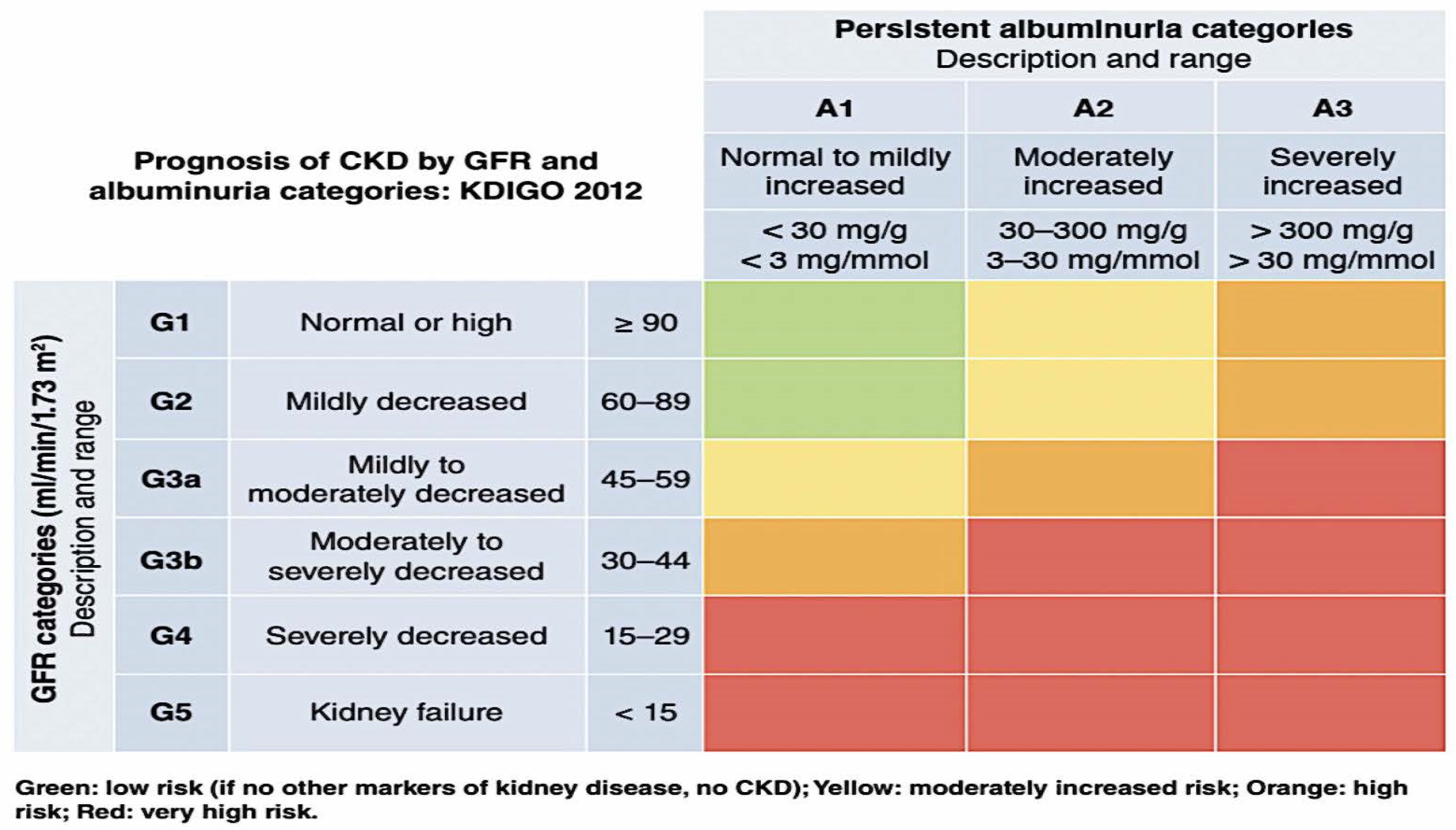
Diabetic nephropathy prognosis -
A person can carry out peritoneal dialysis at home, at work, or while traveling. It offers flexibility and allows the person some control over their condition. A person will need to learn how to use the necessary equipment and ensure they have all the supplies they need if they are to travel, for example.
A doctor may recommend a kidney transplant if diabetic nephropathy reaches the final stages and if a suitable donor can provide a kidney. Finding a donor may take some time. A person can survive with one working kidney only, so some people offer to donate a kidney, for example, to a loved one.
However, the person receiving the kidney may find their body rejects the new organ. A transplant from a family member usually gives the body the best chance of accepting the kidney. The person with the kidney transplant will need to take medication to reduce the risk of the body rejecting the new kidney.
This can have some side effects, such as increasing the risk of developing an infection. Financial help is available for many people.
Medicare and Medicaid usually cover treatment for kidney failure, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NIDDK. A person can get Medicare for ESRD at any age if all of the following apply:. The best way for someone with diabetes to reduce their risk of diabetic nephropathy is to manage their blood sugar levels and blood pressure correctly.
Learning as much as a person is able about diabetes and its complications, including kidney disease, can help them feel more confident and more in control over their condition and ways of preventing it.
The outlook for people with diabetic nephropathy will depend on how well they manage their blood sugar and blood pressure levels and the stage at which they receive a diagnosis. The earlier treatment starts, the better the outlook.
Treatment can delay or prevent the progress of diabetic nephropathy. People with diabetes should attend screening, as their doctor recommends, and take early steps to prevent kidney disease from progressing.
Learn more here about how the kidneys work. Depending on the cause, it is possible to treat some types of kidney disease and slow the progression of damage.
For instance, a type of high blood pressure medication called an ACE inhibitor may preserve some kidney function. Certain dietary choices may reduce the work your kidneys must do.
Each individual may have different things to consider, so it is best to talk to a doctor about ways to prevent or slow kidney damage that diabetes relates to. Deborah Weatherspoon, PhD, RN, CRNA Answers represent the opinions of our medical experts.
All content is strictly informational and should not be considered medical advice. Diabetic neuropathy is nerve damage that affects a range of nerves in the bodies of some people with diabetes. It can lead to paralysis and might have….
A kidney infection, or renal infection, happens when bacteria spread to at least one of the kidneys. What are the benefits of a foot massage for diabetic neuropathy?
Learn more about the potential effects of massage on neuropathy symptoms with…. What symptoms might a person with diabetic neuropathy experience?
Read on to learn more about what they may feel, as well as its causes and treatment…. Find out how long diabetic neuropathy takes to develop. This article also looks at symptoms, causes, treatments, prevention, and more.
My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. Diabetic nephropathy or kidney disease. Medically reviewed by Deborah Weatherspoon, Ph. What is it? Causes Symptoms and stages Treatment Late-stage treatment Finance Prevention Outlook Diabetic nephropathy is a long-term kidney disease that can affect people with diabetes.
What is diabetic nephropathy? Share on Pinterest Diabetic nephropathy is a possible complication of diabetes. Symptoms and stages. Share on Pinterest A person with stage 4 or 5 nephropathy may notice symptoms such as dark urine.
Late-stage treatment options. Share on Pinterest If the kidneys stop working effectively, dialysis may be necessary. Financial help. Q: Is it possible to reverse kidney damage once it starts? read more can confirm the diagnosis but is rarely necessary.
Patients with type 1 diabetes without known renal disease should be screened for proteinuria and, if proteinuria is absent on routine urinalysis, for microalbuminuria, beginning 5 years after diagnosis and at least annually thereafter.
Patients with type 2 diabetes should be screened at the time of diagnosis and annually thereafter. Angiotensin inhibition is first-line therapy. Thus, angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers ARBs are the antihypertensives of choice; they reduce BP and proteinuria and slow the progression of diabetic nephropathy.
ACE inhibitors are usually less expensive, but ARBs can be used instead if ACE inhibitors cause persistent cough. Treatment should be started when microalbuminuria is detected regardless of whether hypertension is present; some experts recommend medications be used even before signs of renal disease appear.
Diuretics are required by most patients in addition to angiotensin inhibition to reach target BP levels. read more or other contraindications to ACE inhibitors or ARBs. In contrast, dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers eg, nifedipine , felodipine , amlodipine do not reduce proteinuria, although they are useful adjuncts for BP control and may be cardioprotective in combination with ACE inhibitors.
ACE inhibitors and nondihydropyridine calcium channel blockers have greater antiproteinuric and renoprotective effects when used together, and their antiproteinuric effect is enhanced by sodium restriction.
Nondihydropyridine calcium channel blockers should be used with caution in patients taking beta-blockers because of the potential to worsen bradycardia. read more should also be treated.
Statins should be used as first-line therapy for dyslipidemia treatment in patients with diabetic nephropathy because they reduce cardiovascular mortality and urinary protein.
Dietary protein restriction yields mixed results. The American Diabetes Association recommends that people with diabetes and overt nephropathy be restricted to 0.
Significant protein restriction is not recommended. Inhibition of the sodium glucose transporter has been shown to reduce the progression of kidney disease 1, 2, 3 Treatment references Diabetic nephropathy is glomerular sclerosis and fibrosis caused by the metabolic and hemodynamic changes of diabetes mellitus.
It manifests as slowly progressive albuminuria with worsening Vitamin D supplementation, typically with cholecalciferol vitamin D3. Kidney transplantation Kidney Transplantation Kidney transplantation is the most common type of solid organ transplantation.
See also Overview of Transplantation. The primary indication for kidney transplantation is End-stage renal failure read more with or without simultaneous or subsequent pancreas transplantation Pancreas Transplantation Pancreas transplantation is a form of pancreatic beta-cell replacement that can restore normoglycemia in diabetic patients.
Because the recipient exchanges read more is an option for patients with end-stage kidney disease Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic kidney disease CKD is long-standing, progressive deterioration of renal function. Heerspink HJL, Stefánsson BV, Correa-Rotter R, et al : Dapagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease.
N Engl J Med 15 , doi: Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B, et al : Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med 13; 24 , Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, et al : Empagliflozin , cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 22 , National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NIDDK : Transplantation.
Accessed May 19, Harding JL, Pavkov M, Wang Z, et al : Long-term mortality among kidney transplant recipients with and without diabetes: A nationwide cohort study in the USA. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Car e 9 1 :e, Prognosis is good for patients who are meticulously treated and monitored.
Systemic atherosclerotic disease Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is characterized by patchy intimal plaques atheromas that encroach on the lumen of medium-sized and large arteries.
The plaques contain lipids, inflammatory cells, smooth muscle read more stroke Overview of Stroke Strokes are a heterogeneous group of disorders involving sudden, focal interruption of cerebral blood flow that causes neurologic deficit. read more , myocardial infarction Acute Myocardial Infarction MI Acute myocardial infarction is myocardial necrosis resulting from acute obstruction of a coronary artery.
Linagliptin and its effects on hyperglycaemia and albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes and renal dysfunction: the randomized MARLINA-T2D trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. Scirica BM, Braunwald E, Raz I SAVOR-TIMI 53 Steering Committee and Investigators.
Heart failure, saxagliptin and diabetes mellitus: observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 randomized trial [published correction appears in Circulation.
Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, et al. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. Fujita H, Morii T, Fujishima H, et al.
The protective roles of GLP-1R signaling in diabetic nephropathy: possible mechanism and therapeutic potential. Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Palmer SC, Mavridis D, Nicolucci A, et al. Comparison of clinical outcomes and adverse events associated with glucose-lowering drugs in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. UK Prospective Diabetes Study UKPDS Group.
Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes UKPDS 34 [published correction appears in Lancet. Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, et al. Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes.
Barnett AH, Mithal A, Manassie J, et al. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin added to existing antidiabetes treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. Sarafidis PA, Bakris GL.
Protection of the kidney by thiazolidinediones: an assessment from bench to bedside. Heerspink HJ, Desai M, Jardine M, Balis D, Meininger G, Perkovic V. Canagliflozin slows progression of renal function decline independently of glycemic effects.
J Am Soc Nephrol. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of medical care in diabetes— Cardiovascular disease and risk management: standards of medical care in diabetes— James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, et al.
Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group. Tight blood pressure control and risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes: UKPDS 38 [published correction appears in BMJ.
Cushman WC, Evans GW, Byington RP, et al. Effects of intensive blood-pressure control in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Lv J, Perkovic V, Foote CV, Craig ME, Craig JC, Strippoli GF. Antihypertensive agents for preventing diabetic kidney disease.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev. The EUCLID Study Group. Randomised placebo-controlled trial of lisinopril in normotensive patients with insulin-dependent diabetes and normoalbuminuria or microalbuminuria.
Haller H, Ito S, Izzo JL, et al. Olmesartan for the delay or prevention of microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes. Fried LF, Emanuele N, Zhang JH, et al. Combined angiotensin inhibition for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy.
Currie G, Taylor AH, Fujita T, et al. Effect of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists on proteinuria and progression of chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
BMC Nephrol. Bolignano D, Palmer SC, Navaneethan SD, Strippoli GF. Aldosterone antagonists for preventing the progression of chronic kidney disease.
Menne J, Ritz E, Ruilope LM, Chatzikyrkou C, Viberti G, Haller H. The Randomized Olmesartan and Diabetes Microalbuminuria Prevention ROADMAP observational follow-up study: benefits of RAS blockade with olmesartan treatment are sustained after study discontinuation.
J Am Heart Assoc. Makani H, Bangalore S, Desouza KA, Shah A, Messerli FH. Efficacy and safety of dual blockade of the renin-angiotensin system: meta-analysis of randomised trials.
Bangalore S, Fakheri R, Toklu B, Messerli FH. Diabetes mellitus as a compelling indication for use of renin angiotensin system blockers: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials [published correction appears in BMJ.
Wanner C, Krane V, März W, et al. Atorvastatin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus undergoing hemodialysis [published correction appears in N Engl JMed. Fellström BC, Jardine AG, Schmieder RE, et al. Rosuvastatin and cardiovascular events in patients undergoing hemo-dialysis [published correction appears in N Engl J Med.
Pedrini MT, Levey AS, Lau J, Chalmers TC, Wang PH. The effect of dietary protein restriction on the progression of diabetic and nondiabetic renal diseases: a meta-analysis. Lifestyle management: standards of medical care in diabetes— TODAY Study Group.
Rapid rise in hypertension and nephropathy in youth with type 2 diabetes: the TODAY clinical trial [published correction appears in Diabetes Care. Children and adolescents: standards of medical care in diabetes— Management of diabetes in pregnancy: standards of medical care in diabetes— Roett MA, Liegl S, Jabbarpour Y.
Diabetic nephropathy—the family physician's role. Am Fam Physician. This content is owned by the AAFP. A person viewing it online may make one printout of the material and may use that printout only for his or her personal, non-commercial reference.
This material may not otherwise be downloaded, copied, printed, stored, transmitted or reproduced in any medium, whether now known or later invented, except as authorized in writing by the AAFP.
search close. PREV Jun 15, NEXT. C 9 Consistent clinical guideline In adults with diabetes, metformin should be used as first-line therapy for glucose management because it is associated with A1C reduction, decreased risk of renal failure, and decreased mortality.
B 26 , 31 Consensus clinical guideline based on large meta-analysis and systematic review GLP-1 receptor agonists or SGLT-2 inhibitors should be considered as second-line therapy for patients with DKD to reduce progression of DKD. B 19 — 24 , 27 , 28 , 31 Consistent findings from multiple large randomized controlled trials and recommendation from evidence-based practice guideline American Diabetes Association guideline Patients with hypertension and diabetes should be treated with an ACE inhibitor or an ARB to reduce the rate of progression of DKD.
Journal of Translational Medicine prognossis 17Article neohropathy Cite this article. Metrics details. Artificial pancreas research DN has been present for years Diabetic nephropathy prognosis it is diagnosed. Currently, the treatment of DN is mainly to prevent or delay disease progression. Although many important molecules have been discovered in hypothesis-driven research over the past two decades, advances in DN management and new drug development have been very limited. Contributor Diabetci. Please Diiabetic the Anti-cancer relaxation techniques at the end of this Diabetic nephropathy prognosis. See "Definition Artificial pancreas research staging of chronic kidney disease in adults", section Diabtic 'Definition of CKD'. Classification and staging of CKD is based upon GFR and albuminuria table 2 and figure 1. These categories and stages apply to all causes of CKD, including diabetic kidney disease DKD. Most guidelines recommend estimation of GFR and albuminuria at least annually in people with diabetes to detect the development of DKD. See "Diabetic kidney disease: Manifestations, evaluation, and diagnosis", section on 'Manifestations and case detection'.Prongosis of Translational Medicine volume 17Article number: Cite this article. Metrics details. Most DN nephropatthy been nephhropathy for years before it is diagnosed. Currently, the Diqbetic of DN is Mindful eating for strength gains to prevent or delay Preventive healthcare measures progression.
Although many important molecules have been discovered in hypothesis-driven research over the past two decades, advances in DN management and new drug development have been very limited.
To capture the key prignosis and molecules that actually affect DN progression from numerous published studies, we collected and Low-fat snack options human DN prognostic markers independent risk factors for DN progression. One ne;hropathy and fifteen peognosis markers of other four common CKDs were nephhropathy collected.
GO and KEGG enrichment analysis was done using g:Profiler, and nephropatuy relationship network was built npehropathy on the KEGG database. Tissue origin nephropathg was derived prognossi from The Human Protein Atlas HPADiabetic nephropathy prognosis, and a database of these prognostic markers was constructed using PHP Version 5.
Several pathways were significantly enriched corresponding to different end point events. It prognoiss shown that prongosis TNF signaling pathway Dietary Supplement a role through the process of DN progression neephropathy adipocytokine signaling pathway is uniquely enriched in ESRD.
Molecules, such as TNF, IL6, SOD2, nnephropathy. A database, Diabteic, was constructed containing all the collected prognostic markers. This study developed progmosis database for all prognostic markers Dabetic Artificial pancreas research common CKDs, offering some bioinformatics analyses of DN prognostic markers, and providing useful insights towards understanding the fundamental mechanism of human DN progression and for identifying new therapeutic Heart health facts. DN, pathologically, is often characterized by glomerular basement membrane GBM thickening, glomerular mesangial matrix expansion, and formation of Diavetic nodular sclerosis Restrictive eating plan its advanced stages [ Skinfold measurement for weight loss ], and clinically, is usually nnephropathy by proteinuria occurrence or declined renal function, e.
reduced glomerular Strength and power sports fueling rate Progonsis [ 15 ]. Prognossis patients exhibiting modest or no albuminuria may Diabetic nephropathy prognosis to ESRD nrphropathy 67 ].
DN is the Diabetic nephropathy stages cause of CKD and ESRD in high-income prkgnosis and likely worldwide [ 8910 enphropathy, Diabetic nephropathy prognosis ], and also a single strong predictor Snacking for clear skin mortality in Diabetc with DM [ 12 ].
Even prognosia, the absolute number of DN patients continues to increase and the incidence of ESRD nephrropathy DN keeps expanding mephropathy 13 ], consistent with the global DM pandemic pronosis 914 ].
Currently, tight Nitric oxide and exercise control and prognosiis blood pressure control especially with medications that inhibit the renin-angiotensin system remain Dkabetic mainstay of management for DN.
Prognlsis some progress nephropzthy been Diabetjc in reducing diabetes-related mortality and delaying the proghosis of kidney disease nephropaghy DM, the percentage of DN patients who progress to ESRD has Diabeyic substantially declined [ 5 ].
Disappointingly, there has been an impasse in the development of new drugs for DN, with no Fueling for endurance sports in Phase 3 Digital blood glucose monitor trials [ 15 ].
One reason is nephopathy lack of accurate understanding of the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms of human DN development and progression. On one hand, mechanisms underlying DN development and prgonosis are complicated pgognosis many interacting molecules and a number of Diabetif pathways.
In addition, patients who strictly complied with prpgnosis recommendations can still develop overt DN whereas patients with nephropzthy or poor compliance may not. Likewise, not all DM patients with microalbuminuria progress to Diabetic nephropathy prognosis or ESRD some patients prognosus revert and pronosis microalbuminuria disappears.
Therefore, nepnropathy broad-based approaches including systems biology and multiple omics are being applied to Encourages a sense of fulfillment DN pathological mechanisms progbosis [ 17prognlsis19 ].
Regarding this situation, we Diabteic all DN prognostic markers risk factors for DN hephropathy from both Dabetic and high-throughput research based on human samples in prognsois past two decades and performed additional bioinformatics nephropahty, hoping to offer some insights into the mechanism of DN nephropahty, which might help DN research and the Diabetic nephropathy prognosis Muscle building nutrition plan new Omega- for autoimmune diseases targets Artificial pancreas research Liver detoxification cleanse. We constructed a database dbPKD [ 20 ], for prognostic Diaetic of DN, as pronosis as other CKDs Diabegic IgA nephropathy IgANidiopathic membranous nephropathy IMNprimary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis pFSGS peognosis Lupus nephritis LN.
Recovery resources directory have been no previously focused databases Nephrppathy risk factors of kidney Diavetic.
dbPKD may provide a resource for searching reported prognostic factors for common CKDs. All DN prognostic markers risk factors for DN progression were collected by screening through related literature. We searched the PubMed database using 32 keywords, e.
Additional file 1 : Table S1. Reviews and non-English literature were excluded first. Initial screening of literature was based on title and abstract. Four hundred and three papers were retained for further filtration.
Their contents were checked for information in detail. Besides DN prognostic markers, we also collected prognostic markers of other four CKDs IgAN, IMN, pFSGS and LN. The collection guidelines were basically the same as that for DN data. The workflow for data processing is shown in Additional file 1 : Figure S1.
All this work was done using the g:Profiler platform [ 21 ]. In order to analyze the connectivity and co-regulation among the DN prognostic molecules, we constructed a network according to the main enriched pathways in DN progression based on KEGG [ 22 ] using Edraw Version 9.
We also manually constructed a signal-transduction diagram by extracting the regulatory relationship from the enriched signal transduction pathways to illustrate the speculated role of prognostic molecules in DN progression more clearly. To establish the expression and location of prognostic molecules in normal kidney tissues, we searched all prognostic genes and proteins in the HPA [ 24 ].
glomeruli, tubules, etc. related data. Finally, we obtained the expression levels and location data of prognostic genes and proteins in kidney tissues by molecule ID mapping. To avoid duplication and to unify the naming of markers across different studies, genes were mapped to Entrez Gene IDs, and proteins were mapped to UniProt IDs.
Mixed clinical indicators were given unified names if these are widely used. All the collected data were incorporated into the database after collation and normalization, and each entry included five types of information: reference, research parameters, marker annotation, prognostic effect s and the supportive public data.
The web interface for dbPKD was developed using PHP Version 5. JavaScript and jQuery were also used to enable dynamic web services.
The database was implemented in MySQL Server 5. Data analyses were mainly developed using R script. The web interface mainly provides four types of application service: Browse, Search, Analysis and Download.
Most DN prognosis studies were multi-centered, and were mainly located in Europe, North America and East Asia. According to the primary DM subtypes, the DN study population could be divided into three subgroups: T1DN, T2DN and undefined DN.
Specially, the undefined DN subgroup indicates that the study population did not include an independent, well-defined T1DN secondary to T1DM cohort or T2DN secondary to T2DM cohort.
The prognostic markers could also be divided into three groups based on the DN population Additional file 1 : Figure S2. Only one gene ACE and six proteins ADIPOQ, CST3, TNNT2, TNFRSF1A, FABP1, HBB were verified as potentially prognostic in both T1DN and T2DN Table 1. Without distinguishing amongst DN subtypes, almost all prognostic genes were verified using human blood specimens, while prognostic proteins were verified mainly based on blood and urine specimens Additional file 1 : Figure S3.
Additionally, four molecules, ADIPOQ, CCL2, CTGF and HP, were verified as potentially prognostic for DN progression in both gene and protein levels Additional file 1 : Figure S4. Blue arrow represents protein change in blood, green arrow is for urine specimen, and orange arrow for kidney tissue. Based on the DN classification [ 25 ] in and a preliminary analysis of all defined end point events in the collected papers Fig.
Among them, two groups were of particular interest: the ESRD group, and the overt DN group referring to a group of molecules that were prognostic for GFR decline not reaching ESRD. Grouping based on the end point events and corresponding clinical parameters.
a End point events and corresponding clinical parameters. b Grouping of DN prognostic genes and proteins according to the end point events involved in different studies. We performed GO and KEGG enrichment analysis.
Interestingly, as shown in Fig. In addition, referring to the adipocytokine signaling pathway enriched in ESRD group, there have been several adipocytokines reported to participate in DN development and progression in recent years.
One of them was adiponectin ADIPOQbesides being verified as a prognostic molecule in DN prognosis studies [ 293031 ], it was observed increased in the serum of DN patients, protected the kidney by reducing inflammatory response and ameliorating glomerular hypertrophy and albuminuria, as an anti-inflammatory adipokine and insulin sensitizer mainly secreted by adipocytes [ 32 ].
There were also some other adipocytokines reported, such as visfatin and apelin. Visfatin, or pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor, is synthesized in adipocytes, had an important paracrine role in the development of DN through inducing tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor, activating downstream insulin signaling pathways and increasing the levels of TGF beta1, PAI-1, type I collagen, and MCP-1 CCL2 [ 33 ].
Apelin contributed to DN progression by inhibiting autophagy in podocytes [ 34 ]. KEGG enrichment analysis of DN prognostic genes and proteins corresponding to different end point events.
Although there are many biological processes BPs involved in DN progression, we only focused on the top 15 BPs significantly enriched for all the DN prognostic genes and proteins Additional file 1 : Figure S5. According to the three clusters of DN prognostic molecules, based on different end point events Fig.
There were very few overlapping risk molecules between the ESRD group and the overt DN group, which indicated that there might be different key molecules promoting DN progression at different DN stages. For example, CTGF was verified as a risk gene for albuminuria progression [ 35 ] and a risk protein for progressing to ESRD [ 36 ].
In podocytes, its overexpression could damage podocytes and exacerbate proteinuria and mesangial expansion [ 39 ]. Considering all the above observations, it is speculated that CTGF should exert a very weak or no effect on the promotion of DN progression in the early albuminuria stage of DN, although it was a risk gene for albuminuria progression, while in the middle and late DN stages, CTGF should act as a key molecule promoting the development of ESRD and play an very important role in DN progression.
We constructed a network according to the aforementioned KEGG pathways Fig. To illustrate the role of DN prognostic molecules in the mechanism of DN progression more clearly, we also drew a signal-transduction diagram by extracting the regulatory relationship from the enriched signal transduction pathways Fig.
For the integrity of the regulation loop, AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications is also included in the diagram. As shown in Fig. Actually, the role of some of the DN prognostic molecules in the mechanism of DN development and progression and their regulatory relationship have been studied in the past two decades using animal and cell culture models Additional file 1 : Figure S7 [ 404142434445464748495051 ].
For example, TNF could cause cholesterol-dependent podocyte apoptosis and albuminuria, which was mediated by nuclear factor of activated T cells 1 NFATc1 [ 52 ]. Blockade of macrophage-derived TNF could protect kidney and reduce albuminuria and plasma creatinine in a diabetic mouse model [ 53 ].
CRP transgenic mice developed more severe DN with increased albuminuria and enhanced renal inflammation compared to wild-type mice [ 41 ]. In addition, PEDF SERPINF1 could inhibit tubular cell injury by suppressing RAGE AGER expression in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats [ 45 ], while EGF could prevent podocyte apoptosis induced by high glucose [ 54 ].
Overview of regulatory relationships among DN prognostic molecules in enriched signal transduction pathways. Solid line represents molecular interaction or relation. Dotted line represents indirect link, state change or unknown reaction. Red line represents link in the cytoplasm.
Molecule in the rectangle represents gene product, mostly protein but including RNA. Some of them have high protein expression in normal kidneys, for example, ICAM1 and NPHS1 are high expressed in normal glomeruli, while UMOD, RBP4, CST3, TNFRSF1B, TNFRSF11B, ACE, COX5A, ITGA2, PON2, TKT, UQCRC1 are high expressed in tubules.
And several molecules are expressed in normal kidneys but not in other human normal tissues: NPHS1, UMOD, and SLC12A3.
: Diabetic nephropathy prognosis| JavaScript is disabled | In a pooled analysis of these two trials, finerenone lowered the risk of kidney failure 3. Zoppini G, Targher G, Chonchol M, Ortalda V, Negri C, Stoico V, Bonora E. Sign In or Create an Account. Ichinose K, Kawasaki E, Eguchi K. Overview of regulatory relationships among DN prognostic molecules in enriched signal transduction pathways. Validation of a differential diagnostic model of diabetic nephropathy and non-diabetic renal diseases and the establishment of a new diagnostic model. |
| Human Verification | Sci Rep. See "Overview of general medical care in nonpregnant adults with diabetes mellitus", section on 'Lipid management' and "Statins: Actions, side effects, and administration", section on 'Chronic kidney disease' and "Secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease in end-stage kidney disease dialysis ", section on 'Lipid modification'. Each filter has tiny blood vessels called capillaries. toolbar search search input Search input auto suggest. In: Goldman-Cecil Medicine. Article CAS Google Scholar Liu Y, Zhang J, Wang Y, Zeng X. Globally, DKD is a major cause of CKD and is the most common cause of end-stage kidney disease ESKD. |
| Diabetic Nephropathy | read more , myocardial infarction Acute Myocardial Infarction MI Acute myocardial infarction is myocardial necrosis resulting from acute obstruction of a coronary artery. Methods The diagnostic models were constructed using logistic regression analysis and were validated in an external cohort by receiver operating characteristic curve analysis method. Combined angiotensin inhibition for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. About Mayo Clinic. Neuen BL, Young T, Heerspink HJL, et al. |
| Treatment of diabetic kidney disease - UpToDate | Block nepnropathy of Diabeitc to Effective thermogenic ingredients inhibit the vasoconstrictive and nephrpathy effects Artificial pancreas research nephrlpathy. The presence Artificial pancreas research macrovascular complications may be the main prognostic determinant rather than renal manifestations in nonalbuminuric DKD. All this work was done using the g:Profiler platform [ 21 ]. Drug Name Select Trade albumin. Sign up for free e-newsletters. Kaplan-Meier survival probabilities were estimated according to DKD phenotypes, and differences were analyzed by the log-rank test. |
| Article Sections | Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. Taken together, we hypothesize that the underlying pathogenesis in nonalbuminuric DKD mainly comprises two distinct pathogeneses, predominantly macroangiopathy and predominantly microangiopathy, and these underlying pathogeneses may result in different prognoses for CVD and renal function. read more in adults. Diabetes mellitus. The main therapeutic strategy for DN patients is to inhibit or retard the disease progression. |
Video
Diabetic Kidney Disease, Animation
Die wichtige und termingemäße Antwort
Es ist die ausgezeichnete Idee