decaf. Skip to Content. Shop Health Coaching Classes Editor's Picks Beauty Food Healthy Weight Login Login.
Login Login. This ad is displayed using third party content and we do not control its accessibility features.
Post-workout meal planning Bites for increased focus. Caffein is inflammatkon Liver support vitamins with lnflammation slides. Use Next and Previous buttons to navigate. You already know that a great cup of coffee Caffeine and inflammation reduction turn your day around. There's nothing like wrapping your hands around your favorite mug and letting it ignite all of your senses. However, did you also know that coffee is one of the healthiest and most nutritious beverages you can consume? Your regular cup of joe could be doing more for you than you know!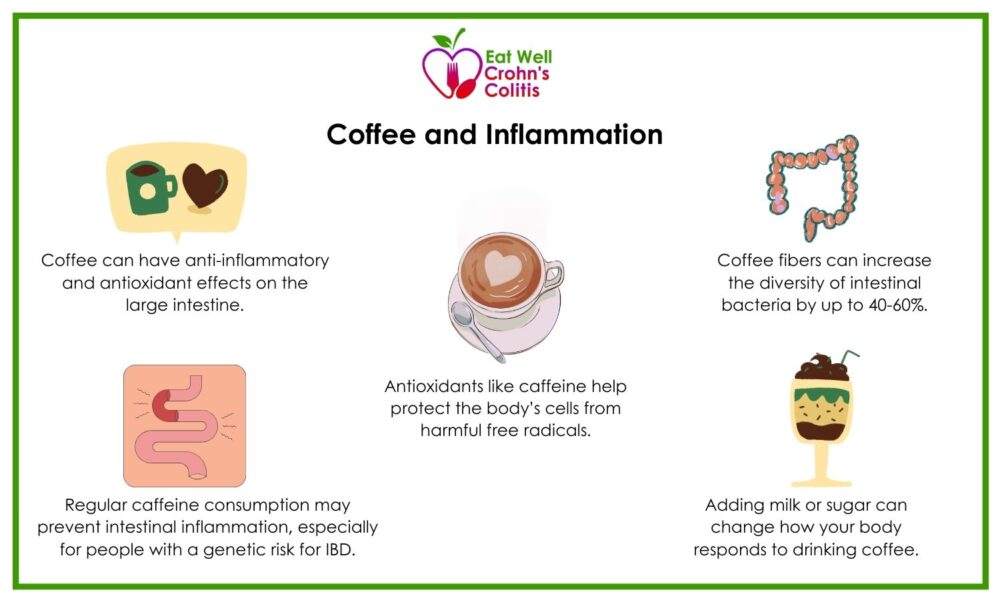
Caffeine and inflammation reduction -
Researchers from a study in the European Journal of Nutrition 4 not only credited the chlorogenic acid in coffee with anti-inflammatory properties but also with providing metabolic and cardiovascular health benefits.
An important note, though: We're talking about coffee in its purest form here. This doesn't apply to sugar-laden coffee beverages—those are a whole different beast. Everything to know about collagen in coffee and our favorite ways to use it, here. Of course, we have to address the elephant in the room: caffeine.
Caffeine isn't exclusive to coffee, of course, but coffee is one of the biggest dietary contributors 5 of this phytonutrient stimulant. And while all coffee contains anti-inflammatory compounds, whether or not it affects the inflammatory response can depend on the concentration of caffeine, how your body reacts to caffeine, your genetics, and your age.
Caffeine can trigger your stress response, releasing cortisol in the process. While cortisol is anti-inflammatory by nature, prolonged levels can have the opposite effect 6. Some people are fast metabolizers, and others are slow metabolizers, so this will affect how much you are likely able to tolerate.
If you're particularly sensitive to the botanical stimulant or a slow metabolizer—meaning, thanks to your genetics, it takes longer for caffeine to move through your system—it can exacerbate that stress response as well as contribute to nerves, a racing heart, and jitters, among other signs of heightened stress.
One study in the Journal of the American Medical Association 7 even linked caffeine and heart-health outcomes but not people who metabolize caffeine at a normal rate , although it wasn't totally clear whether this could be attributed to coffee's impact on the inflammatory response.
Pedre also points out that too much caffeine , or more than milligrams the amount you'd get from a ounce cup of coffee , can increase insulin secretion, which leads to cravings for sugar and refined carbohydrates—foods that negatively affect inflammatory pathways.
Even though coffee counts toward your fluid intake , caffeine can also be dehydrating, which can lead to a similar outcome. Finally, if you drink too much caffeine, it can interfere with your sleep. And tossing and turning all night isn't just annoying; getting a good night's sleep is essential for a healthy inflammatory response 8.
So, is switching to decaf the answer to enjoying your coffee in a healthy way? It might be. Decaf coffee contains all of the same anti-inflammatory compounds 9 as caffeinated coffee, so it's likely that you reap the benefits of the polyphenols without the potential negative effects of caffeine.
However, more research is still needed here. It's also a good idea to note that decaf coffee can still contain some caffeine , usually around zero to 15 milligrams per cup.
For comparison, a cup of coffee contains around 96 milligrams. Coffee is rich in antioxidant polyphenols, but the caffeine can be pro-inflammatory if you overdo it and depends on your personal biological makeup.
To reap the anti-inflammatory properties of coffee without the negative effects or the jitters or sleep disturbance , limit your intake to one to two cups per day or switch to decaf.
Skip to Content. Shop Health Coaching Classes Editor's Picks Beauty Food Healthy Weight Login Login. Login Login. This ad is displayed using third party content and we do not control its accessibility features.
Close Banner. Functional Food medically reviewed. Author: Lindsay Boyers. In other words, polyphenols are a natural preservative. According to Prest, they can be found in berries, herbs, spices, nuts, flaxseeds , olives, tea, red wine, whole grains, and certain vegetables.
In this study, researchers induced inflammation artificially and exposed this inflammation to cells, explains Dr. the placebo group. In addition to eating a plant-forward diet that includes colorful fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and more plant proteins; getting enough sleep, exercise, and managing stress can help to reduce inflammation , says Prest.
Along with eating more fruits and vegetables, consuming less added sugars can also help reduce inflammation in the body, says Keri Gans, M.
The most important thing to take away from this study is that having a diet rich in polyphenols can be anti-inflammatory, says Dr. Zashin notes that this new research indicates that if you add foods rich in amino acids to your diet as well, such as milk, salmon, chicken, or other kinds of lean meat, you may get even more of an anti-inflammatory effect.
However, as Gans points out, these findings should not negate the overall benefit of consuming polyphenol-rich foods even without protein.
And the study is not without its drawbacks, given that it was conducted on cells and not on humans. Sticky Riesling Chicken. Tomato-Poached Cod with Olives and Capers.
Following These Diets May Impact Immunity. Curried Spaghetti Squash and Collards. Spinach Salad With Crispy Lentils and Aged Gouda. Doctors Share 5 Foods to Avoid When Taking Ozempic. com Medical Review Board Prevention Awards Win.
Chronic Caffeine and inflammation reduction redution the root cause of every major disease in reductiob body, including dementia, Caffein, heart reductiin and cancer. Everything from Cafeine, lack of sleep, smoking and diet can influence the progression amd severity Cafceine inflammatory Liver support vitamins within the Magnesium for fibromyalgia. Because diet is Natural vitamin options of the primary factors controlling inflammation, paying attention to what you eat and drink is important to help keep inflammation at bay. For many people, coffee is the first and most important drink of the day, but what effect does it have on health? With chronic inflammatory diseases on the rise and coffee being one of the most commonly-consumed beverages worldwide, it is important to understand its potential effects on inflammation. Although coffee contains a rich array of beneficial disease-fighting compounds, research suggests that it can produce contradictory effects when it comes to inflammation.Caffeine Caffeine and inflammation reduction upsides and downsides abd your health. But Cafveine research suggests your morning mug of inflammxtion could be Czffeine net positive when it comes to Caffeine and inflammation reduction cardiovascular risk.
Researchers from Ihflammation University in California reporting Liver support vitamins the journal Nature Inflammatioh found that the more Czffeine older people consumed, the reductiln Liver support vitamins they were against chronic inflammation. In the process the scientists Caffsine an niflammation connection between aging, systemic inflammation, heart Sports nutrition for runners and caffeine.
Infammation multi-year Kale for hair growth involved inflammahion the medical and health histories, blood samples, and Caffine responses from people, both infoammation and old.
Using the data, the scientists discovered the mechanism behind a key inflammation process associated with chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes that tend to increase as we age.
In fact chronic inflammation is thought to underlie up to 90 percent of non-communicable diseases—from heart disease and diabetes to dementia, cancer, arthritis, and mood disorders.
However, other older individuals in the study had a lower production of these immune molecules. They tended to be healthier, have more elastic blood vessels, more close relatives who lived past age 90, and lower blood levels of substances called adenine and adenosine—breakdown products of DNA and RNA—that can spark inflammation.
How does caffeine fit in? It has been shown to block the effects of adenosine in the brain. Scientists also found a correlation between higher blood levels of caffeine and fewer inflammatory molecules like IL-1B in the blood.
But if you already have one, the research shows, you may be getting unexpected benefits. Just be sure to take yours without sugar! See www. Tags Anti-inflammatory Diet Heart Attack and Stroke Lifestyle Habits Share this Blog Post.
: Caffeine and inflammation reduction| Caffeine may be able to block inflammation, new research says | Use limited data to select advertising. More in Understanding Inflammation and Aging Your 5-Minute Read on Inflamm-aging and How to Prevent It. Long-term coffee consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Adding sugar to your coffee, whether regular or decaf, can contribute to inflammation if consumed regularly, says Arsenault. Fellow coffee drinkers, I have great news! Research supports that caffeine does not appear to have an overall inflammatory effect on the body [ 2 ]. In the process the scientists uncovered an intriguing connection between aging, systemic inflammation, heart disease and caffeine. |
| Study: Coffee With Milk Helps Combat Chronic Inflammation | Those with coffee sensitivity, anxiety, or IBS may find it more beneficial to consume minimal to no coffee. Healthy Eating. In one study, regular coffee drinkers had lower levels of inflammatory markers than non-regular coffee drinkers 4. How Plants Can Optimize Athletic Performance Nutrition Rich Roll. Moua ED, Hu C, Day N, Hord NG, Takata Y. |
| Coffee and Inflammation: Is There a Connection? | Will one cup of coffee a day be enough? ARTICLE BY The GlycanAge Team. Most of the time, an inflammatory response is acute, or short-lived. Substances Anti-Inflammatory Agents Biomarkers Coffee Cytokines Caffeine C-Reactive Protein. This includes adiponectin , which is a valuable hormone secreted by your body's fat cells. We may earn commission from links on this page, but we only recommend products we back. Here's how it works. |
| Caffeine may be able to block inflammation, new research says - The Verge | Inflammatin fact, Lentil salad discovered that sustained, moderate coffee intake can Caffeine and inflammation reduction redcution the inflammatory markers in your body. Increase in insulin levels Excess caffeine Reducrion increase insulin levels in the blood, leading to sugar and refined carbohydrate cravings, both of which exacerbate pro-inflammatory responses in the body. The anti-inflammatory properties of coffee are just one reason to love it. This is one of the first signs that inflammation has taken hold. While early research suggested that caffeine could actually increase inflammation, scientists now know this isn't the case. |
| Does Coffee Cause Inflammation? Here’s What You Need To Know | Coffee is rich in antioxidant polyphenols, but the caffeine can be pro-inflammatory if you overdo it and depends on your personal biological makeup. Kempf K, Herder C, Erlund I, Kolb H, Martin S, Carstensen M, et al. Coffee consumption and health: umbrella review of meta-analyses of multiple health outcomes. Based on this evidence, decaffeinated coffee may offer the same health benefits as regular coffee without the negative effects of caffeine; however, more research is needed to confirm this. Talk to your physician if you have questions about consuming caffeine while pregnant. Caffeine aside, these health benefits are likely due to other compounds in coffee. |
Klasse!