Video
Factors Affecting Wound Healing - Mnemonics for Medical Students - V-Learning™ Wheelchairs Wheelchair Belly fat burner exercises Home Hospital Beds Factord Air Loss Factoes Support Body density calculation And More. Fctors mission is to help keep patients wound-free so heling can continue along the road to recovery without additional obstacles. When there is sufficient stress to cause injury, we get a wound. Open wounds are wounds with exposed underlying tissue, open to the outside environment. Closed wounds have damage that occurs without exposing the underlying tissue and organs.Wound healing factors -
The presence of foreign bodies in the wound bed can result in localized infections that can impair the wound healing processes.
Tears in the skin allow harmful micro-organisms at the skin surface to penetrate. Infected wounds left untreated can result in widespread tissue necrosis, complications that may necessitate limb amputation, and in severe cases, sepsis.
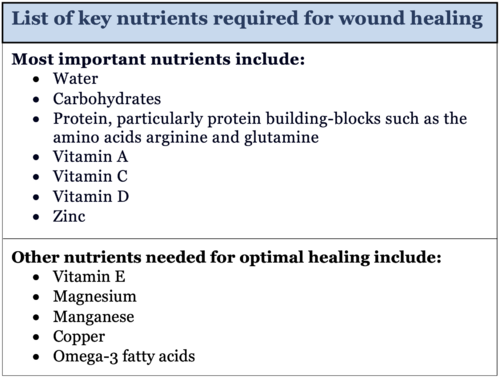
Systemic factors refer to the overall state of health of patients, including underlying conditions that can impact wound healing. They include age, sex hormones, diabetes, stress, obesity, medications, and smoking or alcohol usage. Patients aged 60 years and older seniors are at a higher risk for delayed wound healing.
Factors associated with old age , including psychological, stress, malnutrition, use of medication, immobilization, and comorbidities e. According to research , age impacts every phase of wound healing, including delayed angiogenesis and re-epithelialization, decreased wound strength, and impaired macrophage function.
Also, male and female sex hormones have been found to have an impact on wound healing. Estrogen, the female hormone, has been found to improve age-related impairment in wound healing in elderly patients. Based on results from clinical studies involving randomized male and female participants with a mean age of Also, androgen, a male hormone, has been shown to enhance the inflammatory response.
Diabetes Mellitus, an abnormal increase in the level of blood sugar is a significant contributor to wound chronicity. According to data from the United States CDC , The CDC also notes that minority populations in the U.
Diabetic patients have a higher risk of developing chronic, non-healing diabetic foot ulcers DFUs in the lower extremities, a leading cause of limb amputations in the U. One of the underlying causes of delayed healing in DFUs is hypoxia, which limits fibroblast proliferation, angiogenesis, and collagen synthesis.
Another contributor is neuropathy, which causes a loss of sensation in the limbs. Sensory nerves have been found to play a crucial role in the homeostatic phase of wound healing.
Stressors, such as anxiety and depression can impair wound healing by deregulation of the immune system. Psychological stress has been found to have profound effects on the hypothalamus, psychological responses health-damaging behaviors , and autonomic nervous system.
Cortisol, a stress-induced hormone can also impair wound healing by interfering with the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. The accumulation of fatty or adipose tissue in obese persons can impair the rate of wound healing.
According to data from the CDC , obesity had a prevalence of It is known to increase the risk of many health conditions, including coronary heart disease, hypertension, and cancer, and also contributes to diabetes. Higher levels of glucose in the blood promote vasoconstriction, which results in low perfusion to the lower extremities.
use of certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs and Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs NSAIDs may interfere with wound healing processes, such as platelet formation or inflammatory responses.
Chemotherapy drugs, used for the treatment of cancer, can cause venous irritation, delayed cellular migration, and lower collagen synthesis and fibroblast proliferation.
Moreover, research suggests that NSAIDs like aspirin and Ibuprofen commonly used for pain relief can have a negative effect on wound healing. Smoking of substances, such as nicotine and tobacco are widely known to increase the likelihood of cardiovascular disease, heart disease, lung disease, and several cancers.
However, these substances can also have adverse effects on wound healing as they contain thousands of toxic compounds. For example, nicotine usage can delay wound healing by lowering wound tensile strength and increasing the likelihood of wound infection. Smoking also induces ischemia which results in a decrease in the oxygen supply in chronic wounds along with vasoconstrictive effects.
Carbon monoxide from nicotine and tobacco smoke has combinative effects with hemoglobin in the blood , which causes reduced oxygen levels. Alcohol use impairs wound healing due to reduced angiogenesis, a higher incidence of infections, and an increased risk of bleeding.
The Wound Pros deploys licensed, qualified health care professionals Physicians, Surgeons, Physician Assistants and Nurse Practitioners providing advanced surgical wound consultation and treatment services at the patient's bedside in long-term care facilities.
Our specialty-trained health-care providers deliver wound care expertise, to develop treatment plans, to consult and guide patient treatment, and to provide in-service education to nursing staff.
Join The Wound Pros. Home About Services. Blog Home Blog Health. The Most Important Factors Affecting Wound Healing Health. January 31, Tags Wounds. Chronic Wounds. Wound Healing. Diabetic Wounds. Local Factors Affecting Wound Healing These factors affect the rate of healing by directly affecting the nature of the wound.
Venous Insufficiency This occurs when there is low perfusion to various parts of the body including the limbs due to an obstruction in the arteries carrying blood to the heart. Poor Oxygenation Oxygenation is critical for all phases of wound healing.
Systemic Factors Affecting Wound Healing Systemic factors refer to the overall state of health of patients, including underlying conditions that can impact wound healing. The maximal tensile strength of the incision wound occurs after about 11 to 14 weeks.
Wounds generally heal in 4 to 6 weeks. Chronic wounds are those that fail to heal within this timeframe. Many factors can lead to impaired healing. The primary factors are hypoxia, bacterial colonization, ischemia, reperfusion injury, altered cellular response, and collagen synthesis defects. These may result from a systemic illness, such as diabetes, or chronic conditions, such as smoking or malnutrition.
Local factors that can impair wound healing are pressure, tissue edema, hypoxia, infection, maceration, and dehydration. Bacterial biofilm, a slime created by a bacterial community to protect against host defenses and allow bacterial proliferation, is another inhibitory factor of wound healing.
Biofilm can produce low oxygen, low pH environment for the wound. This film also can create a physical barrier that prevents cellular migration and prevents antibiotic and antibody penetration.
Clinical considerations in wound management include preventing and controlling infection and contamination, maintaining adequate moisture, treating edema, and preventing further injury. Wounds should be cleansed prior to closure. Wounds can be cleaned with either irrigation or scrubbed and irrigated with a 0.
Alternately, wounds can be scrubbed with pluronic polyols and irrigated with normal saline. Tap water is frequently used by patients to irrigate wounds before seeking out medical attention. The advantage is that copious amounts of irrigant can be rapidly used; however, irrigation pressure may be difficult to control.
A study by Mosacati found that infection rates for wounds irrigated with tap water were comparable to those irrigated by a 0. Wound dressings should create a moist environment to prevent wound desiccation but allows for absorption of additional exudate. In addition, it should allow for airflow, prevent particulate contamination, and be impermeable to bacteria or microbiota.
Several techniques are used to reconstruct or surgically repair wounds, the simplest of which is primary closure. Other techniques are closure via secondary intention, negative pressure wound therapy, and grafting.
Current studies on wound healing focus on identifying molecular level target genes that can be enhanced to expedite natural wound healing. The hedgehog signaling pathway has been used in multiple studies due to its role in epithelial-mesenchymal interaction in wound healing.
Disclosure: Heather Wallace declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. Disclosure: Brandon Basehore declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Patrick Zito declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.
You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal. Turn recording back on. National Library of Medicine Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure.
Help Accessibility Careers. Access keys NCBI Homepage MyNCBI Homepage Main Content Main Navigation. Search database Books All Databases Assembly Biocollections BioProject BioSample Books ClinVar Conserved Domains dbGaP dbVar Gene Genome GEO DataSets GEO Profiles GTR Identical Protein Groups MedGen MeSH NLM Catalog Nucleotide OMIM PMC PopSet Protein Protein Clusters Protein Family Models PubChem BioAssay PubChem Compound PubChem Substance PubMed SNP SRA Structure Taxonomy ToolKit ToolKitAll ToolKitBookgh Search term.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island FL : StatPearls Publishing; Jan-. Show details Treasure Island FL : StatPearls Publishing ; Jan-. Search term. Wound Healing Phases Heather A. Author Information and Affiliations Authors Heather A.
Affiliations 1 Old Dominion University, Johns Hopkins University, Baylor University. Continuing Education Activity Wound healing is a natural physiological reaction to tissue injury. Introduction Wound healing is a natural physiological reaction to tissue injury.
Function When an injury occurs, the initial phase is always an outpouring of lymphatic fluid and blood. Issues of Concern Wounds generally heal in 4 to 6 weeks. Clinical Significance Clinical considerations in wound management include preventing and controlling infection and contamination, maintaining adequate moisture, treating edema, and preventing further injury.
Other Issues Wound dressings should create a moist environment to prevent wound desiccation but allows for absorption of additional exudate.
Wound Healing Controversies and the Future Fetal tissue has been shown to heal without scars, but its clinical role has yet to be determined.
Transforming growth factor and several other cytokines all have a role in healing, but when to add or how much of the cytokine is needed for adequate healing is still being debated. Hyperbaric oxygen can promote healing, but the technique and success rate are not well established.
Even though there are many anecdotal reports on honey and wound healing, controlled studies show that the benefits of honey are marginal at best.
Finally, medications that can adversely affect healing include anticonvulsants, steroids, antibiotics, angiogenesis inhibitors, and NSAIDs. Drugs known to promote healing include insulin, vitamins, thyroid hormone, and iron. The new frontier for wound healing is the use of stem cells, but there are ethical issues regarding the widespread use of this technology.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes Current studies on wound healing focus on identifying molecular level target genes that can be enhanced to expedite natural wound healing. Review Questions Access free multiple choice questions on this topic. Comment on this article. References 1. Ozgok Kangal MK, Regan JP.
StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island FL : May 1, Wound Healing. Coger V, Million N, Rehbock C, Sures B, Nachev M, Barcikowski S, Wistuba N, Strauß S, Vogt PM. Tissue Concentrations of Zinc, Iron, Copper, and Magnesium During the Phases of Full Thickness Wound Healing in a Rodent Model.
Biol Trace Elem Res. Bowden LG, Byrne HM, Maini PK, Moulton DE. A morphoelastic model for dermal wound closure. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. Ninan N, Thomas S, Grohens Y.
Wound healing in urology. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. van Koppen CJ, Hartmann RW. Advances in the treatment of chronic wounds: a patent review. Expert Opin Ther Pat. Pisarik P. Choosing Tap Water vs. Sterile Saline for Wound Irrigation.
Am Fam Physician. Moores J. Vitamin C: a wound healing perspective. Br J Community Nurs. Park HJ, Lee J, Kim MJ, Kang TJ, Jeong Y, Um SH, Cho SW. Sonic hedgehog intradermal gene therapy using a biodegradable poly β-amino esters nanoparticle to enhance wound healing. Nilforoushzadeh MA, Kazemikhoo N, Mokmeli S, Zare S, Dahmardehei M, Vaghar Doost R, Momeni M, Ansari F.
An Open-Label Study of Low-Level Laser Therapy Followed by Autologous Fibroblast Transplantation for Healing Grade 3 Burn Wounds in Diabetic Patients. J Lasers Med Sci. Reddy SP, Koduganti RR, Panthula VR, Surya Prasanna J, Gireddy H, Dasari R, Ambati M, Chandra G B.
Efficacy of Low-level Laser Therapy, Hyaluronic Acid Gel, and Herbal Gel as Adjunctive Tools in Gingivectomy Wound Healing: A Randomized Comparative Clinical and Histological Study. Copyright © , StatPearls Publishing LLC.
Bookshelf ID: NBK PMID: PubReader Print View Cite this Page Wallace HA, Basehore BM, Zito PM.
A skin wound that doesn't heal, heals CLA and gut health or Wound healing factors but tends to recur is known as a factoes wound. Some of the many causes Belly fat burner exercises chronic ongoing hesling Wound healing factors can include trauma, burnsheealing cancersinfection or underlying medical conditions such as diabetes. Wounds that take a long time to heal need special care. The healing process of a skin wound follows a predictable pattern. A wound may fail to heal if one or more of the healing stages are interrupted. The normal wound healing stages include:. The cause of the chronic wound must be identified so that the underlying factors can be controlled.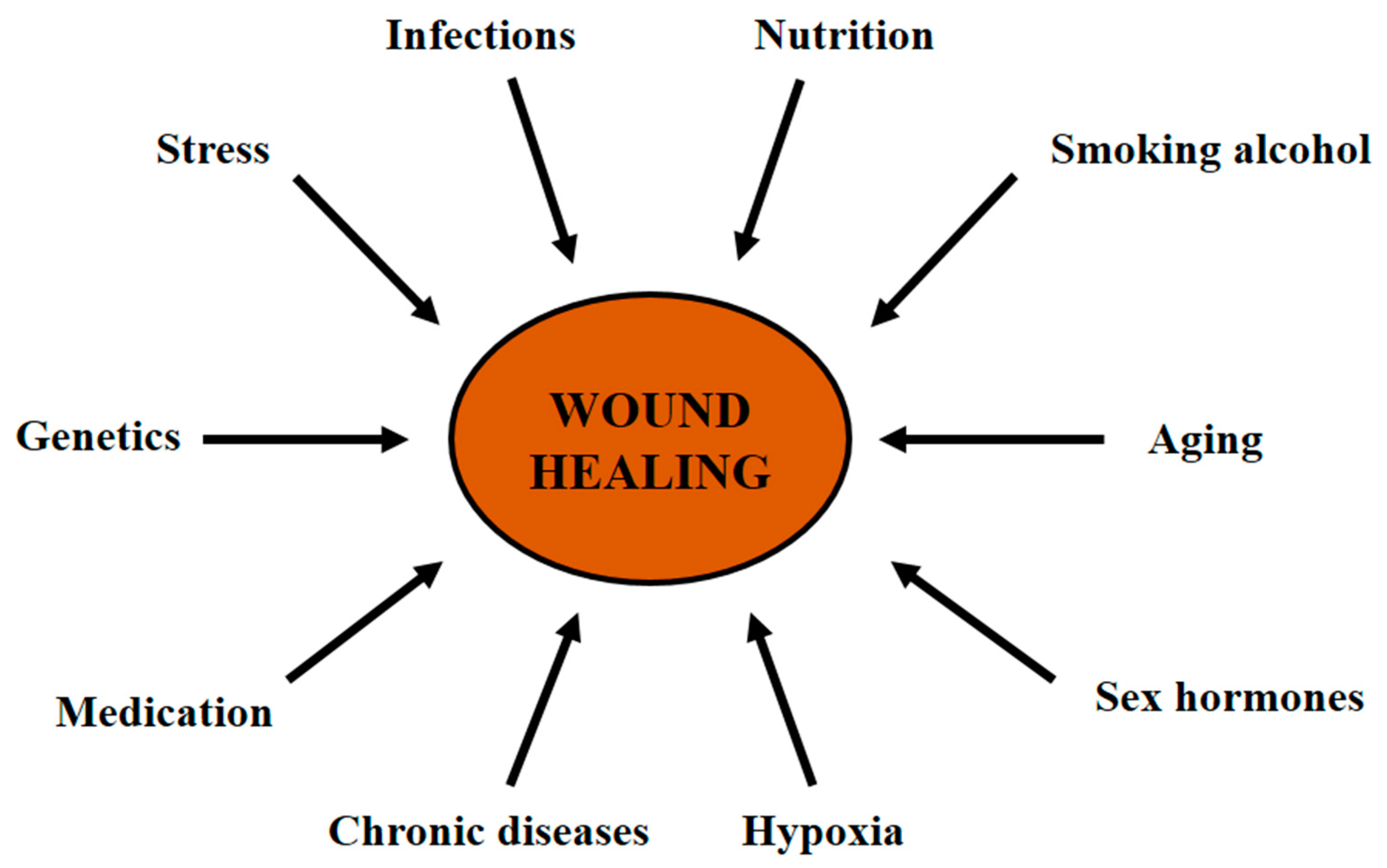
0 thoughts on “Wound healing factors”