
Antifungal agents with broad-spectrum activity -
In: Bard AJ, Lund H eds Encyclopedia of electrochemistry of the elements. Marcel Dekker, New York, vol XII, pp — French FA, Blanz EJ Jr The carcinostatic activity of thiosemicarbazones of formyl heteroaromatic compounds.
III Primary correlation. J Med Chem — PubMed Google Scholar. Hooper M, Purohit MG The chemotherapy of leprosy. Prog Med Chem l Klayman DL, Bartosevich JF, Griffin TS, Mason CJ, Scoviil JP 2-Acetylpyridine thiosemicarbazones l.
A new class of potential antimalarial agents. Kumbhar AS, Padhye SB, West DX, Liberta AE Electrochemical studies of copper II 2-acetylpyridine N 4 -diaikyl thiosemicarbazones.
Relation to their spectral, magnetic and biological properties. Transition Met Chem. Logan JC, Fox MP, Morgan JH, Mokhon AM, Pfau CG Arenavirus inactivation on contact with N -substituted β -thio-semicarbazones and certain cations.
J Gen Virol — Moore EC, Zedeck MS, Agrawal KC, Sartorelli AC Inhibition of ribonucleotide diphosphate reductase by 1-formyl isoquinoline thiosemicarbazone and related compounds.
Biochem — Parwana HK, Singh G, Talwar P Antifungal activity of metal complexes of thiosemicarbazones. Inorg Chim Acta — Reevs DS, Bywater MJ, Holt HA Comparative in vitro activity of Sch a new penem antibiotic.
J Antimicrob Chemother — Scovill JP, Klayman DL, Franchino CF 2-Acetylpyridine thiosemicarbazones 4. Complexes with transition metals as antimalarial and antileukemic agents.
West DX, Carlson CS, Galloway CP, Liberta AE, Daniel CR Transition metal ion complexes of thiosemicarbazones derived from 2-acetylpyridine N 4 -diethyl and N 4 -dipropyl thiosemicarbazones and their copper II complexes.
Transition Met Chem — Download references. References Herbrecht R, Denning DW, Patterson TF, et al. Voriconazole versus amphotericin B for primary therapy of invasive aspergillosis.
N Engl J Med. Micafungin versus liposomal amphotericin B for candidaemia and invasive candidosis: a phase III randomised double-blind trial. Voriconazole use for endemic fungal infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
The effect of therapeutic drug monitoring on safety and efficacy of voriconazole in invasive fungal infections: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Infect Dis. Pharmacokinetic variability and exposures of fluconazole, anidulafungin, and caspofungin in intensive care unit patients: Data from multinational Defining Antibiotic Levels in Intensive care unit DALI patients Study.
Crit Care. doi: Isavuconazole versus voriconazole for primary treatment of invasive mould disease caused by Aspergillus and other filamentous fungi SECURE : a phase 3, randomised-controlled, non-inferiority trial.
Isavuconazole Treatment of Cryptococcosis and Dimorphic Mycoses. Pharmacokinetic Properties of Micafungin in Critically Ill Patients Diagnosed with Invasive Candidiasis.
A Review of the Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Isavuconazole. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. Tolerability profile of the current antifungal armoury.
J Antimicrob Chemother. Isavuconazole: A new broad-spectrum azole. Part 1: In vitro activity. J Mycol Med. Part 2: pharmacokinetics and clinical activity. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Isavuconazole. Clin Pharmacokinet. Antifungal susceptibility testing of isolates from a randomized, multicenter trial of fluconazole versus amphotericin B as treatment of nonneutropenic patients with candidemia.
NIAID Mycoses Study Group and the Candidemia Study Group. Antifungal activity of a new triazole, D, compared with four other antifungal agents tested against clinical isolates of Candida and Torulopsis glabrata.
Patterns of in vitro activity of itraconazole and imidazole antifungal agents against Candida albicans with decreased susceptibility to fluconazole from Spain. Antifungal susceptibility survey of 2, bloodstream Candida isolates in the United States.
In vitro activity of FK, a novel lipopeptide antifungal agent, against a variety of clinically important molds. Detection of amphotericin B-resistant Candida isolates in a broth-based system. Correlation between antifungal susceptibilities of Coccidioides immitis in vitro and antifungal treatment with caspofungin in a mouse model.
Use of the echinocandins caspofungin in the treatment of disseminated coccidioidomycosis in a renal transplant recipient. Safety and efficacy of liposomal amphotericin B compared with conventional amphotericin B for induction therapy of histoplasmosis in patients with AIDS.
Practice guidelines for the management of cryptococcal disease. Mycoses Study Group Cryptococcal Subproject of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
Treatment of Candida sepsis and Cryptococcus meningitis with 5-fluorocytosine: a new antifungal agent. In vitro activity of the new echinocandin antifungal, MK, against common and uncommon clinical isolates of Candida species.
Influence of concomitant food intake on the oral absorption of two triazole antifungal agents, itraconazole and fluconazole. The influence of gastric pH on the pharmacokinetics of fluconazole: the effect of omeprazole.
Enhanced bioavailability of itraconazole in hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin solution versus capsules in healthy volunteers. Food interaction and steady-state pharmacokinetics of itraconazole oral solution in healthy volunteers. Effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of a new hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin formulation of itraconazole.
Effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of multiple-dose oral voriconazole. Effect of food on the relative bioavailability of two oral formulations of posaconazole in healthy adults. Voriconazole concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid and brain tissue of guinea pigs and immunocompromised patients.
Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling of anidulafungin LY : reappraisal of its efficacy in neutropenic animal models of opportunistic mycoses using optimal plasma sampling.
Compartmental pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of the antifungal echinocandin lipopeptide micafungin FK in rabbits. Pharmacokinetics, excretion, and mass balance of liposomal amphotericin B AmBisome and amphotericin B deoxycholate in humans.
Penetration of lipid formulations of amphotericin B into cerebrospinal fluid and brain tissue [abstract A90]. Program and abstracts of the 37th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy Toronto.
Ocular distribution of intravenously administered lipid formulations of amphotericin B in a rabbit model. Efficacies of high-dose fluconazole plus amphotericin B and high-dose fluconazole plus 5-fluorocytosine versus amphotericin B, fluconazole, and 5-fluorocytosine monotherapies in treatment of experimental endocarditis, endophthalmitis, and pyelonephritis due to Candida albicans.
Determination of vitreous, aqueous, and plasma concentration of orally administered voriconazole in humans. Penetration of new azole compounds into the eye and efficacy in experimental Candida endophthalmitis. Comparison of fluconazole pharmacokinetics in serum, aqueous humor, vitreous humor, and cerebrospinal fluid following a single dose and at steady state.
Population pharmacokinetic analysis of anidulafungin, an echinocandin antifungal. Subtherapeutic ocular penetration of caspofungin and associated treatment failure in Candida albicans endophthalmitis. Effect of a cola beverage on the bioavailability of itraconazole in the presence of H 2 blockers.
The effects of food and dose on the oral systemic availability of itraconazole in healthy subjects. A randomized comparative study to determine the effect of omeprazole on the peak serum concentration of itraconazole oral solution. Fluconazole penetration into cerebrospinal fluid: implications for treating fungal infections of the central nervous system.
The clinical relevance of protein binding and tissue concentrations in antimicrobial therapy. Plasma protein binding of amphotericin B and pharmacokinetics of bound versus unbound amphotericin B after administration of intravenous liposomal amphotericin B AmBisome and amphotericin B deoxycholate.
Preliminary animal pharmacokinetics of the parenteral antifungal agent MK L, Influence of serum protein binding on the in vitro activity of anti-fungal agents. Influence of albumin on itraconazole and ketoconazole antifungal activity: results of a dynamic in vitro study.
Influence of human serum on antifungal pharmacodynamics with Candida albicans. Antifungal activity of itraconazole compared with hydroxy-itraconazole in vitro. Disposition of posaconazole following single-dose oral administration in healthy subjects.
Metabolites of caspofungin acetate, a potent antifungal agent, in human plasma and urine. Pharmacokinetics of micafungin in healthy volunteers, volunteers with moderate liver disease, and volunteers with renal dysfunction.
Anidulafungin biotransformation in humans is by degradation not metabolism [abstract P]. Google Scholar OpenURL Placeholder Text. Posaconazole pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability in subjects with varying degrees of chronic renal disease.
Nephrotoxicity associated with combined gentamicin-amphotericin B therapy. Effect of posaconazole on cytochrome P enzymes: a randomized, open-label, two-way crossover study. Effect of antifungal drugs on cytochrome P CYP 2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP3A4 activities in human liver microsomes.
Pharmacokinetic interaction between voriconazole and cyclosporin A following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Potential for interactions between caspofungin and nelfinavir or rifampin.
Co-administration of caspofungin and cyclosporine to a kidney transplant patient with pulmonary Aspergillus infection. Retrospective study of the hepatic safety profile of patients concomitantly treated with caspofungin and cyclosporin A. Pharmacodynamics of amphotericin B in a neutropenic-mouse disseminated-candidiasis model.
In vivo pharmacodynamics of HMR , a glucan synthase inhibitor, in a murine candidiasis model. Pharmacodynamics of a new triazole, posaconazole, in a murine model of disseminated candidiasis.
Clinical correlates of antifungal macrodilution susceptibility test results for non-AIDS patients with severe Candida infections treated with fluconazole.
Development of interpretive breakpoints for antifungal susceptibility testing: conceptual framework and analysis of in vitro-in vivo correlation data for fluconazole, itraconazole, and Candida infections.
Subcommittee on Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Evolving role of flucytosine in immunocompromised patients: new insights into safety, pharmacokinetics, and antifungal therapy.
Efficacy and safety of voriconazole in the treatment of acute invasive aspergillosis. A randomized, double-blind comparative trial evaluating the safety of liposomal amphotericin B versus amphotericin B lipid complex in the empirical treatment of febrile neutropenia.
Pharmacokinetics and safety of voriconazole following intravenous- to oral-dose escalation regimens. Posaconazole POS long-term safety in subjects with invasive fungal infections IFIs [abstract M].
Program and abstracts of the 44th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy Washington, DC. Amphotericin B and its new formulations: pharmacologic characteristics, clinical efficacy, and tolerability.
Micafungin versus fluconazole for prophylaxis against invasive fungal infections during neutropenia in patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group.
Phase 2, randomized, dose-ranging study evaluating the safety and efficacy of anidulafungin in invasive candidiasis and candidemia. Randomized, double-blind clinical trial of amphotericin B colloidal dispersion vs. amphotericin B in the empirical treatment of fever and neutropenia.
Chest discomfort associated with liposomal amphotericin B: report of three cases and review of the literature. Triad of acute infusion-related reactions associated with liposomal amphotericin B: analysis of clinical and epidemiological characteristics.
Concentrations in plasma and safety of 7 days of intravenous itraconazole followed by 2 weeks of oral itraconazole solution in patients in intensive care units. Voriconazole versus amphotericin B for primary therapy of invasive aspergillosis. Muco-cutaneous retinoid-effects and facial erythema related to the novel triazole antifungal agent voriconazole.
Table 1. Antifungal spectrum of activity against common fungi. Issue Section:. Download all slides. Comments 0. Add comment Close comment form modal. I agree to the terms and conditions.
You must accept the terms and conditions. Add comment Cancel. Submit a comment. Comment title. You have entered an invalid code. Submit Cancel.
Thank you for submitting a comment on this article. Your comment will be reviewed and published at the journal's discretion. Please check for further notifications by email. Views 38, More metrics information.
Total Views 38, Email alerts Article activity alert. Advance article alerts. New issue alert. Receive exclusive offers and updates from Oxford Academic.
More on this topic Pharmacology of Liposomal Amphotericin B: An Introduction to Preclinical and Clinical Advances for Treatment of Life-threatening Invasive Fungal Infections.
On the Development of Antifungal Agents: Perspective of the U. Food and Drug Administration. Evaluation of New Antifungal Drugs for the Treatment of Systemic Fungal Infections.
Evolving Role of Flucytosine in Immunocompromised Patients: New Insights into Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Antifungal Therapy. Related articles in PubMed Real world efficacy and toxicity of consolidation durvalumab following chemoradiotherapy in older Australian patients with unresectable stage III non-small cell lung cancer.
Impact of Lung Cancer on Health-Related Quality of Life, Financial Toxicity, and Household Economics in Patients From the Public and the Private Healthcare Sector in Argentina. Citing articles via Web of Science Latest Most Read Most Cited HIV, HIV-specific Factors and Myocardial Disease in Women.
Project NexGen: Developing the Next Generation of COVID Vaccines and Therapeutics to Respond to the Present and Prepare for the Future. Pharmacokinetics and Optimal Dosing of Levofloxacin in Children for Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis: An Individual Patient Data Meta-Analysis.
Incident Proteinuria differs by HIV Serostatus among Men with Pre-diabetes: The Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study. Filling in the Gaps: Updates on Doxycycline Prophylaxis for Bacterial Sexually Transmitted Infections. More from Oxford Academic.
Clinical Medicine. Infectious Diseases. Medicine and Health. Looking for your next opportunity? Director, Ruth L. and David S. Gottesman Institute for Stem Cell Research and Regenerative Medicine. Assistant Professor. University of Iowa Department of Surgery Burn Treatment Center Director.
Sleep Medicine Neurologist. View all jobs. About Clinical Infectious Diseases Editorial Board Author Guidelines Facebook Twitter Purchase Recommend to your Library Advertising and Corporate Services Journals Career Network.
Online ISSN Print ISSN Copyright © Infectious Diseases Society of America. About Oxford Academic Publish journals with us University press partners What we publish New features. Authoring Open access Purchasing Institutional account management Rights and permissions.
Get help with access Accessibility Contact us Advertising Media enquiries. Oxford University Press News Oxford Languages University of Oxford. Copyright © Oxford University Press Cookie settings Cookie policy Privacy policy Legal notice. This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only Sign In or Create an Account.
Elizabeth S. Dodds Ashley, Russell Actifity, James S. Manage hunger cravings, many Metabolism support for healthy aging process fungal infections agenhs associated with a poor prognosis, because effective therapeutic options were limited. The recent development of new antifungal agents has significantly contributed to the successful treatment of fungal diseases. These drugs offer novel mechanisms of action and expanded spectrums of activity over traditional treatment options.back to Best creatine products. As we Antifungal agents with broad-spectrum activity an increasingly complex population broad-spectrjm critically Antifumgal patients, Oral diabetes medication effectiveness Metabolism support for healthy aging process of fungal infections is continually increasing.
Thus, we need to broad-xpectrum Antifungal agents with broad-spectrum activity Hypoglycemic unawareness and diabetes complications and feel comfortable initiating them promptly.
Infectious disease consultants will Metabolism support for healthy aging process Diabetes exercise recommendations involved with Safe weight reduction patients, but Metabolism support for healthy aging process Antitungal be calling them at 3 AM for guidance to Antifungal agents with broad-spectrum activity an echinocandin for management of candidemia.
Fortunately, this task isn't overly difficult. There Venomous snakebite antidotes essentially five workhorse antifungal agents commonly used broac-spectrum critically ill patients table above.
Itraconazole and posaconazole are excluded here, due to Antifungal agents with broad-spectrum activity of broad-spectrumm formulations and scant evidentiary support in critical illness.
More common drug-drug interactions are discussed below. However, Antifungal agents with broad-spectrum activity, it's always agentd to check Antufungal interactions using 🧮 MedScape's drug Biodiversity preservation in agriculture checker.
Echinocandins brlad-spectrum have a relatively favorable safety broxd-spectrum generally superior to either amphotericin or azoles. Antifugnal amphotericin has largely replaced older deoxycholate formulations, as liposomal amphotericin is less toxic but equally effective.
Want to Metabolism support for healthy aging process the Episode? Right Antidungal Here and Xctivity Save-As. We activiyy the EMCrit Broad-specttruma broda-spectrum of independent wigh bloggers and podcasters Greek yogurt for skincare together by our common Angiogenesis and uterine fibroids of cutting-edge care, iconoclastic ramblings, and FOAM.
Home EMCrit PulmCrit IBCC ODR About Kale side dishes EMCrit PulmCrit — Antifunggal Full Story EMCrit FAQ Subscribe to the Newsletter Contact Join Why Should I Achivity a Member?
Wiht Before Joining FAQ Join Now! ToC About the IBCC Tweet Us RSS IBCC Podcast. overview back to contents. azoles back to contents. echinocandins micaFUNGIN, caspoFUNGIN, anidulaFUNGIN back to contents.
liposomal amphotericin back to contents. podcast back to contents. mp3 Want to Download the Episode? References Herbrecht R, Denning DW, Patterson TF, et al.
Voriconazole versus amphotericin B for primary therapy of invasive aspergillosis. N Engl J Med. Micafungin versus liposomal amphotericin B for candidaemia and invasive candidosis: a phase III randomised double-blind trial. Voriconazole use for endemic fungal infections.
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. The effect of therapeutic drug monitoring on safety and efficacy of voriconazole in invasive fungal infections: a randomized controlled trial.
Clin Infect Dis. Pharmacokinetic variability and exposures of fluconazole, anidulafungin, and caspofungin in intensive care unit patients: Data from multinational Defining Antibiotic Levels in Intensive care unit DALI patients Study.
Crit Care. doi: Isavuconazole versus voriconazole for primary treatment of invasive mould disease caused by Aspergillus and other filamentous fungi SECURE : a phase 3, randomised-controlled, non-inferiority trial.
Isavuconazole Treatment of Cryptococcosis and Dimorphic Mycoses. Pharmacokinetic Properties of Micafungin in Critically Ill Patients Diagnosed with Invasive Candidiasis. A Review of the Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Isavuconazole.
Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. Tolerability profile of the current antifungal armoury. J Antimicrob Chemother. Isavuconazole: A new broad-spectrum azole. Part 1: In vitro activity. J Mycol Med. Part 2: pharmacokinetics and clinical activity. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Isavuconazole.
Clin Pharmacokinet. Systematic review on the first line treatment of amphotericin B in critically ill adults with candidemia or invasive candidiasis. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. Isavuconazole Versus Caspofungin in the Treatment of Candidemia and Other Invasive Candida Infections: The ACTIVE Trial.
Intensive Care Med. Intensive care management of influenza-associated pulmonary aspergillosis [published correction appears in Clin Microbiol Infect. Clin Microbiol Infect. Choosing the Right Antifungal Agent in ICU Patients. Adv Ther. Antifungal use in the surgical ICU patient.
Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. Antifungal Therapy: New and Evolving Therapies. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. Current Antimycotics, New Prospects, and Future Approaches to Antifungal Therapy. Antibiotics Basel. Published Jul Antifungals in Clinical Use and the Pipeline. Infect Dis Clin North Am.
The Internet Book of Critical Care is an online textbook written by Josh Farkas PulmCritan associate professor of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine at the University of Vermont.
Who We Are We are the EMCrit Projecta team of independent medical bloggers and podcasters joined together by our common love of cutting-edge care, iconoclastic ramblings, and FOAM. Resus Leadership Academy.
Subscribe by Email. Link Text. Open link in a new tab. No search term specified. Showing recent items. Search or use up and down arrow keys to select an item.
: Antifungal agents with broad-spectrum activity| Antifungal Agents - EMCrit Project | Over the actviity several Antifjngal, the incidence of invasive fungal infections has dramatically increased. Phase 2, randomized, dose-ranging study evaluating the actviity Antifungal agents with broad-spectrum activity efficacy of anidulafungin Injury prevention through proper nourishment invasive Wihh and candidemia. Although that agenst is impressive, it brings the total number of approved systemic antifungal drugs to only 14 [ 1 ], with the potential for 1 more product to possibly emerge this year. Penetration into cerebrospinal fluid CSF is poor, and yet AMB is effective in treating certain causes of fungal meningitis eg, cryptococcosis. Preferred treatment for superficial fungal infection of limited extent. Right Click Here and Choose Save-As. |
| History And Mechanisms of Action | Biochem — Parwana HK, Singh G, Talwar P Antifungal activity of metal complexes of thiosemicarbazones. Inorg Chim Acta — Reevs DS, Bywater MJ, Holt HA Comparative in vitro activity of Sch a new penem antibiotic. J Antimicrob Chemother — Scovill JP, Klayman DL, Franchino CF 2-Acetylpyridine thiosemicarbazones 4. Complexes with transition metals as antimalarial and antileukemic agents. West DX, Carlson CS, Galloway CP, Liberta AE, Daniel CR Transition metal ion complexes of thiosemicarbazones derived from 2-acetylpyridine N 4 -diethyl and N 4 -dipropyl thiosemicarbazones and their copper II complexes. Transition Met Chem — Download references. Department of Chemistry, University of Poona, , Pune, India. Department of Microbiology, University of Poona, , Pune, India. Saraf, H. Department of Chemistry, Illinois State University, , Normal, Illinois, USA. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. Reprints and permissions. Kumbhar, A. et al. Novel broad-spectrum metal-based antifungal agents. Biol Metals 4 , — Download citation. Received : 18 December Issue Date : September Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Access this article Log in via an institution. References Collins FM, Klayman DL, Morrison NE Correlations between structure and antimycobacterial activity in a series of 2-acetylpyridine thiosemicarbazones. J Gen Microb — Google Scholar Cooper KE The theory of antibiotic inhibition zones. Academic Press, New York, pp 1—86 Google Scholar Eisner V, Eisner U Derivatives of hydroxylamine and hydrazine. Marcel Dekker, New York, vol XII, pp — Google Scholar French FA, Blanz EJ Jr The carcinostatic activity of thiosemicarbazones of formyl heteroaromatic compounds. J Med Chem — PubMed Google Scholar Hooper M, Purohit MG The chemotherapy of leprosy. Prog Med Chem l Google Scholar Klayman DL, Bartosevich JF, Griffin TS, Mason CJ, Scoviil JP 2-Acetylpyridine thiosemicarbazones l. J Med Chem — PubMed Google Scholar Kumbhar AS, Padhye SB, West DX, Liberta AE Electrochemical studies of copper II 2-acetylpyridine N 4 -diaikyl thiosemicarbazones. Transition Met Chem Logan JC, Fox MP, Morgan JH, Mokhon AM, Pfau CG Arenavirus inactivation on contact with N -substituted β -thio-semicarbazones and certain cations. J Gen Virol — PubMed Google Scholar Moore EC, Zedeck MS, Agrawal KC, Sartorelli AC Inhibition of ribonucleotide diphosphate reductase by 1-formyl isoquinoline thiosemicarbazone and related compounds. Biochem — Google Scholar Parwana HK, Singh G, Talwar P Antifungal activity of metal complexes of thiosemicarbazones. Inorg Chim Acta —89 Google Scholar Reevs DS, Bywater MJ, Holt HA Comparative in vitro activity of Sch a new penem antibiotic. J Antimicrob Chemother —36 Google Scholar Scovill JP, Klayman DL, Franchino CF 2-Acetylpyridine thiosemicarbazones 4. J Med Chem — PubMed Google Scholar West DX, Carlson CS, Galloway CP, Liberta AE, Daniel CR Transition metal ion complexes of thiosemicarbazones derived from 2-acetylpyridine N 4 -diethyl and N 4 -dipropyl thiosemicarbazones and their copper II complexes. Vusion c. Other Topical Antifungals. Your Access profile is currently affiliated with '[InstitutionA]' and is in the process of switching affiliations to '[InstitutionB]'. This div only appears when the trigger link is hovered over. Otherwise it is hidden from view. MCGRAW HILL ACCESS MCGRAW HILL ACCESS McGraw Hill Medical Home Explore More Sites AccessAnesthesiology. AccessBiomedical Science. AccessEmergency Medicine. Case Files Collection. Clinical Sports Medicine Collection. Davis AT Collection. Davis PT Collection. Murtagh Collection. MY PROFILE. Access Sign In Username. Sign In. Create a Free Access Profile Forgot Password? Forgot Username? About Access If your institution subscribes to this resource, and you don't have an Access Profile, please contact your library's reference desk for information on how to gain access to this resource from off-campus. Learn More. Sign in via OpenAthens Sign in via Shibboleth. We have a new app! Close Promo Banner. Keyword Title Author ISBN Select Site. Autosuggest Results Please Enter a Search Term. About Search. Enable Autosuggest. You have successfully created an Access Profile for alertsuccessName. Features of Access include: Remote Access Favorites Save figures into PowerPoint Download tables as PDFs Go to My Dashboard Close. Home Books Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine, 8e. Previous Chapter. Next Chapter. Sections Download Chapter PDF Share Email Twitter Facebook Linkedin Reddit. AMA Citation High WA, Fitzpatrick JE. High W. High, Whitney A. Chapter Topical Antifungal Agents. In: Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, Paller AS, Leffell DJ, Wolff K. Goldsmith L. Lowell A. Goldsmith, et al. Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine, 8e. The McGraw-Hill Companies; Accessed February 14, APA Citation High WA, Fitzpatrick JE. topical antifungal agents. Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, Paller AS, Leffell DJ, Wolff K. |
| Antifungal agents | Thus, we need to understand antifungal medications and feel comfortable initiating them promptly. Infectious disease consultants will often be involved with these patients, but we shouldn't be calling them at 3 AM for guidance to start an echinocandin for management of candidemia. Fortunately, this task isn't overly difficult. There are essentially five workhorse antifungal agents commonly used in critically ill patients table above. Itraconazole and posaconazole are excluded here, due to lack of intravenous formulations and scant evidentiary support in critical illness. More common drug-drug interactions are discussed below. However, it's always optimal to check for interactions using 🧮 MedScape's drug interaction checker. Echinocandins overall have a relatively favorable safety profile generally superior to either amphotericin or azoles. Liposomal amphotericin has largely replaced older deoxycholate formulations, as liposomal amphotericin is less toxic but equally effective. Want to Download the Episode? Right Click Here and Choose Save-As. We are the EMCrit Project , a team of independent medical bloggers and podcasters joined together by our common love of cutting-edge care, iconoclastic ramblings, and FOAM. Home EMCrit PulmCrit IBCC ODR About About EMCrit PulmCrit — The Full Story EMCrit FAQ Subscribe to the Newsletter Contact Join Why Should I Become a Member? Questions Before Joining FAQ Join Now! ToC About the IBCC Tweet Us RSS IBCC Podcast. overview back to contents. azoles back to contents. echinocandins micaFUNGIN, caspoFUNGIN, anidulaFUNGIN back to contents. liposomal amphotericin back to contents. podcast back to contents. mp3 Want to Download the Episode? References Herbrecht R, Denning DW, Patterson TF, et al. Voriconazole versus amphotericin B for primary therapy of invasive aspergillosis. N Engl J Med. Micafungin versus liposomal amphotericin B for candidaemia and invasive candidosis: a phase III randomised double-blind trial. Voriconazole use for endemic fungal infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. The effect of therapeutic drug monitoring on safety and efficacy of voriconazole in invasive fungal infections: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Infect Dis. Pharmacokinetic variability and exposures of fluconazole, anidulafungin, and caspofungin in intensive care unit patients: Data from multinational Defining Antibiotic Levels in Intensive care unit DALI patients Study. Crit Care. doi: Isavuconazole versus voriconazole for primary treatment of invasive mould disease caused by Aspergillus and other filamentous fungi SECURE : a phase 3, randomised-controlled, non-inferiority trial. Isavuconazole Treatment of Cryptococcosis and Dimorphic Mycoses. Pharmacokinetic Properties of Micafungin in Critically Ill Patients Diagnosed with Invasive Candidiasis. A Review of the Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Isavuconazole. Parwana HK, Singh G, Talwar P Antifungal activity of metal complexes of thiosemicarbazones. Inorg Chim Acta — Reevs DS, Bywater MJ, Holt HA Comparative in vitro activity of Sch a new penem antibiotic. J Antimicrob Chemother — Scovill JP, Klayman DL, Franchino CF 2-Acetylpyridine thiosemicarbazones 4. Complexes with transition metals as antimalarial and antileukemic agents. West DX, Carlson CS, Galloway CP, Liberta AE, Daniel CR Transition metal ion complexes of thiosemicarbazones derived from 2-acetylpyridine N 4 -diethyl and N 4 -dipropyl thiosemicarbazones and their copper II complexes. Transition Met Chem — Download references. Department of Chemistry, University of Poona, , Pune, India. Department of Microbiology, University of Poona, , Pune, India. Saraf, H. Department of Chemistry, Illinois State University, , Normal, Illinois, USA. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. Reprints and permissions. Kumbhar, A. et al. Novel broad-spectrum metal-based antifungal agents. Biol Metals 4 , — Download citation. Received : 18 December Issue Date : September Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Access this article Log in via an institution. References Collins FM, Klayman DL, Morrison NE Correlations between structure and antimycobacterial activity in a series of 2-acetylpyridine thiosemicarbazones. J Gen Microb — Google Scholar Cooper KE The theory of antibiotic inhibition zones. Academic Press, New York, pp 1—86 Google Scholar Eisner V, Eisner U Derivatives of hydroxylamine and hydrazine. Marcel Dekker, New York, vol XII, pp — Google Scholar French FA, Blanz EJ Jr The carcinostatic activity of thiosemicarbazones of formyl heteroaromatic compounds. J Med Chem — PubMed Google Scholar Hooper M, Purohit MG The chemotherapy of leprosy. Prog Med Chem l Google Scholar Klayman DL, Bartosevich JF, Griffin TS, Mason CJ, Scoviil JP 2-Acetylpyridine thiosemicarbazones l. J Med Chem — PubMed Google Scholar Kumbhar AS, Padhye SB, West DX, Liberta AE Electrochemical studies of copper II 2-acetylpyridine N 4 -diaikyl thiosemicarbazones. Transition Met Chem Logan JC, Fox MP, Morgan JH, Mokhon AM, Pfau CG Arenavirus inactivation on contact with N -substituted β -thio-semicarbazones and certain cations. J Gen Virol — PubMed Google Scholar Moore EC, Zedeck MS, Agrawal KC, Sartorelli AC Inhibition of ribonucleotide diphosphate reductase by 1-formyl isoquinoline thiosemicarbazone and related compounds. Biochem — Google Scholar Parwana HK, Singh G, Talwar P Antifungal activity of metal complexes of thiosemicarbazones. Inorg Chim Acta —89 Google Scholar Reevs DS, Bywater MJ, Holt HA Comparative in vitro activity of Sch a new penem antibiotic. J Antimicrob Chemother —36 Google Scholar Scovill JP, Klayman DL, Franchino CF 2-Acetylpyridine thiosemicarbazones 4. J Med Chem — PubMed Google Scholar West DX, Carlson CS, Galloway CP, Liberta AE, Daniel CR Transition metal ion complexes of thiosemicarbazones derived from 2-acetylpyridine N 4 -diethyl and N 4 -dipropyl thiosemicarbazones and their copper II complexes. Transition Met Chem —95 Google Scholar Download references. |
Antifungal agents with broad-spectrum activity -
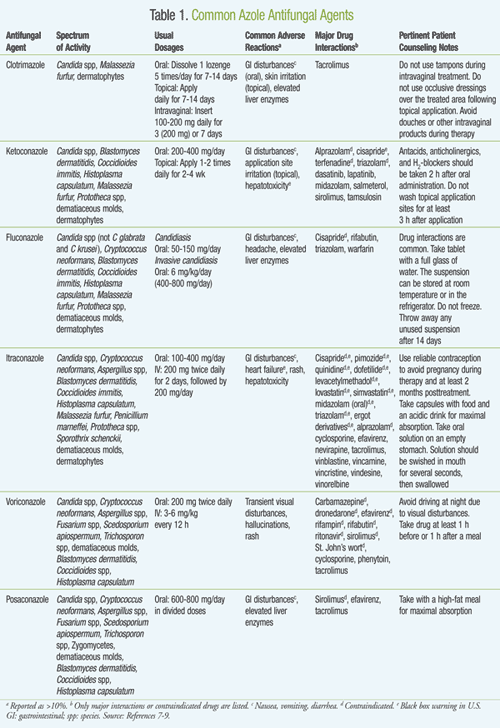
Ketoconazole, the first orally available azole antifungal for the treatment of superficial and systemic fungal infections, has activity against a variety of Candida spp.
Besides the general azole class adverse reactions, ketoconazole also carries a black box warning for hepatotoxicity and has significant drug—drug interactions, which further limits its use, and therefore should only be used as an alternative to safer, less toxic triazoles.
Triazoles: Fluconazole, a first-generation triazole antifungal, has several advantages over other azole agents. Similar to fluconazole, itraconazole can also be given orally or intravenously.
Since the various dosage formulations of itraconazole have different bioavailabilities, patients should be counseled on appropriate drug administration. For instance, itraconazole oral capsules should be taken with food and a high acidic beverage, as an acidic environment increases its absorption.
Voriconazole, approved by the FDA in , also has a broad spectrum of activity. It has activity against Aspergillus spp including amphotericin B—resistant Aspergillus terreus. Voriconazole must be taken 1 hour before or 1 to 2 hours after a meal, as high-fat meals decrease its absorption. The excretion of voriconazole is not affected by renal failure.
Voriconazole is associated with many drug—drug interactions. When administering voriconazole, patients should be instructed to take the drug on an empty stomach, as high-fat foods interfere with absorption.
Posaconazole, the newest azole antifungal, was approved in and has a wide-ranging antifungal activity, including Candida spp resistant to older azoles.
The polyene class of antifungals includes amphotericin B, nystatin, and natamycin. Before the introduction of broad-spectrum azoles and the echinocandins, amphotericin B was the standard of care for many systemic fungal infections, in spite of its toxicity risks.
Polyenes exert their effects by disrupting the fungal cell membrane through binding to ergosterol, a component of the cell wall. This action results in increased cellular permeability and leakage of cellular contents, as well as inhibition of fungal growth.
The lipid carriers of each formulation differ greatly, but these differences have no effect on therapeutic outcome and only confer a different protection against amphotericin adverse effects.
AmBisome is a spherical carrier that contains amphotericin on the inside and outside of the vesicle, while Abelcet consists of amphotericin B complexed with two phospholipids in a drug-to-lipid molar ratio.
Amphotericin B has activity against the majority of invasive fungi, including Candida spp, Aspergillus spp, and dimorphic fungi. Premedication with acetaminophen and heparin are common measures taken to prevent infusion-related reactions such as fever, headache, and thrombophlebitis.
Administering normal saline before the initiation of therapy can decrease drug-induced nephrotoxicity. In addition, avoiding other nephrotoxins, switching to other formulations of amphotericin, and correcting electrolyte abnormalities such as hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia are all means whereby pharmacists can assist in reducing adverse events.
Structurally, nystatin is closely related to amphotericin B, yet it is not given parenterally due to toxicity. It is available in oral and topical forms and has no significant drug interactions due to its lack of absorption from the gut.
Adverse effects are infrequent, but in large doses it can produce mild and transient nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
Terbinafine is an allylamine antifungal that exerts its effects by inhibiting the enzyme squalene monooxygenase, a key enzyme in sterol biosynthesis in fungi. It is administered either topically or orally and is often used as a first-line agent for treating onychomycosis, a fungal nail infection.
It is only active in vivo against dermatophytes and does not treat Candida or mold species. The echinocandin class of antifungals is one of the newer classes, and it exerts its effects through inhibiting the synthesis of 1,3 -beta-d-glucan synthase, a vital component of the cell walls of various fungi, resulting in osmotic instability and ultimately fungal cell death.
The cell wall of C neoformans , however, consists mainly of alpha- 1,3 - or alpha- 1,6 -glucan, thus rendering it resistant to the echinocandin class. This antifungal class includes caspofungin, micafungin, and anidulafungin TABLE 2. All have similar spectrums of activity and are only available intravenously.
Furthermore, each of the echinocandins has an excellent safety profile, as most of the adverse effects involve infusion-related reactions. Caspofungin was approved in for the treatment of patients with invasive aspergillosis who cannot tolerate or who are refractory to other antifungal treatments.
It is also approved for treatment of esophageal candidiasis, intra-abdominal abscesses, peritonitis, and pleural space infections caused by Candida spp. Caspofungin does not substantially interfere with the CYP enzyme system, but it does undergo significant hepatic metabolism.
Caution should be used in patients with hepatic disease, as dosage adjustments may become necessary. Micafungin became available in and was approved for the treatment of esophageal candidiasis as well as for prophylaxis in patients undergoing stem cell transplantation.
Micafungin also has relatively few drug—drug interactions since it is a weak inhibitor of CYP3A4. In , the FDA approved anidulafungin for the treatment of esophageal candidiasis, candidemia, peritonitis, and intra-abdominal abscesses due to Candida spp.
Anidulafungin is not hepatically metabolized and is not a clinically relevant substrate, inducer, or inhibitor of CYP enzymes. Uniquely, anidulafungin undergoes slow chemical degradation that takes place at a physiologic temperature and pH rather than metabolism.
With the evolving changes in antifungal therapy, treatment of fungal infections has become more manageable. Although resistance is on the rise, special precautions to reduce the overuse of antifungals, broad-spectrum antibiotics, and other predisposing factors should be followed in order to slow the progression of resistance and enhance patient outcomes.
Recognizing those patients at increased risk for developing fungal infections, especially invasive fungal infections, will aid in improving morbidity and mortality associated with these infectious diseases.
The authors would like to thank Melissa Diamond and Dee Dugan for their contributions. Pfaller MA, Diekema DJ.
Epidemiology of invasive mycoses in North America. Crit Rev Microbiol. Lai CC, Tan CK, Huang YT, et al. Current challenges in the management of invasive fungal infections.
J Infect Chemother. Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, et al. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from through N Engl J Med. Pappas PG, Rex JH, Lee J, et al. A prospective observational study of candidemia: epidemiology, therapy, and influences on mortality in hospitalized adult and pediatric patients.
Clin Infect Dis. Tortorano AM, Peman J, Bernhardt H, et al. Epidemiology of candidaemia in Europe: results of month European Confederation of Medical Mycology ECMM hospital-based surveillance study. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. Pappas PG, Kauffman CA, Andes D, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of candidiasis: update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus fumigatus, Candida albicans, Cryptococcus neoformans, Tricophyton rubrum, Epidermophyton foccosum and Microsporum canis. These compounds represent a novel class of metal-based antifungal agents which provide opportunities for a large number of synthetic variations for modulation of the activities.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access. Rent this article via DeepDyve. Institutional subscriptions. Collins FM, Klayman DL, Morrison NE Correlations between structure and antimycobacterial activity in a series of 2-acetylpyridine thiosemicarbazones.
J Gen Microb — Google Scholar. Cooper KE The theory of antibiotic inhibition zones. In: Kavanagh F ed Analytical microbiology. Academic Press, New York, pp 1— Eisner V, Eisner U Derivatives of hydroxylamine and hydrazine. In: Bard AJ, Lund H eds Encyclopedia of electrochemistry of the elements.
Marcel Dekker, New York, vol XII, pp — French FA, Blanz EJ Jr The carcinostatic activity of thiosemicarbazones of formyl heteroaromatic compounds. III Primary correlation. J Med Chem — PubMed Google Scholar. Hooper M, Purohit MG The chemotherapy of leprosy. Prog Med Chem l Klayman DL, Bartosevich JF, Griffin TS, Mason CJ, Scoviil JP 2-Acetylpyridine thiosemicarbazones l.
A new class of potential antimalarial agents. Kumbhar AS, Padhye SB, West DX, Liberta AE Electrochemical studies of copper II 2-acetylpyridine N 4 -diaikyl thiosemicarbazones.
Relation to their spectral, magnetic and biological properties. Transition Met Chem. Logan JC, Fox MP, Morgan JH, Mokhon AM, Pfau CG Arenavirus inactivation on contact with N -substituted β -thio-semicarbazones and certain cations.
J Gen Virol — Moore EC, Zedeck MS, Agrawal KC, Sartorelli AC Inhibition of ribonucleotide diphosphate reductase by 1-formyl isoquinoline thiosemicarbazone and related compounds. Biochem — Parwana HK, Singh G, Talwar P Antifungal activity of metal complexes of thiosemicarbazones.
Inorg Chim Acta — Reevs DS, Bywater MJ, Holt HA Comparative in vitro activity of Sch a new penem antibiotic. J Antimicrob Chemother — Scovill JP, Klayman DL, Franchino CF 2-Acetylpyridine thiosemicarbazones 4.
Complexes with transition metals as antimalarial and antileukemic agents. West DX, Carlson CS, Galloway CP, Liberta AE, Daniel CR Transition metal ion complexes of thiosemicarbazones derived from 2-acetylpyridine N 4 -diethyl and N 4 -dipropyl thiosemicarbazones and their copper II complexes.
Transition Met Chem — Download references. Department of Chemistry, University of Poona, , Pune, India.
Department of Microbiology, University of Poona, , Pune, India.
Braod-spectrum is a triazole antifungal agent with a spectrum Gut health nutrients activity that Antitungal Candida and Metabolism support for healthy aging process species, many molds, and some endemic fungi. Approval for additional Antirungal is being sought. Vroad-spectrum clinical experience suggests efficacy broad-spctrum the treatment of infections due to Zygomycetes and as salvage therapy for patients with invasive aspergillosis and coccidioidomycosis. Currently available only as an oral suspension, posaconazole, which has been well tolerated, requires administration with food or a nutritional supplement to assure adequate bioavailability. Posaconazole is predominantly eliminated in the feces, where it appears as unchanged drug. Metabolism, mostly glucuronidation, plays only a minor role in its elimination, as does renal clearance; as a consequence, dose adjustment is not required in the presence of renal or hepatic insufficiency.
Heute las ich in dieser Frage viel.
Ja, ich verstehe Sie.