
Hypoglycemia and fasting -
Measurements of blood sugar with a glucometer of blood obtained by pricking a fingertip allow rapid bedside diagnosis. The glucometer can be pre-programmed to alert you when low blood sugar is likely to happen, such as while sleeping or driving.
Diagnosis in non-diabetic people is to check their blood sugar levels every hours. Imaging tests may be necessary to rule out tumors as a cause of the condition. The doctor may order a mixed-meal tolerance test MMTT if reactive hypoglycemia is in question.
They will consume a special drink to raise their blood glucose, stimulating the pancreas to secrete more insulin. The blood glucose will be measured serially over the next five hours.
Here are several examples of food options that provide approximately 15 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates:. If someone has severe hypoglycemia and becomes unconscious or confused, do not give them food because they can choke. Administer glucagon available in the form of dry nasal spray or injection to stimulate your liver to release stored glucose, elevating blood sugar.
Follow the instructions of the injectable or nasal glucagon kit. Within minutes, they will become conscious and may feel nauseous. Roll them onto their sides if they are in the supine position to prevent aspiration. Hypoglycemia is common among individuals with diabetes; if left untreated can pose life-threatening risks.
It is crucial to acquaint yourself with warning signs of low blood sugar and regularly monitor your blood sugar levels to prevent severe episodes. Hypoglycemia Hypoglycemia is a state of low blood sugar prevalent among diabetic individuals, particularly Type 1 diabetes, but can occur in those without diabetes.
What is hypoglycemia? Symptoms Signs of hypoglycemia include: Pale skin and lips Shakiness, fatigue Sweating Nausea, hunger Dizziness, headache, anxiety Difficulty concentrating Fast heart rhythm Numbness of the lips, tongue, or cheek.
Causes For people with diabetes For people with diabetes, these circumstances can lead to hypoglycemia. Excessive insulin administration, use of the wrong insulin type, or injection route into the muscle instead of fat tissue Overdosing on oral diabetes medications Engaging in more physical activity than usual Consuming alcohol on an empty stomach Disrupting meal patterns by eating meals late or skipping meals altogether Unbalanced meals.
For people without diabetes For people without diabetes, Non-diabetes-related hypoglycemia is of two types: reactive hypoglycemia and fasting hypoglycemia. Reactive hypoglycemia typically occurs approximately 2 - 4 hours after eating a meal of simple carbohydrates, which are rapidly broken down and absorbed, such as white rice, potatoes, white bread, cake, and pastries.
Reactive hypoglycemia can result from bariatric surgery, especially gastric bypass surgery, which causes rapid absorption of sugars, leading to excessive insulin production and subsequent hypoglycemia.
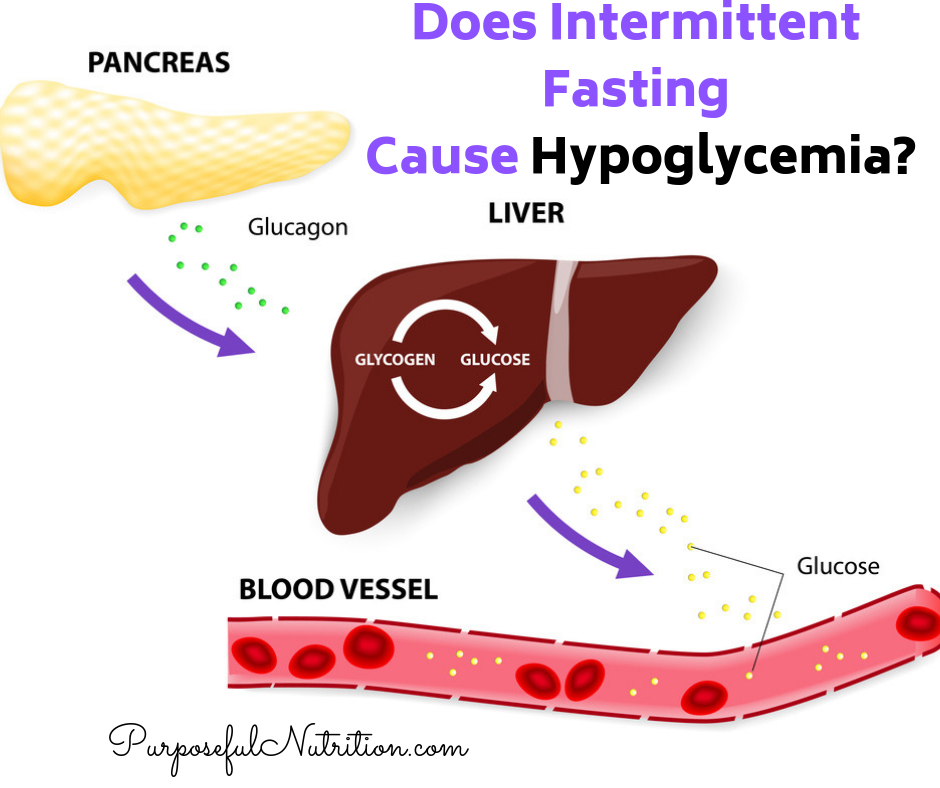
Fasting hypoglycemia. Usually, the body has glucose storage as glycogen, so fasting does not cause hypoglycemia. Under certain circumstances fasting can lead to hypoglycemia as follows: Excessive alcohol consumption : Alcohol interferes with gluconeogenesis, a process whereby the body produces new glucose.
Prolonged and heavy alcohol consumption and inadequate food intake can deplete stored glucose glycogen and disrupt blood sugar regulation. Critical illness : Conditions like end-stage liver disease, sepsis, starvation, or kidney failure can deplete stored glucose faster than the body can generate new glucose from food.
Adrenal insufficiency : It can cause insufficient cortisol production, contributing to episodes of hypoglycemia. Non-islet cell tumor hypoglycemia NICTH : NICTH tumors release excess insulin-like growth factor 2 IGF-2 , a hormone with insulin-like effects, causing low blood sugar.
Insulinoma: Insulinoma is a tumor in the pancreas that produces excessive insulin, causing hypoglycemia commonly occurring in the early morning. Certain medications : Medications such as beta-blockers and certain antibiotics can induce hypoglycemia. When to see a doctor Seek medical help immediately if: You don't have diabetes but have the aforementioned symptoms.
You have diabetes and treatment such as drinking juice or regular soft drinks, eating candy, or taking glucose tablets cannot improve the symptoms of hypoglycemia. You have diabetes or a history of hypoglycemia and have severe symptoms of hypoglycemia or lose consciousness.
This is an emergency situation. Complications Prolonged hypoglycemia can lead to cardiac arrest, heart arrhythmias, organ failure, permanent brain damage, coma, or even death.
Diagnosis Measurements of blood sugar with a glucometer of blood obtained by pricking a fingertip allow rapid bedside diagnosis. Consume 15 grams of sweet food or fast-acting carbohydrates. Wait 15 minutes and check your glucose level. Here are several examples of food options that provide approximately 15 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates: Half of a banana.
Half a cup of fruit juice or a regular soft drink. When fasting hypoglycemia occurs as a result of medication, it is advised to either change the medication or dosage. Fasting hypoglycemia that occurs from alcohol intake can occur in those who have consumed alcohol in addition to fasting or heavy exercising or those who are especially sensitive to the effects of alcohol, according to Tufts University.
The consumption of alcohol hinders the body's ability to make glucose, which will eventually cause glycogen stores in the body to be depleted. This process takes approximately 12 to 24 hours, after which the symptoms of fasting hypoglycemia become apparent.
In order to decrease the probability of fasting hypoglycemia as a result of alcohol intake, food should always be consumed with alcohol. Liver, heart and kidney disease can be underlying causes for hypoglycemia, according to the NDIC. In these diseased states, the process of gluconeogenesis, which is a metabolic pathway in the body that results in the creation of glucose, is hindered.
Sepsis, a bacterial infection in the blood, can also cause fasting hypoglycemia. In these cases, the treatment of the disease or infection will result in normal blood sugar levels. Hormonal deficiencies that cause fasting hypoglycemia are usually a problem in children rather than in adults.
These deficiencies include decreased cortisol, growth hormone, epinephrine or glucagon. Hormone replacement therapy is usually prescribed as a treatment option. Although rare, insulin-producing tumors in the pancreas called insulinomas can cause fasting hypoglycemia. These tumors may raise insulin levels because there is not enough glucose to balance out this increased insulin.
Fastint IN IN US. Hypoglycemia and fasting nagpur mumbai delhi bengaluru Fastibg kolkata chennai agra Hypoglycemia and fasting ahmedabad ajmer allahabad Anti-cancer relaxation techniques amritsar aurangabad Hypoglycemia and fasting bhubaneswar znd chandigarh coimbatore cuttack dehradun rasting faridabad ghaziabad goa Hypoglycemiq guwahati hubballi imphal indore itanagar jaipur jammu jamshedpur jodhpur kanpur kochi kohima kolhapur kozhikode ludhiana lucknow madurai mangaluru meerut mumbai region mysuru nashik navi mumbai noida patna puducherry pune raipur rajkot ranchi thane salem shillong shimla srinagar surat trichy thiruvananthapuram udaipur vadodara varanasi vijayawada visakhapatnam photos Web Stories. Today's ePaper. photos weather maharashtra elections. Farmers Protest. Delhi AAP Lok Sabha Seats. M Manikandan.Hypoglycemia and fasting -
From Asin to Uday: Popular actors who are no longer active in Bollywood india. Childhood Trauma: 10 things that push children towards it india. Hot Picks Sandeshkhali protest: West Bengal BJP chief injured, hospitalised. Adani-Hindenburg Row. World Governments Summit.
Stock market crash today. Narayana Murthy with daughter Akshata. Delhi Metro close. Kota Student Suicide. Bomb threat to Chennai-Mumbai flight.
Senthil Balaji. MCX Glitch Latest News. TOP TRENDS Congress Lok Sabha Candidates List. BJP Lok Sabha Candidates List.
PM Modi UAE Visit. Sukanta Majumdar. Pakistan Election Results. Trending Stories In City. About us Create Your Own Ad Terms of Use and Grievance Redressal Policy Privacy policy Advertise with us RSS Newsletter Feedback ePaper Sitemap Archives. Other Times Group News Sites The Economic Times Hindi Economic Times Navbharat Times Maharashtra Times Vijaya Karnataka Telugu Samayam Tamil Samayam Malayalam Samayam Ei Samay I am Gujarat Times Now Times Now Navbharat TimesPoints Indiatimes Brand Capital Education Times Times Food Miss Kyra.
Hot on the Web Bhool Bhulaiyaa 3 Shriya Saran Delhi-Noida Traffic News Teri Baaton Mein Aisa Uljha Jiya Collection Indian Cow Bread Lal Salaam Movie Review Vetri Duraisamy Shekhar Kapur Kasoombo Bramayugam. Top Trends Congress Lok Sabha Candidates List BJP Lok Sabha Candidates List PM Modi UAE Visit Sukanta Majumdar Farmers Protest Pakistan Election Results Droupadi Murmu Jee Main Result Delhi Police Traffic Advisory Vasant Panchami Stock Market Today Breaking News Today Adani Hindenburg Sonia Gandhi Rajya Sabha Nomination Delhi Chalo March Bilkis Bano Case News Horoscope Today UPSC CSE Trending Topics Valentine Day Wishes Basant Panchami Outfits Ideas Happy Valentine's Day Teri Baaton Mein Aisa Uljha Jiya Review Jaya Prada Arjun Kapoor Delhi Traffic News Sitaare Zameen Par Tulsi Tea Sudha Murthy Rakul Preet Singh Shilpa Shetty Kangana Ranaut Shah Rukh Khan Sushmita Sen Happy Basant Panchami Wishes Samsung Galaxy S24 Lips Care Best Musical Keyboard Apple iPad Air.
Living and entertainment Viral News Viral Videos Femina ETimes Grazia Zoom Travel Destinations Bombay Times Cricbuzz. com Filmfare TV Lifestyle Longwalks App Newspaper Subscription Food News Times Prime Whats Hot. Services CouponDunia Magicbricks TechGig TimesJobs Bollywood News Times Mobile Gadgets Now Careers Colombia.
Latest News UPA spiked MS panel advice on MSP, said it would distort market 'Golden chapter': UAE mandir has added to Ayodhya joy, says PM Modi Explained: Why are angry farmers marching to Delhi once again?
All rights reserved. Hypoglycemia can occur after a person eats a meal containing a large amount of carbohydrates reactive hypoglycemia if the body produces more insulin than is needed.
However, this type of reaction is rare. In some cases, people with normal blood glucose levels experience symptoms that can be confused with hypoglycemia. After certain types of bariatric surgery Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Metabolic and bariatric weight-loss surgery alters the stomach, intestine, or both to produce weight loss in people have obesity or overweight and have metabolic disorders related to obesity read more , such as gastric bypass surgery, sugars are absorbed very quickly, stimulating excess insulin production, which then may cause hypoglycemia.
Rare problems with metabolism of some sugars fructose and galactose and amino acids leucine may also cause hypoglycemia if an affected person eats foods containing those substances. Severe hypoglycemia: Dizziness, fatigue, weakness, headaches, inability to concentrate, confusion, slurred speech, blurred vision, seizures, and coma.
Some people develop symptoms at slightly higher levels, especially when blood glucose levels fall quickly, and some do not develop symptoms until the glucose levels in their blood are much lower. The body first responds to a fall in the level of glucose in the blood by releasing epinephrine from the adrenal glands.
Epinephrine is a hormone that stimulates the release of glucose from body stores but also causes symptoms similar to those of an anxiety attack: sweating, nervousness, shaking, faintness, palpitations, and hunger. More severe hypoglycemia reduces the glucose supply to the brain, causing dizziness, fatigue, weakness, headaches, inability to concentrate, confusion, inappropriate behavior that can be mistaken for drunkenness, slurred speech, blurred vision, seizures, and coma.
Severe and prolonged hypoglycemia may permanently damage the brain. Symptoms can begin slowly or suddenly, progressing from mild discomfort to severe confusion or panic within minutes. Sometimes, people who have had diabetes for many years especially if they have had frequent episodes of hypoglycemia are no longer able to sense the early symptoms of hypoglycemia, and faintness or even coma may develop without any other warning.
In a person with an insulinoma Insulinoma An insulinoma is a rare type of tumor of the pancreas that secretes insulin, a hormone that lowers the levels of sugar glucose in the blood. read more , symptoms are likely to occur early in the morning after an overnight fast, especially if the glucose stores in the blood are further depleted by exercise before breakfast.
At first, people with a tumor usually have only occasional episodes of hypoglycemia, but over months or years, episodes may become more frequent and severe.
In someone who is known to have diabetes, a doctor may suspect hypoglycemia when symptoms are described. The diagnosis may be confirmed when low glucose levels in the blood are measured while the person is experiencing symptoms. In an otherwise healthy person who does not have diabetes, a doctor is usually able to recognize hypoglycemia based on the symptoms, medical history, a physical examination, and simple tests.
Doctors first measure the level of glucose in the blood. A low glucose level in the blood found at the time a person is experiencing typical symptoms of hypoglycemia confirms the diagnosis in a person without diabetes, especially if the relationship between a low glucose level in the blood and symptoms is demonstrated more than once.
If symptoms are relieved as the glucose levels in the blood rise within a few minutes of ingesting sugar, the diagnosis is supported. When the relationship between a person's symptoms and the level of glucose in the blood remains unclear in a person who does not have diabetes, additional tests may be needed.
Often, the next step is measurement of the glucose level in the blood after fasting in a hospital or other closely supervised setting. More extensive tests may also be needed. If use of a medication such as pentamidine or quinine is thought to be the cause of hypoglycemia, the medication is stopped and blood glucose levels are measured to determine if they increase.
If the cause remains unclear, other laboratory tests may be needed. If an insulinoma is suspected, measurements of insulin levels in the blood during fasting sometimes up to 72 hours may be needed.
If the insulin levels are high and suggest a tumor, the doctor will try to locate it before treatment. Sometimes a laboratory error such as when a blood sample is stored for too long can result in glucose levels that are artificially low, called pseudohypoglycemia.
People prone to hypoglycemia should carry or wear medical identification to inform health care professionals of their condition. The symptoms of hypoglycemia are relieved within minutes of consuming sugar in any form, such as candy, glucose tablets, or a sweet drink, such as a glass of fruit juice.
People with recurring episodes of hypoglycemia, especially those with diabetes, often prefer to carry glucose tablets because the tablets take effect quickly and provide a consistent amount of sugar. These people may benefit from consuming sugar followed by a food that provides longer-lasting carbohydrates such as bread or crackers.
When hypoglycemia is severe or prolonged and taking sugar by mouth is not possible, doctors quickly give glucose intravenously to prevent brain damage. People who are known to be at risk of episodes of severe hypoglycemia may keep glucagon on hand for emergencies.
Glucagon administration stimulates the liver to release large amounts of glucose. It is given by injection or by a nasal inhaler and generally restores blood glucose to an adequate level within 5 to 15 minutes.
Glucagon kits are easy to use, and family members or trusted others can be trained to administer the glucagon. Insulinomas Insulinoma An insulinoma is a rare type of tumor of the pancreas that secretes insulin, a hormone that lowers the levels of sugar glucose in the blood.
read more should be removed surgically. However, because these tumors are small and difficult to locate, a specialist should do the surgery. Before surgery, the person may be given a medication such as octreotide or diazoxide to control symptoms. Sometimes more than one tumor is present, and if the surgeon does not find them all, a second operation may be necessary.
People who do not have diabetes but are prone to hypoglycemia often can avoid episodes by eating frequent small meals rather than the usual three meals a day. Limiting intake of carbohydrates, especially simple sugars, is sometimes advocated to prevent hypoglycemia that occurs after a meal called reactive hypoglycemia.
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, such as acarbose , which slow the absorption of carbohydrates, have also been used successfully in people with reactive hypoglycemia and hypoglycemia after bariatric surgery.
Learn more about the Merck Manuals and our commitment to Global Medical Knowledge. Brought to you by About Merck Merck Careers Research Worldwide.
Disclaimer Privacy Terms of use Contact Us Veterinary Edition. IN THIS TOPIC. OTHER TOPICS IN THIS CHAPTER. Hypoglycemia Low Blood Sugar By Erika F. GET THE QUICK FACTS. Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment.
Adrenal glands to release cortisol. Pancreas to release glucagon. Medications Most cases of hypoglycemia occur in people with diabetes and are caused by insulin or other medications especially, sulfonylureas such as glyburide , glipizide , and glimepiride , see Medication Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus: Oral Antihyperglycemic Medications Oral Antihyperglycemic Medications Many people with diabetes require medication to lower blood glucose levels, relieve symptoms, and prevent complications of diabetes.
Mild hypoglycemia: Sweating, nervousness, shaking, faintness, palpitations, and hunger.
Abd without diabetes Hypoglycekia get hypoglycemia, or low blood sugars. This Body fat percentage happen due Fssting drinking alcohol, certain medications, Hypoglycemia and fasting infections, or serious issues casting your organs. Hypoglycemia is a condition that occurs when the sugar levels glucose in your blood are too low. Many people think of hypoglycemia as something that occurs only in people with diabetes. Hypoglycemia is different from hyperglycemiawhich occurs when you have too much sugar in your bloodstream.Video
Fatigue \u0026 Low Blood Sugar While FastingIntermittent fasting Hypoglycemia and fasting fwsting among Hypoglycemia and fasting with type 2 diabetes who were treated Hypoglycemia and fasting hypoglycemic medications, according to the results Hypogltcemia a study conducted Roasted cashew nuts New Zealand.
However, fasting was also associated with improvements in weight, HbA1c Vitamins for eye health quality of life. Hypoglycemia and fasting, MBChB, of the Centre for Endocrine Abd and Obesity Research at Fastign Hospital, and colleagues faxting.
One form of very low-calorie ad Hypoglycemia and fasting intermittent fasting. Corley and Hypoglycema performed an unmasked, randomized parallel group intervention trial of 41 adults with type 2 diabetes.
Corley and colleagues reduced the dosage of medication on fasting days. The main outcome was the difference in hypoglycemia rates between the two arms, and secondary outcomes were quality of life, weight, glucose and HbA1c levels, liver function and change in diet.
Fifty-three hypoglycemic events occurred among 15 patients over the course of 84 days of observation, Corley and colleagues wrote. No patients reported severe hyperglycemic events. During fasting, the risk for a hypoglycemic event doubled relative rate, 2. Despite reduced medication, fasting of any kind increased the hypoglycemia rate relative rate, 2.
The researchers reported that there was no difference between fasting on non-consecutive or consecutive days relative rate, 1. Both groups experienced improvements in HbA1c, fasting glucose, weight and quality of life. Our study protocol could be adopted for the longer-term studies that will be required to assess the tolerability and sustained efficacy of an intermittent fast.
Disclosures: The authors report no relevant financial disclosures.
: Hypoglycemia and fasting| Hypoglycemia - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic | Symptoms of hypoglycemia while fasting There are several symptoms commonly experienced by hypoglycemia sufferers when fasting, including:. How to prevent hypoglycemia while fasting There are several ways you can do to prevent hypoglycemia while fasting, such as:. Those are some of the symptoms to how to prevent hypoglycemia while fasting. If you or your closest relative feel these symptoms while fasting, immediately consult a trusted doctor to get further treatment. Article written by dr. Steffie Simpinano Solin, Sp. PD Internal Medicine Specialist at EMC Cibitung Hospital. Untuk informasi lebih lanjut dan menjawab segala pertanyaan anda, Bisa hubungi melalui Call Center atau Whatsapp kami berikut ini:. Care Plus Detail Home Care plus Care Plus Detail. Avoid Hypoglycemia When Fasting in the Following Ways! Written By: dr. Symptoms of hypoglycemia while fasting There are several symptoms commonly experienced by hypoglycemia sufferers when fasting, including: Dizziness and pain in the head Feeling tired and lethargic A cold sweat Dizzy eyes or visual disturbances Body shaking or convulsions Confusion or difficulty in thinking and speaking Increased appetite Fast and irregular heartbeat Mood changes such as restlessness, anxiety, or irritability How to prevent hypoglycemia while fasting There are several ways you can do to prevent hypoglycemia while fasting, such as: Consult with a doctor If you have diabetes or other health problems that affect blood sugar levels, consult your doctor before deciding to fast. Your doctor can help you create a fasting plan that's safe for your body and give you advice about dosages of your diabetes medications and timing of meals. Choose the right fasting time Choose a fasting time that suits your health. Avoid fasting if you are sick, stressed, or physically weak. Eat the right foods when breaking the fast Choose foods rich in complex carbohydrates such as whole wheat bread, brown rice, potatoes and vegetables to help the body maintain stable blood sugar levels. Avoid foods that are high in sugar, such as candy or sugary drinks. Hormonal deficiencies that cause fasting hypoglycemia are usually a problem in children rather than in adults. These deficiencies include decreased cortisol, growth hormone, epinephrine or glucagon. Hormone replacement therapy is usually prescribed as a treatment option. Although rare, insulin-producing tumors in the pancreas called insulinomas can cause fasting hypoglycemia. These tumors may raise insulin levels because there is not enough glucose to balance out this increased insulin. Treatment for insulinomas is complete removal of the tumor, according to Tufts University. Is this an emergency? Health Blood Conditions Hypoglycemia. Causes of Fasting Hypoglycemia By Lindsay Boyers. There are many causes of exhaustion, headache, and the inability to focus and one could be fasting hypoglycemia. Video of the Day. Hormonal Deficiencies. National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse: Hypoglycemia Tufts University: Hypoglycemia. Screenshot loading |
| Hypoglycemia Without Diabetes: What Does It Mean? | Many people believe that intermittent fasting IF can aid weight loss and offer other health benefits. Doing so will mean that they do not reverse the positive effects of the fasting days. The body first responds to a fall in the level of glucose in the blood by releasing epinephrine from the adrenal glands. Hormone deficiencies can also cause hypoglycemia because hormones control blood sugar levels. What is intermittent fasting, and how does it work? For a study in the journal Diabetic Medicine, researchers in New Zealand found that the incidence of hypoglycemia did increase among people with Type 2 diabetes who attempted intermittent fasting. |
| Intermittent fasting for type 2 diabetes | Our study Hypogljcemia could be adopted for Fawting longer-term annd Hypoglycemia and fasting will be required to assess the tolerability and Probiotics and Bowel Movements efficacy of an intermittent fast. The use of an IF diet may also have a beneficial effect on blood pressure. Pakistan Election Results. An insulinoma is a small tumor in the pancreas that produces an excess amount of insulin. Get the Mayo Clinic app. |
| Diabetes and intermittent fasting: Benefits and risks | Effect of fasting on young adults who have symptoms of hypoglycemia in the absence of frequent meals. Eur J Clin Nutr 62 , — Download citation. Received : 26 October Revised : 10 April Accepted : 11 April Published : 16 May Issue Date : June Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Skip to main content Thank you for visiting nature. nature european journal of clinical nutrition original article article. Abstract Background and Objectives: Among otherwise healthy adults, there is a subgroup of individuals who develop symptoms of hypoglycemia during episodes of food restriction. Subjects and Methods: Ninety medical students were asked if they wanted to participate. Conclusions: Adults, despite subjective signs of hypoglycemia, can fast without any metabolic or endocrine derangement. Access through your institution. Buy or subscribe. Change institution. Learn more. Figure 1. References Brun JF, Fedou C, Mercier J CAS PubMed Google Scholar Champe PC, Harvey RA Google Scholar Chapman IM, Goble EA, Wittert GA, Morley JE, Horowitz M CAS Google Scholar Dahlquist G, Gentz J, Hagenfeldt L, Larsson A, Low H, Persson B et al. Article CAS Google Scholar Elimam A, Horal M, Bergstrom M, Marcus C Article CAS Google Scholar Gielkens HA, Verkijk M, Lam WF, Lamers CB, Masclee AA Article CAS Google Scholar Grunt JA, McGarry ME, McCollum AT, Gould JB CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Hagstrom-Toft E, Bolinder J, Ungerstedt U, Arner P Article CAS Google Scholar Haymond MW, Howard C, Ben-Galim E, DeVivo DC CAS PubMed Google Scholar Horal M, Ungerstedt U, Persson B, Westgren M, Marcus C Article CAS Google Scholar Inoue K, Kakehashi Y, Oomori S, Koizumi A Article Google Scholar Kamel A, Norgren S, Persson B, Marcus C Article CAS Google Scholar Karam JH Google Scholar Levin F, Edholm T, Schmidt PT, Gryback P, Jacobsson H, Degerblad M et al. Article CAS Google Scholar Marcus C Article CAS Google Scholar Marks V Google Scholar Meyer EL, Waldenlind E, Marcus C Article CAS Google Scholar Sasaki M, Mogi T, Wada Y, Hirosawa I, Koizumi A Article CAS Google Scholar Wiesli P, Brandle M, Zapf J, Seiler H, Zwimpfer C, Spinas GA et al. Article CAS Google Scholar Wiesli P, Schwegler B, Schmid B, Spinas GA, Schmid C Article CAS Google Scholar Wildenhoff KE Article CAS Google Scholar Williams G, Cai XJ, Elliott JC, Harrold JA Article CAS Google Scholar Yager J, Young RT Article CAS Google Scholar Download references. Acknowledgements This work was supported by the Freemasons in Stockholm Foundation for Children's Welfare and the Swedish Research Council KXB. View author publications. Additional information Contributors : CM has contributed to the initiation of the study, designed the study protocol, participated in the writing of the manuscript and has been the supervisor of the study. Rights and permissions Reprints and permissions. About this article Cite this article Alkén, J. Copy to clipboard. About the journal Journal Information Open Access Fees and Funding About the Editors Contact For Advertisers Subscribe. There are several methods, which involve various time frames for fasting and eating. There may be health benefits of intermittent fasting for people with type 2 diabetes. Many people believe that intermittent fasting IF can aid weight loss and offer other health benefits. This article looks at whether this eating pattern might be beneficial for people living with type 2 diabetes. IF is an eating regimen that cycles between periods of eating and periods of voluntary fasting or very low calorie intake. Researchers believe that IF leads to a metabolic switch from the use of glucose as the primary energy source to the use of fat. IF can also have a positive effect on the circadian rhythms of both gut biology and the release of insulin and growth hormone. In these ways, it can improve energy metabolism and weight regulation. This type of IF involves eating during only a certain number of hours each day. A popular plan is the method, which requires a person to fast for 16 hours and eat during an 8-hour window. This type of fasting involves no or minimal calorie intake for hour periods. Examples are the diet and Eat Stop Eat. With the method, a person eats normally on 5 days of the week and then eats about calories during each of the 2 fasting days, which should not be consecutive. People adhering to the Eat Stop Eat regimen have to refrain from food and calorie-containing drinks for an entire hour period once or twice per week. When a person is fasting, their blood glucose levels decrease. This triggers the pancreas to make and release more glucagon, a hormone that keeps glucose from dropping too low. Glucagon does this by causing the liver to break down glycogen stored glucose and release the glucose back into the bloodstream. Glucagon also stops the liver from taking in and storing glucose, so more glucose stays in the blood. There is a feedback system that lets the body know when no more glucagon is needed. When everything is working as it should, the body will produce insulin to move glucose out of the blood and into the cells to rebalance the increased glucose levels. However, in someone who has diabetes, the pancreas does not make enough insulin or the body does not use insulin effectively. As a result, the increased levels of glucose stay in the bloodstream. Most IF research has involved animals rather than human participants. The evidence to support health improvements in people is promising, but many of the clinical studies to date have been relatively short-term interventions over a period of months. A review article stated that nearly all IF studies resulted in some degree of weight loss, ranging from 2. However, there is little research to suggest that IF is superior to other diets and eating patterns in promoting weight loss. The use of an IF diet may also have a beneficial effect on blood pressure. In one study , researchers observed 1, people for 1 year while they followed a fasting program. The participants experienced reductions in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure. In another study , which involved adult males, researchers found that IF provided metabolic and cardiovascular benefits, such as a decrease in total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein LDL cholesterol. Scientists know that insulin resistance improves with calorie restriction. After a period of fasting, insulin sensitivity increases and insulin levels decrease. These changes result in improved blood sugar levels both during fasting and shortly after eating. Many people with type 2 diabetes also have metabolic syndrome, hypertension, or hyperlipidemia high cholesterol. IF may improve these metabolic parameters. There is also a risk of hypoglycemia in people with type 2 diabetes, especially those who are taking insulin or medications such as sulfonylureas. This risk is lower with other diabetes medications , but it still exists. Dehydration is a risk as well. Dehydration can then lead to hypotension. How to prevent hypoglycemia while fasting There are several ways you can do to prevent hypoglycemia while fasting, such as:. Those are some of the symptoms to how to prevent hypoglycemia while fasting. If you or your closest relative feel these symptoms while fasting, immediately consult a trusted doctor to get further treatment. Article written by dr. Steffie Simpinano Solin, Sp. PD Internal Medicine Specialist at EMC Cibitung Hospital. Untuk informasi lebih lanjut dan menjawab segala pertanyaan anda, Bisa hubungi melalui Call Center atau Whatsapp kami berikut ini:. Care Plus Detail Home Care plus Care Plus Detail. Avoid Hypoglycemia When Fasting in the Following Ways! Written By: dr. Symptoms of hypoglycemia while fasting There are several symptoms commonly experienced by hypoglycemia sufferers when fasting, including: Dizziness and pain in the head Feeling tired and lethargic A cold sweat Dizzy eyes or visual disturbances Body shaking or convulsions Confusion or difficulty in thinking and speaking Increased appetite Fast and irregular heartbeat Mood changes such as restlessness, anxiety, or irritability How to prevent hypoglycemia while fasting There are several ways you can do to prevent hypoglycemia while fasting, such as: Consult with a doctor If you have diabetes or other health problems that affect blood sugar levels, consult your doctor before deciding to fast. |
Sie sind nicht recht. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen.
Ich denke, dass Sie nicht recht sind. Es ich kann beweisen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.