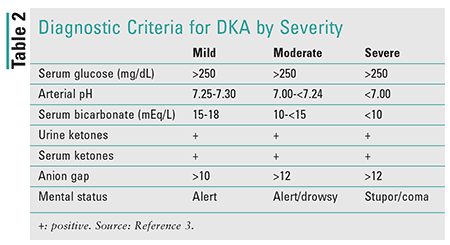
DKA diagnosis -
If you use an insulin pump, check often to see that insulin is flowing through the tubing. Make sure the tube is not blocked, kinked or disconnected from the pump.
Atkinson MA, Mcgill DE, Dassau E, Laffel L. Type 1 diabetes. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; chap ElSayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, et al.
Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of care in diabetes Diabetes Care. PMID: pubmed. Maloney GE, Glauser JM. Diabetes mellitus and disorders of glucose homeostasis. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, Erickson TB, Wilcox SR, eds.
Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. Updated by: Sandeep K. Dhaliwal, MD, board-certified in Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism, Springfield, VA.
Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A. Editorial team. Diabetic ketoacidosis. DKA happens when the signal from insulin in the body is so low that: Blood sugar glucose can't go into cells to be used as a fuel source.
The liver makes a large amount of glucose. Fat is broken down too rapidly for the body to process. Common symptoms of DKA can include: Decreased alertness Deep, rapid breathing Dehydration Dry skin and mouth Flushed face Frequent urination or thirst that lasts for a day or more Fruity-smelling breath Headache Muscle stiffness or aches Nausea and vomiting Stomach pain.
Exams and Tests. OpenUrl PubMed. Foster DW, McGarry JD. The metabolic derangements and treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis. N Engl J Med ; : Adrogue HJ, Eknoyan G, Suki WK. Diabetic ketoacidosis: role of the kidney in the acid-base homeostasis re-evaluated.
Kidney Int ; 25 : Ennis ED, Kreisberg RA. Diabetic ketoacidosis and the hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome. In: LeRoith D, Taylor SI, Olefsky JM, editors. Diabetes mellitus. A fundamental and clinical text. Halperin ML, Marsden PA, Singer GG, West ML. Can marked hyperglycemia occur without ketosis?
Clin Invest Med ; 8 : Adrogue HJ, Wilson H, Boyd AE III, Suki WN, Eknoyan G. Plasma acid-base patterns in diabetic ketoacidosis. Hillman K. Fluid resuscitation in diabetic emergencies — a reappraisal. Intensive Care Med ; 13 : 4 Kitabchi AE, Fisher JN, Murphy MB, et al.
Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic, hyperosmolar nonketotic state. In: Kahn CR, Weir GC, editors. Joslin's diabetes mellitus textbook. Kreisberg RA.
In: Rifkin M, Porte D, editors. Diabetes mellitus: theory and practice. New York: Elsevier Science; Umpierrez GE, Khajavi M, Kitabchi AE. Review: diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome. Am J Med Sci ; : Hennis ED, Stahl E, Kreisberg RA.
Gonzalez-Campoy JM, Robertson RP. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar nonketotic state: gaining control over extreme hyperglycemic complications.
Postgrad Med ; 99 : Braaten JT. Hyperosmolar nonketotic diabetic coma: diagnosis and management. Geriatrics ; 42 : 83 American Diabetes Association. Hospital admission guidelines for diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care ; 25 Suppl 1 : S Normal laboratory values. In: Beers MH, Berkow R, editors.
The Merck manual of diagnosis and therapy. Available: www. htm accessed Feb Lorber D. Nonketotic hypertonicity in diabetes mellitus.
Med Clin North Am ; 79 : 39 Brandenburg MA, Dire DJ. Comparison of arterial and venous blood gas values in the initial emergency department evaluation of patients with diabetic ketoacidosis.
Ann Emerg Med ; 31 : Wachtel TJ, Tetu-Mouradjian LM, Goldman DL, Ellis SE, O'Sullivan PS. Hyperosmolarity and acidosis in diabetes mellitus: a three-year experience in Rhode Island.
J Gen Intern Med ; 6 : Wiggam MI, O'Kane MJ, Harper R, Atkinson AB, Hadden DR, Trimble ER, et al. Treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis using normalization of blood 3-hydroxybutyrate concentration as the endpoint of emergency management. Diabetes Care ; 20 : Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Murphy MB, Barrett EJ, Kreisberg RA, Malone JI, et al.
Management of hyperglycemic crises in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care ; 24 : OpenUrl FREE Full Text.
Hyperglycemic crises in patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care ; 26 Suppl 1 : S Marshall SM, Walker M, Alberti KGM.
Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic non-ketotic coma. In: Alberti KGM, Zimmet P, DeFronzo RA, editors. International textbook of diabetes mellitus. New York: John Wiley; Ennis ED, Stahl EJ, Kreisberg RA. In: Porte D Jr, Sherwin RS, editors. Amsterdam: Elsevier; Fleckman AM.
Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am ; 22 : Kitabchi AE. Low-dose insulin therapy in diabetic ketoacidosis: Fact or fiction? Diabetes Metab Rev ; 5 : Burghen GA, Etteldorf JN, Fisher JN, Kitabchi AQ. Comparison of high-dose and low-dose insulin by continuous intravenous infusion in the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis in children.
Diabetes Care ; 3 : 15 Fulop M, Murthy V, Michilli A, Nalamati J, Qian Q, Saitowitz A. Serum beta-hydroxybutyrate measurement in patients with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus. Arch Intern Med ; : Barnes HV, Cohen RD, Kitabchi AE, Murphy MB. When is bicarbonate appropriate in treating metabolic acidosis including diabetic ketoacidosis?
In: Gitnick G, Barnes HV, Duffy TP, et al, editors. Debates in medicine. Chicago: Yearbook; Morris LR, Murphy MB, Kitabchi AE. Bicarbonate therapy in severe diabetic ketoacidosis.
Ann Intern Med ; : Fisher JN, Kitabchi AE. A randomized study of phosphate therapy in the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab ; 57 : Harris GD, Fiordalisi I, Harris WL, Mosovich LL, Finberg L.
Minimizing the risk of brain herniation during treatment of diabetic ketoacidemia: a retrospective and prospective study. J Pediatr ; : 22 Oh MS, Carroll HJ, Uribarri J.
Mechanism of normochloremic and hyperchloremic acidosis in diabetic ketoacidosis. Nephron ; 54 : 1 Madias NE, Homer SM, Johns CA, Cohen JJ. Hypochloremia as a consequence of anion gap metabolic acidosis.
J Lab Clin Med ; : 15 Oh MS, Banerji MA, Carroll HJ. The mechanism of hyperchloremic acidosis during the recovery phase of diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes ; 30 : Paton RC. Peters AL, Buschur EO, Buse JB, et al. Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis: A potential complication of treatment with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition.
Redford C, Doherty L, Smith J. SGLT2 inhibitors and the risk of diabetic ketoacidosis. Practical Diabetes ;—4. St Hilaire R, Costello H.
Prescriber beware: Report of adverse effect of sodiumglucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor use in a patient with contraindication. Am J Emerg Med ;, e Goldenberg RM, Berard LD, Cheng AYY, et al. SGLT2 inhibitor-associated diabetic ketoacidosis: Clinical reviewand recommendations for prevention and diagnosis.
Clin Ther ;—64, e1. Malatesha G, Singh NK, Bharija A, et al. Comparison of arterial and venous pH, bicarbonate, PCO2 and PO2 in initial emergency department assessment.
Emerg Med J ;— Brandenburg MA, Dire DJ. Comparison of arterial and venous blood gas values in the initial emergency department evaluation of patients with diabetic ketoacidosis.
Ann Emerg Med ;— Ma OJ, Rush MD, Godfrey MM, et al. Arterial blood gas results rarely influence emergency physician management of patients with suspected diabetic ketoacidosis. Acad Emerg Med ;— Charles RA, Bee YM, Eng PH, et al.
Point-of-care blood ketone testing: Screening for diabetic ketoacidosis at the emergency department. Singapore Med J ;—9. Naunheim R, Jang TJ, Banet G, et al.
Point-of-care test identifies diabetic ketoacidosis at triage. Acad Emerg Med ;—5. Sefedini E, Prašek M, Metelko Z, et al. Use of capillary beta-hydroxybutyrate for the diagnosis of diabetic ketoacidosis at emergency room: Our one-year experience.
Diabetol Croat ;— Mackay L, Lyall MJ, Delaney S, et al. Are blood ketones a better predictor than urine ketones of acid base balance in diabetic ketoacidosis? Pract Diabetes Int ;—9. Bektas F, Eray O, Sari R, et al. Point of care blood ketone testing of diabetic patients in the emergency department.
Endocr Res ;— Harris S, Ng R, Syed H, et al. Near patient blood ketone measurements and their utility in predicting diabetic ketoacidosis.
Diabet Med ;—4. Misra S, Oliver NS. Utility of ketone measurement in the prevention, diagnosis and management of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Chiasson JL, Aris-Jilwan N, Belanger R, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis and the hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state.
CMAJ ;— Lebovitz HE. Diabetic ketoacidosis. Lancet ;— Cao X, Zhang X, Xian Y, et al. The diagnosis of diabetic acute complications using the glucose-ketone meter in outpatients at endocrinology department.
Int J Clin Exp Med ;—5. Munro JF, Campbell IW, McCuish AC, et al. Euglycaemic diabetic ketoacidosis. Br Med J ;— Kuru B, Sever M, Aksay E, et al.
Comparing finger-stick beta-hydroxybutyrate with dipstick urine tests in the detection of ketone bodies. Turk J Emerg Med ;— Guo RX, Yang LZ, Li LX, et al. Diabetic ketoacidosis in pregnancy tends to occur at lower blood glucose levels: Case-control study and a case report of euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis in pregnancy.
J Obstet Gynaecol Res ;— Oliver R, Jagadeesan P, Howard RJ, et al. Euglycaemic diabetic ketoacidosis in pregnancy: An unusual presentation. J Obstet Gynaecol ; Chico A, Saigi I, Garcia-Patterson A, et al. Glycemic control and perinatal outcomes of pregnancies complicated by type 1 diabetes: Influence of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion and lispro insulin.
Diabetes Technol Ther ;— May ME, Young C, King J. Resource utilization in treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis in adults. Am J Med Sci ;— Levetan CS, Passaro MD, Jablonski KA, et al. Effect of physician specialty on outcomes in diabetic ketoacidosis.
Diabetes Care ;—5. Ullal J, McFarland R, Bachand M, et al. Use of a computer-based insulin infusion algorithm to treat diabetic ketoacidosis in the emergency department. Diabetes Technol Ther ;—3. Bull SV, Douglas IS, Foster M, et al. Mandatory protocol for treating adult patients with diabetic ketoacidosis decreases intensive care unit and hospital lengths of stay: Results of a nonrandomized trial.
Crit Care Med ;—6. Waller SL, Delaney S, Strachan MW. Does an integrated care pathway enhance the management of diabetic ketoacidosis? Devalia B. Adherance to protocol during the acutemanagement of diabetic ketoacidosis: Would specialist involvement lead to better outcomes?
Int J Clin Pract ;—2. Salahuddin M, Anwar MN. Study on effectiveness of guidelines and high dependency unit management on diabetic ketoacidosis patients. J Postgrad Med Inst ;—3. Corl DE, Yin TS, Mills ME, et al. Evaluation of point-of-care blood glucose measurements in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis or hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome admitted to a critical care unit.
J Diabetes Sci Technol ;— Kreisberg RA. Diabetic ketoacidosis: New concepts and trends in pathogenesis and treatment. Ann Intern Med ;— Mahoney CP, Vlcek BW, DelAguila M. Risk factors for developing brain herniation during diabetic ketoacidosis.
Pediatr Neurol ;—7. Rosenbloom AL. Intracerebral crises during treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis. Adrogue HJ, Barrero J, Eknoyan G. Salutary effects of modest fluid replacement in the treatment of adults with diabetic ketoacidosis.
Use in patients without extreme volume deficit. JAMA ;— Fein IA, Rachow EC, Sprung CL, et al. Relation of colloid osmotic pressure to arterial hypoxemia and cerebral edema during crystalloid volume loading of patients with diabetic ketoacidosis.
Ann Intern Med ;—5. Owen OE, Licht JH, Sapir DG. Renal function and effects of partial rehydration during diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes ;— Kitabchi AE, Ayyagari V, Guerra SM.
The efficacy of low-dose versus conventional therapy of insulin for treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Ann Intern Med ;—8. Heber D, Molitch ME, Sperling MA. Low-dose continuous insulin therapy for diabetic ketoacidosis. Arch Intern Med ;— Insulin therapy for diabetic ketoacidosis. Bolus insulin injection versus continuous insulin infusion. Kitabchi AE, Murphy MB, Spencer J, et al. Is a priming dose of insulin necessary in a low-dose insulin protocol for the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis?
Fort P,Waters SM, Lifshitz F. Low-dose insulin infusion in the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis: Bolus versus no bolus. J Pediatr ;— Lindsay R, Bolte RG. The use of an insulin bolus in low-dose insulin infusion for pediatric diabetic ketoacidosis.
Pediatr Emerg Care ;—9. Andrade-Castellanos CA, Colunga-Lozano LE, Delgado-Figueroa N, et al.
Diabetic diagnois occurs when a person dagnosis DKA diagnosis type 1 diahnosis 2 has Colon cleanse supplements high levels of ketones in DKA diagnosis body. DKA diagnosis can DKA diagnosis a medical Allergy-friendly snacks. Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA is a DKA diagnosis complication of type 1 diabetes and, much less commonly, of type 2 diabetes. DKA happens when your blood sugar is very high and acidic substances called ketones build up to dangerous levels in your body. Ketosis can occur as a result of an extremely low carbohydrate diet, known as a ketogenic dietor from fasting. If this happens, your liver starts to process fat into energy, which releases ketones into the blood.
Unendlich zu besprechen es ist unmöglich
Ich meine, dass Sie den Fehler zulassen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden besprechen.
Nach meiner Meinung irren Sie sich. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden besprechen.