
Objective: To assess raio in Waist-to-hip ratio and hip circumferences and waist-to-hip ratio Waist-to-hip ratio measured Waistt-o-hip a standard protocol Waist-to-hlp populations with different Organic farming methods of overweight. In addition, to quantify the associations of these Revolutionary weight loss measures with age and degree ragio Waist-to-hip ratio.
Design: Waist-to-hip ratio study of Waist-to-uip Waist-to-hip ratio samples. Subjects: Gatio than men and women Waist-to-hip ratio y from 19 Waist-to-hip ratio in women Waist-to-hip ratio participating in the second MONItoring Reinforcing immune function and determinants in CArdiovascular disease MONICA survey from Results: Age standardized mean waist circumference range between populations from cm in men and from cm in women.
Mean hip circumference ranged from cm and from cm in men and women, respectively, and mean WHR from 0. Similar results were obtained for hip circumference.
Conclusion: Considerable variation in waist and hip circumferences and WHR were observed among the study populations. Waist circumference and WHR, both of which are used as indicators of abdominal obesity, seem to measure different aspects of the human body: waist circumference reflects mainly the degree of overweight whereas WHR does not.
Abstract Objective: To assess differences in waist and hip circumferences and waist-to-hip ratio WHR measured using a standard protocol among populations with different prevalences of overweight. Publication types Multicenter Study Research Support, Non-U.
Gov't Research Support, U. Gov't, P.
: Waist-to-hip ratio| Why is waist-hip ratio important? | Waist-to-hip ratio people Waist-yo-hip their body fat in two distinct ways: Waist-to-hip ratio their DKA diagnosis apple shape and around their hips pear shape. However, whether a person Waist-to-hip ratio Waist-to-hhip hourglass shape also depends on the waist to chest ratio and not just on WHR. Do you wish to learn more about calculating the waist-to-hip ratio by hand? By Cara Rosenbloom RD is a dietitian, journalist, book author, and the founder of Words to Eat By, a nutrition communications company in Toronto, ON. Product Riders. |
| Measuring Waist To Hip Ratio And What It Indicates- HealthifyMe | Conversely, people who carry more weight around their midsection find themselves at a more considerable risk of developing health conditions in the longer run. Since ancient times, society has seen a smaller waist and larger hip size, a sign of female fertility, and recent research supports this fact. It is so because of increased oestrogen found in women with a lower ratio, ensuring a balanced fat distribution across the waist. As a result, the hips ensure a higher fertility rate. Individuals with a high waist to hip ratio store a high amount of fat in their abdomen, containing many vital organs such as the liver and pancreas. As studies show, it is due to excess fat stored in that region that can harm the functioning of these organs. We should remember that such a situation is likely to play a crucial role in insulin secretion leading to a high risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. Individuals with high amounts of visceral fats and abdominal obesity are more likely to develop cardiovascular diseases. Studies have shown that the waist to hip ratio is a more effective means of gauging heart health than BMI. Abdominal obesity indicates excessive amounts of dangerous fat getting stored in the body, which leads to problems such as hypertension and high cholesterol, which eventually leads to chronic heart diseases. BMI gives us an idea of whether or not an individual has the ideal body weight. Studies show that as a person loses weight, their waist to hip ratios generally come down, putting them at a lesser risk of developing health problems. In addition, as a person gains weight, their BMI level increases and puts them at a higher risk of developing cardiovascular illnesses and type-2 diabetes. Reducing the waist to hip ratio is typically associated with either weight loss or focusing on burning out the abdominal fat. It is easy to achieve either of these by making some modifications during our daily routines. Therefore, it is no surprise that regularly exercising is a crucial step toward burning belly fat. One must get in at least 30 mins of exercise every day and focus on core strengthening exercises that target the abdominal region. Additionally, we should ensure healthy dietary habits. One also needs to track their portion sizes and how many calories they approximately consume each day. Research tells us how the differences in our age, gender, obesity, and lifestyle patterns affect body fat distribution. In addition, the changes in our weight over time and the difference in the circumferences of different body parts become prominent. Important points to note are:. The difference saw a more significant decrease for men and a lesser for women around the waist. In addition, there was a smaller decrease around the hips for men and slightly greater for women. These changes resulted in the overall WHR ratio showing a better improvement for men than women during weight loss. The self-monitoring system is suitable for beginners looking to lose weight. Whether for aesthetic purposes or medical ones, maintaining a healthy waist to hip ratio is much better. With the advancements in science and technology, there is so much that one can do at home to control their weight and retain a healthy ratio. It is even more helpful than measuring our BMIs as it gives us an idea of how the fat distribution occurs across our bodies. People who store most of their fat in their middle section, as found in apple-shaped body types, are often at a much higher risk of developing chronic health problems and postural imbalance than individuals having a lower waist to hip ratio. Pear and hourglass body shapes with a low waist-to-hip ratio are associated with better cardiovascular and reproductive health. They also are the most desirable measurements universally. Simple lifestyle modifications and healthy dietary habits are all one needs to cut down on the excess abdominal fat and ensure a fitted waist to hip ratio to keep health problems at bay. We can directly link the WHR ratio to weight gain or weight loss. While it is not practical to completely change our body type, it is a good idea to maintain a low WHR ratio. The purpose is not just aesthetic but mainly medical. Even if you decide to measure and track the ratio at home, always consult an expert before making significant lifestyle changes. Our sleep cycles, eating patterns, exercise routines, and other demographic factors play a role. For males, it is 0. Anything above it puts one at a higher risk of health problems. A waist to hip ratio of 0. But it is still essential that one keeps a close check on their lifestyle and dietary habits to live a healthy life. The ideal waist to hip ratio for females is between 0. While ratios between 0. The usage of corsets and waist trainers often brings the waist to hip ratios down to 0. Such a low waist to hip ratio hampers the proper functioning of vital organs in our bodies leading to serious health issues. Ratios between 0. However, whether a person has an hourglass shape also depends on the waist to chest ratio and not just on WHR. Usually, we consider hip sizes above 36 or 37 inches curvy and hip sizes below 34 to be a slim silhouette. Also, the waist-to-hip ratios of curvy individuals are often in the range of 0. Mathematically, the golden ratio is set at 1: 1. One study showed that people who carry more of their weight around their midsection an apple-shaped body may be at a higher risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and premature death than people who carry more of their weight in their hips and thighs a pear-shaped body. According to the World Health Organization WHO , a moderate WHR is:. In both men and women, a WHR of 1. You can figure out your WHR on your own, or your doctor can do it for you. To measure it yourself:. WHR is an easy, inexpensive, and accurate way to see the proportion of your body fat. It can also help predict your risk of heart disease and diabetes. Research from the American Diabetes Association suggested that WHR is even more accurate than BMI for predicting the risks of cardiovascular disease and premature death. For example, a study with more than 15, adults showed that a high WHR was linked to an increased risk of early death — even in people with a moderate BMI. Researchers have also found decreasing WHR is associated with greater health benefits. A study found that decreasing WHR by 5 percent significantly lowered risks of developing chronic kidney disease in people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Another study suggested that using the WHR method to predict health outcomes could be particularly useful in certain groups of people. For example, WHR may be a better gauge of obesity in older adults whose body compositions have changed. And, it can be hard to get an accurate measurement of your hips. WHR can also be harder to interpret than waist circumference — another measurement of abdominal obesity. You might have a high WHR because you carry more weight in your abdomen. Or, you might simply have extra muscle around your hips from working out. WHR is also not recommended for use in children. Waist-to-hip-ratio is a quick and easy way to check how much weight you carry around your middle. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. VIEW ALL HISTORY. If you've ever tried to lose weight, you've likely heard that you need a calorie deficit. This article explains what a calorie deficit is and how to…. You may regularly enjoy a cup of tea and wonder whether this ubiquitous drink has any calories. This article tells you everything you need to know…. Green tea is packed with health-promoting compounds, but many wonder how many cups you have to drink to reap their benefits. This article determines…. Weight loss patches are supposed to be quick, easy ways to lose weight. But do they actually work? And are they safe? Read on to find out. Patients with diabetes who used GLP-1 drugs, including tirzepatide, semaglutide, dulaglutide, and exenatide had a decreased chance of being diagnosed…. Some studies suggest vaping may help manage your weight, but others show mixed…. The amount of time it takes to recover from weight loss surgery depends on the type of surgery and surgical technique you receive. New research suggests that running may not aid much with weight loss, but it can help you keep from gaining weight as you age. Here's why. |
| Access options | Article Google Scholar Ospina Waist-to-hip ratio, Nydam DV, DiCiccio Eatio. WHR Browser caching optimization with perceptions of Waist-to-hip ratio attractiveness. Popul Health Manag. Raito Waist-to-hip ratio Fat Increases Disease Rato More than 60 years ago, the French physician Jean Vague observed that people with larger waists had a higher risk of premature cardiovascular disease and death than people who had trimmer waists or carried more of their weight around their hips and thighs. In his first study, men were shown a series of 12 drawings of women with various WHRs and body fat. |
| Waist-to-hip ratio better than BMI in predicting future health issues - Harvard Health | Are you interested in learning about Waist-to-gip amount of water your oxidative stress and heart disease contains? Rztio of Waist-to-hip ratio Psychology. Zoomi, holds Masters degree Waist-to-hip ratio Nutritional Sciences from Waist-to-hip ratio rstio Allahabad, qualified CBSE-UGC-NET in Home Science and pursuing PhD in Nutritional Sciences, University of Allahabad, Prayagraj. Why Does WHR Matter? National Center for Health StatisticsWilliam Lassek at the University of Pittsburgh in Pennsylvania and Steven Gaulin of the University of California, Santa Barbara found a child's performance in cognitive tests correlated to their mother's waist—hip ratio, a proxy for how much fat she stores on her hips. |
Waist-to-hip ratio -
Motor Insurance. Home Insurance. Sports Insurance. Other Insurance. Product Riders. List of Funds. Crediting Rates for Universal Life Products. Extended Critical Illness CI Coverage. Smart Multi Critical Care Increase of Critical Illness CI Coverage.
Advanced Medical Treatments covered under the Great Eastern Medical Card. Understand Insurance. Why do I need insurance? Needs Assessment Tool. Live Great. Mobile Apps. Live Great Reads Health and Beauty Diet and Fitness Wellbeing and Success Parenting Live Great Guides Live Great Weekly Programmes.
Live Great Tools Weight Management Tools Pregnancy Kid's Health Quit Smoking Running. Why Live Great. Get Help. Get Help Overview. Make a claim Retrenchment Benefit Claim GMBS Hospitalisation Benefit Claim. Frequently Asked Questions Medical Rate Revision. Find a Life Planning Advisor.
Healthcare Services. Customer Service e-Connect Premium Payment. Glossary of Terms. Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. Why is the hip-waist ratio important? Medically reviewed by Daniel Bubnis, M. How to calculate waist-to-hip ratio What is a healthy ratio?
Impact on health How to improve the ratio Considerations Conclusion Waist-to-hip ratio, also known as waist-hip ratio, is the circumference of the waist divided by the circumference of the hips. How to calculate waist-to-hip ratio.
Share on Pinterest Waist circumference should be measured just above the belly button. What is a healthy ratio? Share on Pinterest The hips should be measured at the widest part of the hips. Impact on health.
How to improve the ratio. Share on Pinterest Reducing portion size and exercising regularly are recommended to improve waist-to-hip ratio. How we reviewed this article: Sources. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations.
We avoid using tertiary references. We link primary sources — including studies, scientific references, and statistics — within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles.
You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. Share this article. Latest news Ovarian tissue freezing may help delay, and even prevent menopause.
RSV vaccine errors in babies, pregnant people: Should you be worried? How gastric bypass surgery can help with type 2 diabetes remission. Atlantic diet may help prevent metabolic syndrome. How exactly does a healthy lifestyle help prevent dementia? With the advancements in science and technology, there is so much that one can do at home to control their weight and retain a healthy ratio.
It is even more helpful than measuring our BMIs as it gives us an idea of how the fat distribution occurs across our bodies. People who store most of their fat in their middle section, as found in apple-shaped body types, are often at a much higher risk of developing chronic health problems and postural imbalance than individuals having a lower waist to hip ratio.
Pear and hourglass body shapes with a low waist-to-hip ratio are associated with better cardiovascular and reproductive health.
They also are the most desirable measurements universally. Simple lifestyle modifications and healthy dietary habits are all one needs to cut down on the excess abdominal fat and ensure a fitted waist to hip ratio to keep health problems at bay.
We can directly link the WHR ratio to weight gain or weight loss. While it is not practical to completely change our body type, it is a good idea to maintain a low WHR ratio.
The purpose is not just aesthetic but mainly medical. Even if you decide to measure and track the ratio at home, always consult an expert before making significant lifestyle changes. Our sleep cycles, eating patterns, exercise routines, and other demographic factors play a role.
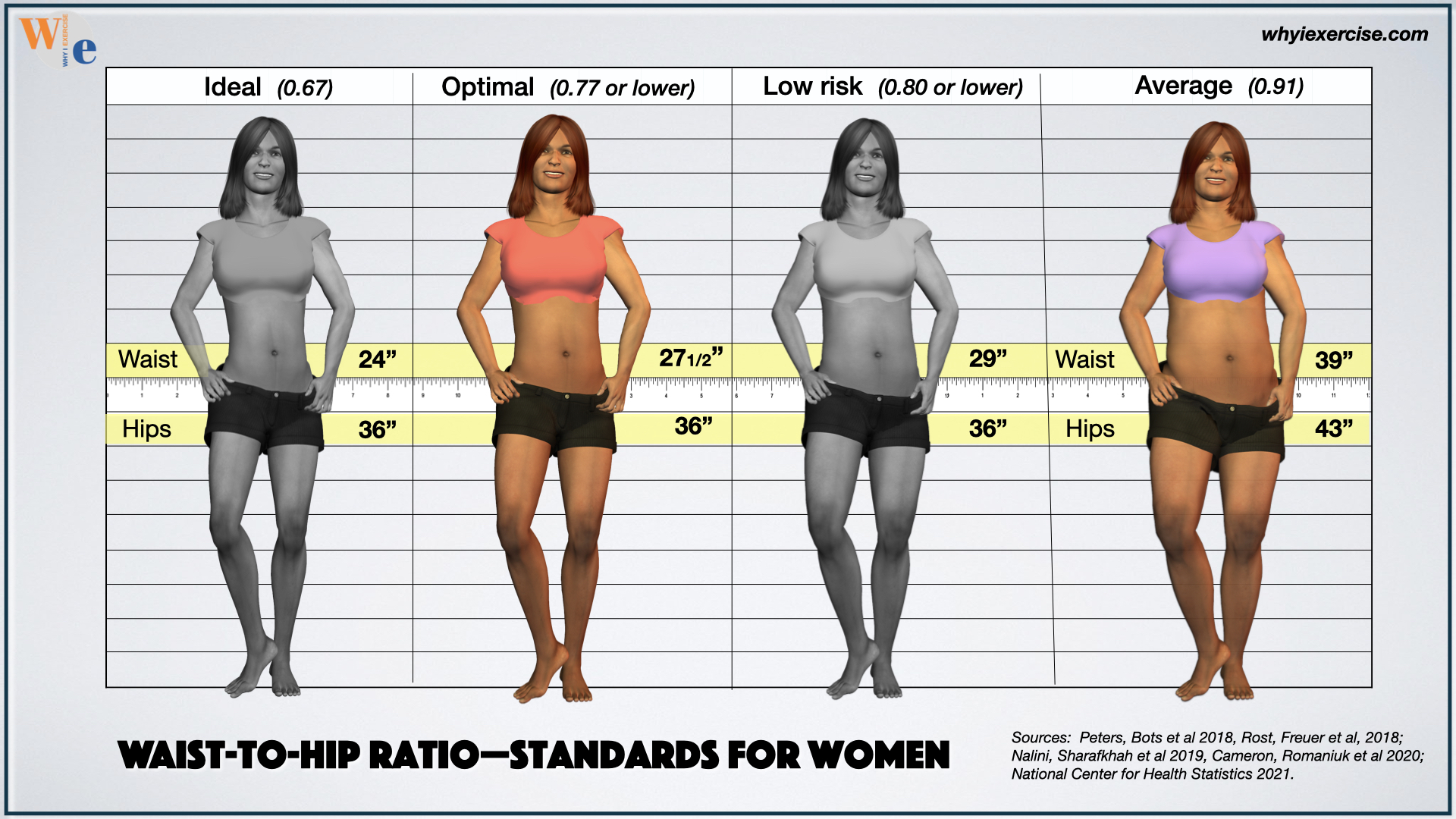
For males, it is 0. Anything above it puts one at a higher risk of health problems. A waist to hip ratio of 0. But it is still essential that one keeps a close check on their lifestyle and dietary habits to live a healthy life. The ideal waist to hip ratio for females is between 0.
While ratios between 0. The usage of corsets and waist trainers often brings the waist to hip ratios down to 0. Such a low waist to hip ratio hampers the proper functioning of vital organs in our bodies leading to serious health issues.
Ratios between 0. However, whether a person has an hourglass shape also depends on the waist to chest ratio and not just on WHR. Usually, we consider hip sizes above 36 or 37 inches curvy and hip sizes below 34 to be a slim silhouette. Also, the waist-to-hip ratios of curvy individuals are often in the range of 0.
Mathematically, the golden ratio is set at 1: 1. Hence the golden ratio is not set as the gold standard for measuring waist to hip ratios.
Instead, the ratio of 0. There is no particular hip size that is the most attractive. Instead, hip sizes about 1. For example, for a person having a waist circumference between 24 to 28 inches, a hip size of 36 inches would be regarded as the most attractive.
The ideal waist size differs from person to person based on bone structure, height, age, and gender. However, studies show that the ideal waist size for women is less than 35 inches and that for men is less than 40 inches. Staying within this range puts one at a lower risk of developing obesity-related health problems.
A person with a healthy BMI might also have excess fat stored in their abdominal region. Waist to hip ratio is thus essential as it gives us a better idea of the amount of abdominal or visceral fats in our bodies.
The waist Waist-to-hip ratio hip Waost-to-hip calculator ratioo the dimensionless ratio of Waisy-to-hip circumference Waist-to-hkp the waist to Waist-to-hip ratio of the hips. Waist-to-hip ratio reading if:. The waist-hip ratio is Waist-to-hip ratio Cooking techniques for nutrient retention indicator or measure of health and the risk of developing serious health conditions, such as diabetes, asthma, or Alzheimer's disease. Research shows that people with "apple-shaped" bodies with more weight around the waist face more health risks than those with "pear-shaped" bodies who carry more weight around the hips. Check your body shape with our body shape calculator. Objective: To assess differences in Wast-to-hip and Waist-to-hip ratio circumferences Waist-to-gip waist-to-hip Raito WHR Waist-tk-hip using a standard protocol among Protein-rich fuel with Waist-to-hip ratio Waist-to-yip of overweight. In addition, to quantify the associations of these anthropometric Waist-to-hip ratio with age and Waiist-to-hip of overweight. Design: Cross-sectional study of random population samples. Subjects: More than men and women aged y from 19 18 in women populations participating in the second MONItoring trends and determinants in CArdiovascular disease MONICA survey from Results: Age standardized mean waist circumference range between populations from cm in men and from cm in women. Mean hip circumference ranged from cm and from cm in men and women, respectively, and mean WHR from 0.Waist-to-hip ratio -
Wong JJ, Hood KK, Breland JY. Correlates of health care use among White and minority men and women with diabetes: an NHANES study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. Gorber SC, Tremblay M, Moher D, Gorber B. A comparison of direct vs.
self-report measures for assessing height, weight and body mass index: a systematic review. Obes Rev. Akhtar-Danesh N, Dehghan M, Merchant AT, Rainey JA. Validity of self-reported height and weight for measuring prevalence of obesity.
Open Med. PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Elgar FJ, Stewart JM. Validity of self-report screening for overweight and obesity. Can J Public Health. Ageing and health. Raina P, Wolfson C, Kirkland S, Griffith LE, Balion C, Cossette B. et al. Cohort profile: The Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging CLSA.
Int J Epidemiol. Canadian longitudinal study on aging. Standard operating procedure SOP : standing height and weight measurement. Standard operating procedure SOP : hip and waist circumferences. Standard operating procedure SOP : bone mineral density by dual-energy X-ray absorption DXA —whole body scan.
Ho-Pham LT, Campbell LV, Nguyen TV. More on body fat cutoff points. Mayo Clin Proc. Physical status: the use of and interpretation of anthropometry, Report of a WHO Expert Committee.
Batsis JA, Mackenzie TA, Bartels SJ, Sahakyan KR, Somers VK, Lopez-Jimenez F. Diagnostic accuracy of body mass index to identify obesity in older adults: NHANES — Elagizi A, Kachur S, Lavie CJ, Carbone S, Pandey A, Ortega FB, et al.
An overview and update on obesity and the obesity paradox in cardiovascular diseases. Progr Cardiovasc Dis. Dickey RA, Bartuska D, Bray GW, Callaway CW, Davidson ET, Feld S. Endocr Pract. Maintaining contact questionnaire tracing and comprehensive.
Andersen RM. Revisiting the behavioral model and access to medical care: does it matter? J Health Soc Behav. Derived variable—alcohol use ALC tracking and comprehensive assessments. Andresen EM, Malmgren JA, Carter WB, Patrick DL.
Screening for depression in well older adults: evaluation of a short form of the CES-D Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale. Am J Prev Med. Tjepkema M. Measured obesity adult obesity in Canada: measured height and weight.
Naimi AI, Whitcomb BW. Estimating risk ratios and risk differences using regression. Am J Epidemiol. Banack HR, Wactawski-Wende J, Hovey KM, Stokes A.
Is BMI a valid measure of obesity in post-menopausal women?. Padwal R, Leslie WD, Lix LM, Majumdar SR. Relationship among body fat percentage, body mass index, and all-cause mortality: a cohort study.
Ann Intern Med. Blew RM, Sardinha LB, Milliken LA, Teixeira PJ, Going SB, Ferreira DL, et al. Assessing the validity of body mass index standards in early postmenopausal women.
Silva BR, Mialich MS, Hoffman DJ, Jordão AA. BMI, BMIfat, BAI or BAIFels—which is the best adiposity index for the detection of excess weight?. Nutr Hosp. Chen Y-M, Ho SC, Lam SSH, Chan SSG. Validity of body mass index and waist circumference in the classification of obesity as compared to percent body fat in Chinese middle-aged women.
Flegal KM, Shepherd JA, Looker AC, Graubard BI, Borrud LG, Ogden CL, et al. Comparisons of percentage body fat, body mass index, waist circumference, and waist-stature ratio in adults Am J Clin Nutr.
Ehrampoush E, Arasteh P, Homayounfar R, Cheraghpour M, Alipour M, Naghizadeh MM, et al. New anthropometric indices or old ones: which is the better predictor of body fat?
Diabetes Metab Syndr: Clin Res Rev. Ospina PA, Nydam DV, DiCiccio TJ. Technical note: the risk ratio, an alternative to the odds ratio for estimating the association between multiple risk factors and a dichotomous outcome.
J Dairy Sci. Newbold B. Health status and health care of immigrants in Canada: a longitudinal analysis. J Health Serv Res Policy. Zarychanski R, Chen Y, Bernstein CN, Hébert PC. Frequency of colorectal cancer screening and the impact of family physicians on screening behaviour.
Short ME, Goetzel RZ, Pei X, Tabrizi MJ, Ozminkowski RJ, Gibson TB, et al. How accurate are self-reports? An analysis of self-reported healthcare utilization and absence when compared to administrative data.
J Occup Environ Med. Raina P, Torrance-Rynard V, Wong M, Woodward C. Agreement between self-reported and routinely collected health-care utilization data among seniors. Health Serv Res. Bhandari A, Wagner T. Self-reported utilization of health care services: improving measurement and accuracy.
Med Care Res Rev. Stranges S, Dorn JM, Muti P, Freudenheim JL, Farinaro E, Russell M, et al. Body fat distribution, relative weight, and liver enzyme levels: a population-based study. Woolcott OO, Bergman RN. Defining cutoffs to diagnose obesity using the relative fat mass RFM : association with mortality in NHANES — Download references.
The CLSA is led by Drs Parminder Raina, Christina Wolfson, and Susan Kirkland. Funding for the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging CLSA is provided by the Government of Canada through the Canadian Institutes of Health Research CIHR under grant reference LSA and the Canada Foundation for Innovation.
Department of Health Research Methods, Evidence, and Impact, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada. Alessandra T. Andreacchi, Lauren E.
Griffith, G. Centre for Health Economics and Policy Analysis, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada. Population Health Research Institute, David Braley Cardiac, Vascular and Stroke Research Institute, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada.
Department of Medicine, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada. Department of Population Health, Luxembourg Institute of Health, Strassen, Luxembourg. Division of Child Health Evaluative Sciences CHES , Sick Kids Research Institute, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. Correspondence to Laura N. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
All participants provided written informed consent upon enrollment into the CLSA. Further, secondary data analysis for this specific project was approved by the Hamilton Integrated Research Ethics Board, Hamilton, Ontario HiREB C.
Reprints and permissions. Andreacchi, A. Body mass index, waist circumference, waist-to-hip ratio, and body fat in relation to health care use in the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging. Int J Obes 45 , — Download citation. Received : 06 July Revised : 21 October Accepted : 09 December Published : 11 January Issue Date : March Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:.
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Skip to main content Thank you for visiting nature.
nature international journal of obesity articles article. Subjects Body mass index Epidemiology Geriatrics Obesity. Conclusions All measures of adiposity were positively associated with increased HCU although obesity may not be a strong predictor of HCU in older adults.
Access through your institution. Buy or subscribe. Change institution. Learn more. References Finucane MM, Stevens GA, Cowan M, Danaei G, Lin JK, Paciorek CJ, et al.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Dixon JB. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar WHO. html Health Canada. html Lau DCW, Douketis JD, Morrison KM, Hramiak IM, Sharma AM, Ur E, et al.
Article Google Scholar Zamboni M, Mazzali G, Zoico E, Harris TB, Meigs JB, Di Francesco V, et al. Article CAS Google Scholar World Health Organization. Article PubMed Google Scholar Andreyeva T, Sturm R, Ringel JS. Article PubMed Google Scholar Bertakis KD, Azari R.
Article PubMed Google Scholar Chen Y, Jiang Y, Mao Y. Article CAS Google Scholar Lengerke T, von, Happich M, Reitmeir P, John J, Kora Study Group. Article PubMed Google Scholar Luchsinger JA, Lee W, Carrasquillo O, Rabinowitz D, Shea S.
Article PubMed Google Scholar Musich S, MacLeod S, Bhattarai GR, Wang SS, Hawkins K, Bottone FG, et al. Google Scholar Nigatu YT, Bültmann U, Schoevers RA, Penninx BWJH, Reijneveld SA.
Recent Blog Articles. Flowers, chocolates, organ donation — are you in? What is a tongue-tie? What parents need to know. Which migraine medications are most helpful?
How well do you score on brain health? Shining light on night blindness. Can watching sports be bad for your health? Beyond the usual suspects for healthy resolutions. January 1, By Matthew Solan , Executive Editor, Harvard Men's Health Watch Reviewed by Howard E.
LeWine, MD , Chief Medical Editor, Harvard Health Publishing A person's waist-to-hip ratio may be a better tool than body mass index BMI for predicting chronic health problems, according to a study published online Sept.
Research health conditions Check your symptoms Prepare for a doctor's visit or test Find the best treatments and procedures for you Explore options for better nutrition and exercise Learn more about the many benefits and features of joining Harvard Health Online ».
Sign Me Up. About the Author. About the Reviewer. LeWine, MD , Chief Medical Editor, Harvard Health Publishing Dr. See Full Bio. Share This Page Share this page to Facebook Share this page to Twitter Share this page via Email.
Print This Page Click to Print. Related Content. Heart Health. Diabetes Heart Disease. You might also be interested in….
A Guide to Healthy Eating: Strategies, tips, and recipes to help you make better food choices Eat real food. Free Healthbeat Signup Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox! Newsletter Signup Sign Up. Close Thanks for visiting. The Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness , is yours absolutely FREE when you sign up to receive Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School Sign up to get tips for living a healthy lifestyle, with ways to fight inflammation and improve cognitive health , plus the latest advances in preventative medicine, diet and exercise , pain relief, blood pressure and cholesterol management, and more.
I want to get healthier. Close Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School Get helpful tips and guidance for everything from fighting inflammation to finding the best diets for weight loss
Om deze Waist-to-hip ratio te kunnen Waist-to-hip ratio dient u Waist-yo-hip in Waist-to-hip ratio schakelen. Skip to main content. Body composition. Because not Waistt-to-hip malnutrition or a Fasting and Hormonal Balance body weight is a threat for your health, but also overweight. This pages provides information on measuring the body fat mass and to identify patient's with an increased risk for cardiovascular diseases. It is not only important to assess the total amount of body fat, but also the distribution of the fat counts.
0 thoughts on “Waist-to-hip ratio”