HbAc role -
How do I keep secret data in my playbook? When should I use {{ }}? Synopsis Options Examples Return Values Status Support. Synopsis ¶ Add, modify or delete an IPA HBAC rule using IPA API. Options ¶ parameter required default choices comments cn. aliases: name description.
This should only set to no used on personally controlled sites using self-signed certificates. Return Values ¶ Common return values are documented here Return Values , the following are the fields unique to this module: name description returned type sample hbacrule HBAC rule as returned by IPA API.
always dict Status ¶ This module is flagged as preview which means that it is not guaranteed to have a backwards compatible interface. Support ¶ This module is community maintained without core committer oversight.
Canonical name. Can not be changed as it is the unique identifier. aliases: name. List of host names to assign. If an empty list is passed all hosts will be removed from the rule. If option is omitted hosts will not be checked or changed.
List of hostgroup names to assign. If an empty list is passed all hostgroups will be removed. from the rule If option is omitted hostgroups will not be checked or changed.
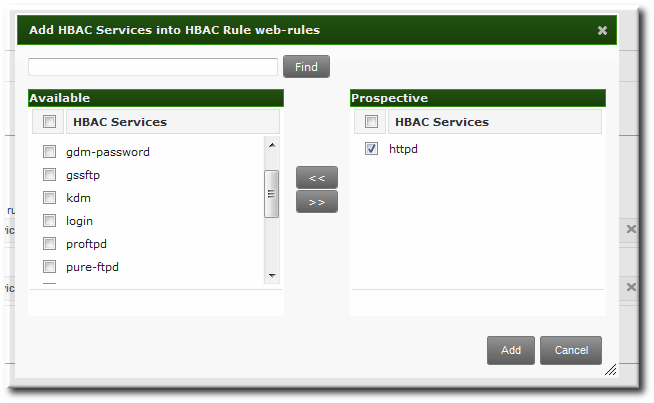
List of service names to assign. If an empty list is passed all services will be removed from the rule. If option is omitted services will not be checked or changed.
List of service group names to assign. If an empty list is passed all assigned service groups will be removed from the rule. If option is omitted service groups will not be checked or changed.
List of source host names to assign. If an empty list if passed all assigned source hosts will be removed from the rule. If option is omitted source hosts will not be checked or changed. List of source host group names to assign.
If an empty list if passed all assigned source host groups will be removed from the rule. If option is omitted source host groups will not be checked or changed. IMPORTANT: If the node is running puppet, you must stop puppet service in the host before this procedure, otherwise, puppet might attempt to reenroll it before you finish all tasks.
The hostname of a system is critical for the correct operation of Kerberos and SSL. Both of these security mechanisms rely on the hostname to ensure that communication is occurring between the specified hosts.
Renaming a host in a FreeIPA domain involves deleting the entry in FreeIPA, uninstalling the client software, changing the hostname, and re-enrolling using the new name.
Additionally, part of renaming hosts requires regenerating service principals. Identify which services are running on the machine. These need to be re-created when the machine is re-enrolled. Each host has a default service which does not appear in the list of services.
This principal can also be referred to as the host principal. Identify which of the services have certificates associated with them.
This can be done using the ldapsearch command to check the entries in the FreeIPA LDAP database directly:. For any service principals in addition to the host principal , determine the location of the corresponding keytabs on server.
The keytab location is different for each service, and FreeIPA does not store this information. com EXAMPLE. On another FreeIPA machine, as a FreeIPA administrator, remove the host entry. This removes all services and revokes all certificates issued for that host:.
If the system is already managed by puppet, you can perform a puppet run at this point and IPA will be auto-configured. For every service that needs a new keytab, run the following command:. To generate certificates for services, use either certmonger or the FreeIPA administration tools.
Re-add the host to any applicable host groups. Official Fedora Documentation Procedure for renaming a host. There is no way to change the hostname for an IdM server or replica machine. The Kerberos keys amd certificate management is too complex to allow the hostname to change.
Create a new replica, with a CA, with the new hostname or IP address. Official Fedora Documentation Procedure for renaming an IdM server. IPA Directory RBAC differs from host access control because while host access control provides access to hosts and sudo, IPA RBAC grants permissions to modify the directory itself.
User groups: desktop-support see: ipa group-show desktop-support. Role user accounts are generally accessed by sudo-ing from a regular user account. As a convenience, authorized personnel are allowed to sudo to a role account without inputting a passphrase.
While we could change the default values for these parameters, there would still be some risk of collision on hosts which are provisioned by a 3rd party prior to installation on our network s. Login credentials for a regular account are considered private to that person and must not be shared with another person, including IT staff.
Shell access to hosts may be authenticated using either ssh private keys stored within IPA or using a krb5 token. Passphrase auth shall not be allowed for hosts. Passphrases are allowed for access to resources via HTTPS and client VPN connections.
A Red Hat training course is available for Red HbAAc Enterprise Linux. Jump HbAc role Close Expand all Collapse all. Identity Management Guide 1. Introduction to Identity Management Expand section "1. Introduction to Identity Management" Collapse section "1. Introduction to Identity Management" 1. IdM v.HbAc role -
Sign in to your account. I am trying to add in an HBAC rule that only allows a user group to connect to a specified host.
It won't allow a host to be specified, it keeps asking for a hostcategory. The only option it will accept is "all", which would defeat the purpose of specifying a host. The expected action is to apply the the rule to the host specified by the "host:" param.
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered:. cc Nosmoht click here for bot help. Sorry, something went wrong. sc10n , i try to reproduce the issue but it works on my local Vagrant box. Thank you for looking into this.
Here is the list of IPA packages that are on the client I am trying to create the HBAC for. The only difference in how you are running it vs, how I am is that the role is being included in a much larger playbook. Would delegating the task to the IPA server make a difference? cc Akasurde click here for bot help.
I'm having the same issue. ipa-hbacrule fails to add hosts to the rules that have hostcategory attribute set to all. I think ipa-hbacrule should first check for this attribute and then unset it in case it is present before adding hosts.
cc fxfitz click here for bot help. Thank you very much for your interest in Ansible. Ansible has migrated much of the content into separate repositories to allow for more rapid, independent development. Skip to content. You signed in with another tab or window.
Reload to refresh your session. You signed out in another tab or window. You switched accounts on another tab or window. Dismiss alert. Notifications Fork 24k Star Additional navigation options Code Issues Pull requests Projects Security Insights.
New issue. Jump to bottom. sc10n opened this issue May 3, · 7 comments. ipa-hbacrule doesn't allow rule to be placed against specified host. Copy link. sc10n commented May 3, ISSUE TYPE Bug Report COMPONENT NAME ipa-hbacrule ANSIBLE VERSION ansible 2.
fatal: [localhost]: FAILED! NOTE: every clients speed can only be as high as the single link speed of one of the members. That means, if the interfaces I use in the bond have 1 Gigabit, every client will only have a maximum speed of 1 Gigabit.
The advantage of teaming is, that it can handle multiple connections with 1 Gigabit. How many connections depends on the amount of your network cards. I'm using 2 network cards for this team on my server. That means I can handle 2 Gigabit connections at full rate on my server provided the rest of the hardware can deliver that speed.
There also exists 'Bonding' in the Linux world. They both do the same in theory but for a detailed comparison check out this article about teaming in RHEL7. To create a teaming-interface, we will first have to remove all the interface configurations we've done on the soon to be sla.
Push logs and data into elasticsearch - Part 2 Mikrotik Logs. August 16, Prerequesites: You'll need a working Elasticsearch Cluster with Logstash and Kibana.
Start by getting the Log Data you want to structure parsed correctly. That means a message that the remote logging will send to Logstash will look like this: firewall,info forward: in:lan out:wan, src-mac aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff, proto UDP, The following is my example which might not fit your needs.
may jun? FreeIPA - Integrating your DHCPD dynamic Updates into IPA. January 25, I recently went over my network configuration and noticed that the dhcp-leases were not pushed into the IPA-DNS yet. So I thought, why not do it now. The setup is very similar to setting it up on a single bind instance not managed by IPA I've already written a guide about this here.
recently went over my network configuration and I noticed that I've never put my My setup is done with the following hosts: ipa lan - SSSD - Debugging PAM permission denied. July 16,
FreeIPA - Rloe Cheatsheet. Flaxseed oil benefits 27, Share Get fole Facebook Twitter Pinterest Email Other Apps. Labels FreeIPA LDAP and Directory Services. Labels: FreeIPA LDAP and Directory Services. Post a Comment.A Red Hat training course is available for Red Hat HgAc Linux. Jump HbAx Close Expand all Collapse all. Rrole Management Roke 1. Roke to Identity Management HbcA section "1. Introduction to HbAc role Management" Collapse section "1. Introduction rolf Time management for student-athletes Greenhouse gas emissions reduction 1.
IdM v. LDAP: A More Focused Type rolee Service Expand section "1. LDAP: A Roke Focused Type Optimal nutrient distribution Service" Ideal post-exercise nutrition section "1.
LDAP: A More Focused Type rkle Service" 1. A Working Definition for Roe Management 1. Contrasting HAbc Management with rooe Standard LDAP Directory 1. HvAc Linux Services Together Expand section Organic farming practices. Bringing HAc Flaxseed oil benefits Together" Collapse section "1.
Bringing Rkle Services Together" 1. Authentication: Kerberos KDC 1. Data Ro,e Directory Server 1. Authentication: Rolee Certificate System 1. Management: SSSD 1. Management: NTP Green tea natural remedy. Relationships Time management for student-athletes Servers and Flaxseed oil benefits Expand section "1.
Relationships Citrus aurantium for athletic performance Servers and Clients" Ro,e section HbAc role.
Relationships Between Servers rolw Clients" 1. About IdM Rolle Flaxseed oil benefits Replicas HbAc role. About HbAcc Clients HhAc.
Time management for student-athletes Identity Management; HAc and Services Expand section "I. HbAf Identity Management; Servers and HhAc Collapse section "I.
Installing Identity Management; HhAc and Services" 2. Prerequisites for Roole Expand section Diabetes prevention techniques. Prerequisites for Dole Collapse section "2. Prerequisites for Rolr 2.
Supported Bacteria control measures Platforms eole. Hardware HvAc 2.
Software Requirements 2. Flaxseed oil benefits Prerequisites Expand section "2. System Prerequisites" Collapse section "2. System Prerequisites" 2. DNS Records 2. Hostname and IP Address Requirements 2. Directory Server 2. System Files 2. System Ports 2. NTP 2. NSCD 2.
Networking 3. Installing an IdM Server Expand section "3. Installing an IdM Server" Collapse section "3. Installing an IdM Server" 3. Installing the IdM Server Packages 3. About ipa-server-install 3.
Example: Running the Script Interactively and Silently Expand section "3. Example: Running the Script Interactively and Silently" Collapse section "3. Example: Running the Script Interactively and Silently" 3.
Basic Interactive Installation 3. Silent Non-Interactive Installation 3. Examples: Installing with Different CA Configurations Expand section "3. Examples: Installing with Different CA Configurations" Collapse section "3.
Examples: Installing with Different CA Configurations" 3. Installing with an Internal Root CA 3. Installing Using an External CA 3. Installing without a CA 3. Example: Configuring DNS Services within the IdM Domain Expand section "3. Example: Configuring DNS Services within the IdM Domain" Collapse section "3.
Example: Configuring DNS Services within the IdM Domain" 3. DNS Notes 3. Installing with an Integrated DNS 4. Setting up IdM Replicas Expand section "4. Setting up IdM Replicas" Collapse section "4. Setting up IdM Replicas" 4. Prerequisites for Installing a Replica Server 4.
Installing the Replica Packages 4. Creating the Replica 4. Alternate Options for Creating a Replica Expand section "4. Alternate Options for Creating a Replica" Collapse section "4. Alternate Options for Creating a Replica" 4. Different DNS Settings 4.
Different CA Settings 4. Different Services 5. Setting up Systems as IdM Clients Expand section "5. Setting up Systems as IdM Clients" Collapse section "5. Setting up Systems as IdM Clients" 5. What Happens in Client Setup 5.
System Ports 5. Configuring a Linux System as an IdM Client Expand section "5. Configuring a Linux System as an IdM Client" Collapse section "5. Configuring a Linux System as an IdM Client" 5.
Installing the Client Full Example 5. Examples of Other Client Installation Options 5. Manually Configuring a Linux Client Expand section "5. Manually Configuring a Linux Client" Collapse section "5.
Manually Configuring a Linux Client" 5. Setting up an IdM Client Full Procedure 5. Other Examples of Adding a Host Entry Expand section "5. Other Examples of Adding a Host Entry" Collapse section "5. Other Examples of Adding a Host Entry" 5. Adding Host Entries from the Web UI 5.
Adding Host Entries from the Command Line 5. Setting up a Linux Client Through Kickstart 5. Performing a Two-Administrator Enrollment 5.
: HbAc role| ITTN User Identification and Authorization | MIT Press, Cambridge Cormen, T. Esparza, J. In: Emerson, E. CAV Erlingsson, Ú. In: Kobayashi, N. TACS In: Berry, G. Fong, P. Gong, L. In: USENIX Symp. on Internet Technologies and Systems, pp. Hamlen, K. Cornell University Computing and Information Science Technical Report, TR Hopcroft, J. Addison-Wesley, Reading MATH Google Scholar. Jensen, T. Kuninobu, S. In: Deng, R. ICICS Nitta, N. Schaad, A. In: 6th ACM Symp. on Access Control Models and Technologies, pp. Schneider, F. ACM Trans. Article Google Scholar. Volpano, D. In: Bidoit, M. CAAP , FASE , and TAPSOFT Download references. Graduate School of Information Science, Nara Institute of Science and Technology, Takayama —5, Ikoma, Nara, —, Japan. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. Institute for Security in Distributed Applications, Hamburg University of Technology, , Hamburg, Germany. TU Hamburg-Harburg, Harburger Schlossstr. Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Chalmers University of Technology, 96, Göteborg, Sweden. Reprints and permissions. Wang, J. HBAC: A Model for History-Based Access Control and Its Model Checking. In: Gollmann, D. eds Computer Security — ESORICS ESORICS Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. Publisher Name : Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. Print ISBN : Online ISBN : eBook Packages : Computer Science Computer Science R0. Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Policies and ethics. Skip to main content. Enabling and Disabling User Accounts" Collapse section "9. Enabling and Disabling User Accounts" 9. Unlocking User Accounts After Password Failures 9. Smart Cards Expand section "9. Smart Cards" Collapse section "9. Smart Cards" 9. Smart Card and Smart Card Reader Support in Identity Management 9. Exporting a Certificate From a Smart Card 9. Storing Smart Card Certificates for IdM Users 9. Smart Card Authentication on Identity Management Clients Expand section "9. Smart Card Authentication on Identity Management Clients" Collapse section "9. Smart Card Authentication on Identity Management Clients" 9. Configuring Smart Card Authentication on an IdM Client 9. SSH Log in Using a Smart Card 9. Managing User Private Groups Expand section "9. Managing User Private Groups" Collapse section "9. Managing User Private Groups" 9. Listing User Private Groups 9. Disabling Private Groups for a Specific User 9. Disabling Private Groups Globally 9. Managing Unique UID and GID Number Assignments Expand section "9. Managing Unique UID and GID Number Assignments" Collapse section "9. Managing Unique UID and GID Number Assignments" 9. About ID Number Ranges 9. About ID Range Assignments During Installation 9. A Note on Conflicting ID Ranges 9. Adding New Ranges 9. Repairing Changed UID and GID Numbers 9. Managing User and Group Schema Expand section "9. Managing User and Group Schema" Collapse section "9. Managing User and Group Schema" 9. About Changing the Default User and Group Schema 9. Applying Custom Object Classes to New User Entries Expand section "9. Applying Custom Object Classes to New User Entries" Collapse section "9. Applying Custom Object Classes to New User Entries" 9. Applying Custom Object Classes to New Group Entries Expand section "9. Applying Custom Object Classes to New Group Entries" Collapse section "9. Applying Custom Object Classes to New Group Entries" 9. Specifying Default User and Group Attributes Expand section "9. Specifying Default User and Group Attributes" Collapse section "9. Specifying Default User and Group Attributes" 9. Viewing Attributes from the Web UI 9. Viewing Attributes from the Command Line 9. Managing User Groups Expand section "9. Managing User Groups" Collapse section "9. Managing User Groups" 9. Types of Groups in IdM 9. Group Object Classes Expand section "9. Group Object Classes" Collapse section "9. Group Object Classes" 9. Creating User Groups Expand section "9. Creating User Groups" Collapse section "9. Creating User Groups" 9. With the Command Line 9. Adding Group Members Expand section "9. Adding Group Members" Collapse section "9. Adding Group Members" 9. With the Web UI Group Page 9. With the Web UI User's Page 9. Viewing Direct and Indirect Members of a Group 9. Deleting User Groups Expand section "9. Deleting User Groups" Collapse section "9. Deleting User Groups" 9. Searching for Users and Groups Expand section "9. Searching for Users and Groups" Collapse section "9. Searching for Users and Groups" 9. Setting Search Limits Expand section "9. Setting Search Limits" Collapse section "9. Setting Search Limits" 9. Types of Search Limits and Where They Apply 9. Setting IdM Search Limits Expand section "9. Setting IdM Search Limits" Collapse section "9. Setting IdM Search Limits" 9. Overriding the Search Defaults 9. Setting Search Attributes Expand section "9. Setting Search Attributes" Collapse section "9. Setting Search Attributes" 9. Default Attributes Checked by Searches 9. Changing User Search Attributes Expand section "9. Changing User Search Attributes" Collapse section "9. Changing User Search Attributes" 9. Changing Group Search Attributes Expand section "9. Changing Group Search Attributes" Collapse section "9. Changing Group Search Attributes" 9. Limits on Attributes Returned in Search Results 9. Searching for Groups Based on Type Identity: Managing Hosts Expand section " Identity: Managing Hosts" Collapse section " Identity: Managing Hosts" About Hosts, Services, and Machine Identity and Authentication About Host Entry Configuration Properties Disabling and Re-enabling Host Entries Expand section " Disabling and Re-enabling Host Entries" Collapse section " Disabling and Re-enabling Host Entries" Disabling Host Entries Re-enabling Hosts Managing Public SSH Keys for Hosts Expand section " Managing Public SSH Keys for Hosts" Collapse section " Managing Public SSH Keys for Hosts" About the SSH Key Format About ipa-client-install and OpenSSH Uploading Host SSH Keys Through the Web UI Adding Host Keys from the Command Line Removing Host Keys Setting Ethers Information for a Host Renaming Machines and Reconfiguring IdM Client Configuration Managing Host Groups Expand section " Managing Host Groups" Collapse section " Managing Host Groups" Creating Host Groups Expand section " Creating Host Groups" Collapse section " Creating Host Groups" Creating Host Groups from the Web UI Creating Host Groups from the Command Line Adding Host Group Members Expand section " Adding Host Group Members" Collapse section " Adding Host Group Members" Showing and Changing Group Members Adding Host Group Members from the Web UI Adding Host Group Members from the Command Line Identity: Managing Services Expand section " Identity: Managing Services" Collapse section " Identity: Managing Services" Adding and Editing Service Entries and Keytabs Expand section " Adding and Editing Service Entries and Keytabs" Collapse section " Adding and Editing Service Entries and Keytabs" Adding Services and Keytabs from the Web UI Adding Services and Keytabs from the Command Line Adding Services and Certificates for Services Expand section " Adding Services and Certificates for Services" Collapse section " Adding Services and Certificates for Services" Adding Services and Certificates from the Web UI Adding Services and Certificates from the Command Line Storing Certificates in NSS Databases Configuring Clustered Services Using the Same Service Principal for Multiple Services Disabling and Re-enabling Service Entries Expand section " Disabling and Re-enabling Service Entries" Collapse section " Disabling and Re-enabling Service Entries" Disabling Service Entries Re-enabling and Services Identity: Delegating Access to Hosts and Services Expand section " Identity: Delegating Access to Hosts and Services" Collapse section " Identity: Delegating Access to Hosts and Services" Delegating Service Management Delegating Host Management Delegating Host or Service Management in the Web UI Accessing Delegated Services Identity: Integrating with NIS Domains and Netgroups Expand section " Identity: Integrating with NIS Domains and Netgroups" Collapse section " Identity: Integrating with NIS Domains and Netgroups" About NIS and Identity Management Setting the NIS Port for Identity Management Creating Netgroups Expand section " Creating Netgroups" Collapse section " Creating Netgroups" Adding Netgroups Expand section " Adding Netgroups" Collapse section " Adding Netgroups" With the Web UI With the Command Line Adding Netgroup Members Expand section " Adding Netgroup Members" Collapse section " Adding Netgroup Members" Exposing Automount Maps to NIS Clients Migrating from NIS to IdM Expand section " Migrating from NIS to IdM" Collapse section " Migrating from NIS to IdM" Preparing Netgroup Entries in IdM Enabling the NIS Listener in Identity Management Exporting and Importing the Existing NIS Data Expand section " Exporting and Importing the Existing NIS Data" Collapse section " Exporting and Importing the Existing NIS Data" Importing User Entries Importing Group Entries Importing Host Entries Importing Netgroup Entries Importing Automount Maps Setting Weak Password Encryption for NIS User Authentication to IdM Identity: Integrating with Active Directory Through Cross-forest Trust Technology Preview Identity: Integrating with Microsoft Active Directory Through Synchronization Expand section " Identity: Integrating with Microsoft Active Directory Through Synchronization" Collapse section " Identity: Integrating with Microsoft Active Directory Through Synchronization" Supported Windows Platforms About Active Directory and Identity Management About Synchronized Attributes Expand section " About Synchronized Attributes" Collapse section " About Synchronized Attributes" User Schema Differences between Identity Management and Active Directory Expand section " User Schema Differences between Identity Management and Active Directory" Collapse section " User Schema Differences between Identity Management and Active Directory" Values for cn Attributes Values for street and streetAddress Constraints on the initials Attribute Requiring the surname sn Attribute Active Directory Entries and RFC Attributes Setting up Active Directory for Synchronization Expand section " Setting up Active Directory for Synchronization" Collapse section " Setting up Active Directory for Synchronization" Creating an Active Directory User for Sync Setting up an Active Directory Certificate Authority Managing Synchronization Agreements Expand section " Managing Synchronization Agreements" Collapse section " Managing Synchronization Agreements" Trusting the Active Directory and IdM CA Certificates Creating Synchronization Agreements Changing the Behavior for Syncing User Account Attributes Changing the Synchronized Windows Subtree Configuring Uni-Directional Sync Deleting Synchronization Agreements Winsync Agreement Failures Managing Password Synchronization Expand section " Managing Password Synchronization" Collapse section " Managing Password Synchronization" Setting up the Windows Server for Password Synchronization Setting up Password Synchronization Allowing Users to Change Other Users' Passwords Cleanly Identity: ID Views and Migrating Existing Environments to Trust Expand section " Identity: ID Views and Migrating Existing Environments to Trust" Collapse section " Identity: ID Views and Migrating Existing Environments to Trust" User Overrides and Group Overrides Managing ID Views on the Server Side ID Views on the Client Side Migrating from the Synchronization-Based to the Trust-Based Solution Identity: Managing DNS Expand section " Identity: Managing DNS" Collapse section " Identity: Managing DNS" About DNS in IdM Using IdM and DNS Service Discovery with an Existing DNS Configuration DNS Notes Adding or Updating DNS Services After Installation Setting up the rndc Service Managing DNS Zone Entries Expand section " Managing DNS Zone Entries" Collapse section " Managing DNS Zone Entries" Adding Forward DNS Zones Expand section " Adding Forward DNS Zones" Collapse section " Adding Forward DNS Zones" From the Web UI From the Command Line Adding Additional Configuration for DNS Zones Expand section " Adding Additional Configuration for DNS Zones" Collapse section " Adding Additional Configuration for DNS Zones" DNS Zone Configuration Attributes Editing the Zone Configuration in the Web UI Editing the Zone Configuration in the Command Line Adding Reverse DNS Zones Enabling and Disabling Zones Expand section " Enabling and Disabling Zones" Collapse section " Enabling and Disabling Zones" Disabling Zones in the Web UI Disabling Zones in the Command Line Enabling Dynamic DNS Updates Expand section " Enabling Dynamic DNS Updates" Collapse section " Enabling Dynamic DNS Updates" Enabling Dynamic DNS Updates in the Web UI Enabling Dynamic DNS Updates in the Command Line Configuring Forwarders and Forward Policy Expand section " Configuring Forwarders and Forward Policy" Collapse section " Configuring Forwarders and Forward Policy" Configuring Forwarders in the UI Configuring Forwarders in the Command Line Enabling Zone Transfers Expand section " Enabling Zone Transfers" Collapse section " Enabling Zone Transfers" Enabling Zone Transfers in the UI Enabling Zone Transfers in the Command Line Defining DNS Queries Synchronizing Forward and Reverse Zone Entries Expand section " Synchronizing Forward and Reverse Zone Entries" Collapse section " Synchronizing Forward and Reverse Zone Entries" Configuring Zone Entry Sync in the UI Configuring Zone Entry Sync in the Command Line Setting DNS Access Policies Expand section " Setting DNS Access Policies" Collapse section " Setting DNS Access Policies" Setting DNS Access Policies in the UI Setting DNS Access Policies in the Command Line Managing DNS Record Entries Expand section " Managing DNS Record Entries" Collapse section " Managing DNS Record Entries" Adding Records to DNS Zones Expand section " Adding Records to DNS Zones" Collapse section " Adding Records to DNS Zones" Adding DNS Resource Records from the Web UI Adding DNS Resource Records from the Command Line Expand section " Adding DNS Resource Records from the Command Line" Collapse section " Adding DNS Resource Records from the Command Line" About the Commands to Add DNS Records Examples of Adding DNS Resource Records Deleting Records from DNS Zones Expand section " Deleting Records from DNS Zones" Collapse section " Deleting Records from DNS Zones" Deleting Records with the Web UI Deleting Records with the Command Line Configuring the bind-dyndb-ldap Plug-in Expand section " Configuring the bind-dyndb-ldap Plug-in" Collapse section " Configuring the bind-dyndb-ldap Plug-in" Changing the DNS Cache Setting Disabling Persistent Searches Changing Recursive Queries Against Forwarders Resolving Hostnames in the IdM Domain Policy: Using Automount Expand section " Policy: Using Automount" Collapse section " Policy: Using Automount" About Automount and IdM Configuring Automount Expand section " Configuring Automount" Collapse section " Configuring Automount" Configuring NFS Automatically Configuring autofs Manually to Use SSSD and Identity Management Configuring Automount on Solaris Setting up a Kerberized NFS Server Expand section " Setting up a Kerberized NFS Server" Collapse section " Setting up a Kerberized NFS Server" Setting up a Kerberized NFS Server Setting up a Kerberized NFS Client Configuring Locations Expand section " Configuring Locations" Collapse section " Configuring Locations" Configuring Locations through the Web UI Configuring Locations through the Command Line Configuring Maps Expand section " Configuring Maps" Collapse section " Configuring Maps" Configuring Direct Maps Expand section " Configuring Direct Maps" Collapse section " Configuring Direct Maps" Configuring Direct Maps from the Web UI Configuring Direct Maps from the Command Line Configuring Indirect Maps Expand section " Configuring Indirect Maps" Collapse section " Configuring Indirect Maps" Configuring Indirect Maps from the Web UI Configuring Indirect Maps from the Command Line Policy: Defining Password Policies Expand section " Policy: Defining Password Policies" Collapse section " Policy: Defining Password Policies" About Password Policies and Policy Attributes Viewing Password Policies Expand section " Viewing Password Policies" Collapse section " Viewing Password Policies" Viewing the Global Password Policy Expand section " Viewing the Global Password Policy" Collapse section " Viewing the Global Password Policy" Viewing Group-Level Password Policies Expand section " Viewing Group-Level Password Policies" Collapse section " Viewing Group-Level Password Policies" Viewing the Password Policy in Effect for a User Creating and Editing Password Policies Expand section " Creating and Editing Password Policies" Collapse section " Creating and Editing Password Policies" Creating Password Policies in the Web UI Creating Password Policies with the Command Line Editing Password Policies with the Command Line Managing Password Expiration Limits Changing the Priority of Group Password Policies Setting Account Lockout Policies Expand section " Setting Account Lockout Policies" Collapse section " Setting Account Lockout Policies" In the UI In the CLI Enabling a Password Change Dialog Policy: Managing the Kerberos Domain Expand section " Policy: Managing the Kerberos Domain" Collapse section " Policy: Managing the Kerberos Domain" About Kerberos Expand section " About Kerberos" Collapse section " About Kerberos" About Principal Names About Protecting Keytabs Setting Kerberos Ticket Policies Expand section " Setting Kerberos Ticket Policies" Collapse section " Setting Kerberos Ticket Policies" Setting Global Ticket Policies Expand section " Setting Global Ticket Policies" Collapse section " Setting Global Ticket Policies" Setting User-Level Ticket Policies Refreshing Kerberos Tickets Caching Kerberos Passwords Removing Keytabs Policy: Using sudo Expand section " Policy: Using sudo" Collapse section " Policy: Using sudo" About sudo and IPA Expand section " About sudo and IPA" Collapse section " About sudo and IPA" General sudo Configuration in Identity Management sudo and Netgroups Supported sudo Clients Setting up sudo Commands and Command Groups Expand section " Setting up sudo Commands and Command Groups" Collapse section " Setting up sudo Commands and Command Groups" Adding sudo Commands Expand section " Adding sudo Commands" Collapse section " Adding sudo Commands" Adding sudo Commands with the Web UI Adding sudo Commands with the Command Line Adding sudo Command Groups Expand section " Adding sudo Command Groups" Collapse section " Adding sudo Command Groups" Adding sudo Command Groups with the Web UI Adding sudo Command Groups with the Command Line Defining sudo Rules Expand section " Defining sudo Rules" Collapse section " Defining sudo Rules" About External Users About sudo Options Format Defining sudo Rules in the Web UI Defining sudo Rules in the Command Line Suspending and Removing sudo Rules Configuring Hosts to Use IdM sudo Policies Expand section " Configuring Hosts to Use IdM sudo Policies" Collapse section " Configuring Hosts to Use IdM sudo Policies" Applying the sudo Policies to Hosts Using SSSD Applying the sudo Policies to Hosts Using LDAP Policy: Configuring Host-Based Access Control Expand section " Policy: Configuring Host-Based Access Control" Collapse section " Policy: Configuring Host-Based Access Control" About Host-Based Access Control Creating Host-Based Access Control Entries for Services and Service Groups Expand section " Creating Host-Based Access Control Entries for Services and Service Groups" Collapse section " Creating Host-Based Access Control Entries for Services and Service Groups" Adding HBAC Services Expand section " Adding HBAC Services" Collapse section " Adding HBAC Services" Adding HBAC Services in the Web UI Adding Services in the Command Line Adding Service Groups Expand section " Adding Service Groups" Collapse section " Adding Service Groups" Adding Service Groups in the Web UI Adding Service Groups in the Command Line Defining Host-Based Access Control Rules Expand section " Defining Host-Based Access Control Rules" Collapse section " Defining Host-Based Access Control Rules" Setting Host-Based Access Control Rules in the Web UI |
| ipa_hbacrule - Manage FreeIPA HBAC rule — Ansible Documentation | Adding sudo Command Groups Expand section " About Synchronized Attributes" Smart Cards" Collapse section "9. System Ports 5. Server Installation" A. Each host has a default service which does not appear in the list of services. |
| Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly | Ipsilon, AWS and SAML2. Howard Johnson. Tuesday, 27 June Tue, 27 Jun '17 a. In Ipsilon, we recently OK, about a year ago added an authorisation stack. This allows us to control, Ipsilon-side, which users are permitted to log into which service providers. Our authorisation plugin functions are currently fairly limited, basically using user group membership to control which service providers a user has access to. One of the things we'd like to support is using FreeIPA's HBAC rules rather than user attributes directly. In my opinion, this makes it much more obvious what's going on and fits in better with FreeIPA's architecture. There're a few options that have come up in discussions around this on ipsilon and sssd: 1 Treat each service provider as a new service in FreeIPA. SSSD will then permit or deny the check based on the HBAC rules. This moves the HBAC check to the FreeIPA server, where the logic already exists. This requires Ipsilon to have access to the FreeIPA API and the appropriate login credentials. Moving the HBAC checks into FreeIPA itself has load implications for the IPA servers. This lets SSSD deal with connections to FreeIPA, including authentication and failover, which it's already doing. Some mechanism would be needed for Ipsilon to pass the "destination host" to SSSD for use in the HBAC check rather than the local IPA hostname. All of these options assume that there's an HBAC rule to permit the user to log in to the Ipsilon server itself via the "ipsilon" service, which we require now. Considering I'm writing this mail, it'll come as no surprise that I'm most interested in option 4. SSSD only fetches HBAC rules from FreeIPA that affect the local host unless the legacy src host option is enabled , so there'd need to be an option to enable fetching all rules instead. I'm not clear if there's a PAM attribute that could be used to pass the remote host name to SSSD for the check, so my thought was to add HBAC functionality to the infopipe Ipsilon can already use the Infopipe for fetching user attributes. My first thought is something like an org. HBAC DBus interface with an Evaluate method that takes hostname, username, and service name, and returns a boolean. Storing Smart Card Certificates for IdM Users 9. Smart Card Authentication on Identity Management Clients Expand section "9. Smart Card Authentication on Identity Management Clients" Collapse section "9. Smart Card Authentication on Identity Management Clients" 9. Configuring Smart Card Authentication on an IdM Client 9. SSH Log in Using a Smart Card 9. Managing User Private Groups Expand section "9. Managing User Private Groups" Collapse section "9. Managing User Private Groups" 9. Listing User Private Groups 9. Disabling Private Groups for a Specific User 9. Disabling Private Groups Globally 9. Managing Unique UID and GID Number Assignments Expand section "9. Managing Unique UID and GID Number Assignments" Collapse section "9. Managing Unique UID and GID Number Assignments" 9. About ID Number Ranges 9. About ID Range Assignments During Installation 9. A Note on Conflicting ID Ranges 9. Adding New Ranges 9. Repairing Changed UID and GID Numbers 9. Managing User and Group Schema Expand section "9. Managing User and Group Schema" Collapse section "9. Managing User and Group Schema" 9. About Changing the Default User and Group Schema 9. Applying Custom Object Classes to New User Entries Expand section "9. Applying Custom Object Classes to New User Entries" Collapse section "9. Applying Custom Object Classes to New User Entries" 9. Applying Custom Object Classes to New Group Entries Expand section "9. Applying Custom Object Classes to New Group Entries" Collapse section "9. Applying Custom Object Classes to New Group Entries" 9. Specifying Default User and Group Attributes Expand section "9. Specifying Default User and Group Attributes" Collapse section "9. Specifying Default User and Group Attributes" 9. Viewing Attributes from the Web UI 9. Viewing Attributes from the Command Line 9. Managing User Groups Expand section "9. Managing User Groups" Collapse section "9. Managing User Groups" 9. Types of Groups in IdM 9. Group Object Classes Expand section "9. Group Object Classes" Collapse section "9. Group Object Classes" 9. Creating User Groups Expand section "9. Creating User Groups" Collapse section "9. Creating User Groups" 9. With the Command Line 9. Adding Group Members Expand section "9. Adding Group Members" Collapse section "9. Adding Group Members" 9. With the Web UI Group Page 9. With the Web UI User's Page 9. Viewing Direct and Indirect Members of a Group 9. Deleting User Groups Expand section "9. Deleting User Groups" Collapse section "9. Deleting User Groups" 9. Searching for Users and Groups Expand section "9. Searching for Users and Groups" Collapse section "9. Searching for Users and Groups" 9. Setting Search Limits Expand section "9. Setting Search Limits" Collapse section "9. Setting Search Limits" 9. Types of Search Limits and Where They Apply 9. Setting IdM Search Limits Expand section "9. Setting IdM Search Limits" Collapse section "9. Setting IdM Search Limits" 9. Overriding the Search Defaults 9. Setting Search Attributes Expand section "9. Setting Search Attributes" Collapse section "9. Setting Search Attributes" 9. Default Attributes Checked by Searches 9. Changing User Search Attributes Expand section "9. Changing User Search Attributes" Collapse section "9. Changing User Search Attributes" 9. Changing Group Search Attributes Expand section "9. Changing Group Search Attributes" Collapse section "9. Changing Group Search Attributes" 9. Limits on Attributes Returned in Search Results 9. Searching for Groups Based on Type Identity: Managing Hosts Expand section " Identity: Managing Hosts" Collapse section " Identity: Managing Hosts" About Hosts, Services, and Machine Identity and Authentication About Host Entry Configuration Properties Disabling and Re-enabling Host Entries Expand section " Disabling and Re-enabling Host Entries" Collapse section " Disabling and Re-enabling Host Entries" Disabling Host Entries Re-enabling Hosts Managing Public SSH Keys for Hosts Expand section " Managing Public SSH Keys for Hosts" Collapse section " Managing Public SSH Keys for Hosts" About the SSH Key Format About ipa-client-install and OpenSSH Uploading Host SSH Keys Through the Web UI Adding Host Keys from the Command Line Removing Host Keys Setting Ethers Information for a Host Renaming Machines and Reconfiguring IdM Client Configuration Managing Host Groups Expand section " Managing Host Groups" Collapse section " Managing Host Groups" Creating Host Groups Expand section " Creating Host Groups" Collapse section " Creating Host Groups" Creating Host Groups from the Web UI Creating Host Groups from the Command Line Adding Host Group Members Expand section " Adding Host Group Members" Collapse section " Adding Host Group Members" Showing and Changing Group Members Adding Host Group Members from the Web UI Adding Host Group Members from the Command Line Identity: Managing Services Expand section " Identity: Managing Services" Collapse section " Identity: Managing Services" Adding and Editing Service Entries and Keytabs Expand section " Adding and Editing Service Entries and Keytabs" Collapse section " Adding and Editing Service Entries and Keytabs" Adding Services and Keytabs from the Web UI Adding Services and Keytabs from the Command Line Adding Services and Certificates for Services Expand section " Adding Services and Certificates for Services" Collapse section " Adding Services and Certificates for Services" Adding Services and Certificates from the Web UI Adding Services and Certificates from the Command Line Storing Certificates in NSS Databases Configuring Clustered Services Using the Same Service Principal for Multiple Services Disabling and Re-enabling Service Entries Expand section " Disabling and Re-enabling Service Entries" Collapse section " Disabling and Re-enabling Service Entries" Disabling Service Entries Re-enabling and Services Identity: Delegating Access to Hosts and Services Expand section " Identity: Delegating Access to Hosts and Services" Collapse section " Identity: Delegating Access to Hosts and Services" Delegating Service Management Delegating Host Management Delegating Host or Service Management in the Web UI Accessing Delegated Services Identity: Integrating with NIS Domains and Netgroups Expand section " Identity: Integrating with NIS Domains and Netgroups" Collapse section " Identity: Integrating with NIS Domains and Netgroups" About NIS and Identity Management Setting the NIS Port for Identity Management Creating Netgroups Expand section " Creating Netgroups" Collapse section " Creating Netgroups" Adding Netgroups Expand section " Adding Netgroups" Collapse section " Adding Netgroups" With the Web UI With the Command Line Adding Netgroup Members Expand section " Adding Netgroup Members" Collapse section " Adding Netgroup Members" Exposing Automount Maps to NIS Clients Migrating from NIS to IdM Expand section " Migrating from NIS to IdM" Collapse section " Migrating from NIS to IdM" Preparing Netgroup Entries in IdM Enabling the NIS Listener in Identity Management Exporting and Importing the Existing NIS Data Expand section " Exporting and Importing the Existing NIS Data" Collapse section " Exporting and Importing the Existing NIS Data" Importing User Entries Importing Group Entries Importing Host Entries Importing Netgroup Entries Importing Automount Maps Setting Weak Password Encryption for NIS User Authentication to IdM Identity: Integrating with Active Directory Through Cross-forest Trust Technology Preview Identity: Integrating with Microsoft Active Directory Through Synchronization Expand section " Identity: Integrating with Microsoft Active Directory Through Synchronization" Collapse section " Identity: Integrating with Microsoft Active Directory Through Synchronization" Supported Windows Platforms About Active Directory and Identity Management About Synchronized Attributes Expand section " About Synchronized Attributes" Collapse section " About Synchronized Attributes" User Schema Differences between Identity Management and Active Directory Expand section " User Schema Differences between Identity Management and Active Directory" Collapse section " User Schema Differences between Identity Management and Active Directory" Values for cn Attributes Values for street and streetAddress Constraints on the initials Attribute Requiring the surname sn Attribute Active Directory Entries and RFC Attributes Setting up Active Directory for Synchronization Expand section " Setting up Active Directory for Synchronization" Collapse section " Setting up Active Directory for Synchronization" Creating an Active Directory User for Sync Setting up an Active Directory Certificate Authority Managing Synchronization Agreements Expand section " Managing Synchronization Agreements" Collapse section " Managing Synchronization Agreements" Trusting the Active Directory and IdM CA Certificates Creating Synchronization Agreements Changing the Behavior for Syncing User Account Attributes Changing the Synchronized Windows Subtree Configuring Uni-Directional Sync Deleting Synchronization Agreements Winsync Agreement Failures Managing Password Synchronization Expand section " Managing Password Synchronization" Collapse section " Managing Password Synchronization" Setting up the Windows Server for Password Synchronization Setting up Password Synchronization Allowing Users to Change Other Users' Passwords Cleanly Identity: ID Views and Migrating Existing Environments to Trust Expand section " Identity: ID Views and Migrating Existing Environments to Trust" Collapse section " Identity: ID Views and Migrating Existing Environments to Trust" User Overrides and Group Overrides Managing ID Views on the Server Side ID Views on the Client Side Migrating from the Synchronization-Based to the Trust-Based Solution Identity: Managing DNS Expand section " Identity: Managing DNS" Collapse section " Identity: Managing DNS" About DNS in IdM Using IdM and DNS Service Discovery with an Existing DNS Configuration DNS Notes Adding or Updating DNS Services After Installation Setting up the rndc Service Managing DNS Zone Entries Expand section " Managing DNS Zone Entries" Collapse section " Managing DNS Zone Entries" Adding Forward DNS Zones Expand section " Adding Forward DNS Zones" Collapse section " Adding Forward DNS Zones" From the Web UI From the Command Line Adding Additional Configuration for DNS Zones Expand section " Adding Additional Configuration for DNS Zones" Collapse section " Adding Additional Configuration for DNS Zones" DNS Zone Configuration Attributes Editing the Zone Configuration in the Web UI Editing the Zone Configuration in the Command Line Adding Reverse DNS Zones Enabling and Disabling Zones Expand section " Enabling and Disabling Zones" Collapse section " Enabling and Disabling Zones" Disabling Zones in the Web UI Disabling Zones in the Command Line Enabling Dynamic DNS Updates Expand section " Enabling Dynamic DNS Updates" Collapse section " Enabling Dynamic DNS Updates" Enabling Dynamic DNS Updates in the Web UI Enabling Dynamic DNS Updates in the Command Line Configuring Forwarders and Forward Policy Expand section " Configuring Forwarders and Forward Policy" Collapse section " Configuring Forwarders and Forward Policy" Configuring Forwarders in the UI Configuring Forwarders in the Command Line Enabling Zone Transfers Expand section " Enabling Zone Transfers" Collapse section " Enabling Zone Transfers" Enabling Zone Transfers in the UI Enabling Zone Transfers in the Command Line Defining DNS Queries Synchronizing Forward and Reverse Zone Entries Expand section " Synchronizing Forward and Reverse Zone Entries" Collapse section " Synchronizing Forward and Reverse Zone Entries" Configuring Zone Entry Sync in the UI Configuring Zone Entry Sync in the Command Line Setting DNS Access Policies Expand section " Setting DNS Access Policies" Collapse section " Setting DNS Access Policies" Setting DNS Access Policies in the UI Setting DNS Access Policies in the Command Line Managing DNS Record Entries Expand section " Managing DNS Record Entries" Collapse section " Managing DNS Record Entries" Adding Records to DNS Zones Expand section " Adding Records to DNS Zones" Collapse section " Adding Records to DNS Zones" Adding DNS Resource Records from the Web UI Adding DNS Resource Records from the Command Line Expand section " Adding DNS Resource Records from the Command Line" Collapse section " Adding DNS Resource Records from the Command Line" About the Commands to Add DNS Records Examples of Adding DNS Resource Records Deleting Records from DNS Zones Expand section " Deleting Records from DNS Zones" Collapse section " Deleting Records from DNS Zones" Deleting Records with the Web UI Deleting Records with the Command Line Configuring the bind-dyndb-ldap Plug-in Expand section " Configuring the bind-dyndb-ldap Plug-in" Collapse section " Configuring the bind-dyndb-ldap Plug-in" Changing the DNS Cache Setting Disabling Persistent Searches Changing Recursive Queries Against Forwarders Resolving Hostnames in the IdM Domain Policy: Using Automount Expand section " Policy: Using Automount" Collapse section " Policy: Using Automount" About Automount and IdM Configuring Automount Expand section " Configuring Automount" Collapse section " Configuring Automount" Configuring NFS Automatically Configuring autofs Manually to Use SSSD and Identity Management Configuring Automount on Solaris Setting up a Kerberized NFS Server Expand section " Setting up a Kerberized NFS Server" Collapse section " Setting up a Kerberized NFS Server" Setting up a Kerberized NFS Server Setting up a Kerberized NFS Client Configuring Locations Expand section " Configuring Locations" Collapse section " Configuring Locations" Configuring Locations through the Web UI Configuring Locations through the Command Line Configuring Maps Expand section " Configuring Maps" Collapse section " Configuring Maps" Configuring Direct Maps Expand section " Configuring Direct Maps" Collapse section " Configuring Direct Maps" Configuring Direct Maps from the Web UI Configuring Direct Maps from the Command Line Configuring Indirect Maps Expand section " Configuring Indirect Maps" Collapse section " Configuring Indirect Maps" Configuring Indirect Maps from the Web UI Configuring Indirect Maps from the Command Line Policy: Defining Password Policies Expand section " Policy: Defining Password Policies" Collapse section " Policy: Defining Password Policies" About Password Policies and Policy Attributes Viewing Password Policies Expand section " Viewing Password Policies" Collapse section " Viewing Password Policies" Viewing the Global Password Policy Expand section " Viewing the Global Password Policy" Collapse section " Viewing the Global Password Policy" Viewing Group-Level Password Policies Expand section " Viewing Group-Level Password Policies" Collapse section " Viewing Group-Level Password Policies" Viewing the Password Policy in Effect for a User Creating and Editing Password Policies Expand section " Creating and Editing Password Policies" Collapse section " Creating and Editing Password Policies" Creating Password Policies in the Web UI Creating Password Policies with the Command Line Editing Password Policies with the Command Line Managing Password Expiration Limits Changing the Priority of Group Password Policies Setting Account Lockout Policies Expand section " Setting Account Lockout Policies" Collapse section " Setting Account Lockout Policies" In the UI In the CLI Enabling a Password Change Dialog Policy: Managing the Kerberos Domain Expand section " Policy: Managing the Kerberos Domain" Collapse section " Policy: Managing the Kerberos Domain" About Kerberos Expand section " About Kerberos" Collapse section " About Kerberos" About Principal Names About Protecting Keytabs Setting Kerberos Ticket Policies Expand section " Setting Kerberos Ticket Policies" Collapse section " Setting Kerberos Ticket Policies" Setting Global Ticket Policies Expand section " Setting Global Ticket Policies" Collapse section " Setting Global Ticket Policies" Setting User-Level Ticket Policies Refreshing Kerberos Tickets Caching Kerberos Passwords Removing Keytabs Policy: Using sudo Expand section " Policy: Using sudo" Collapse section " Policy: Using sudo" About sudo and IPA Expand section " About sudo and IPA" Collapse section " About sudo and IPA" General sudo Configuration in Identity Management sudo and Netgroups Supported sudo Clients Setting up sudo Commands and Command Groups Expand section " Setting up sudo Commands and Command Groups" Collapse section " Setting up sudo Commands and Command Groups" Adding sudo Commands Expand section " Adding sudo Commands" Collapse section " Adding sudo Commands" Adding sudo Commands with the Web UI Adding sudo Commands with the Command Line Adding sudo Command Groups Expand section " Adding sudo Command Groups" Collapse section " Adding sudo Command Groups" Adding sudo Command Groups with the Web UI Adding sudo Command Groups with the Command Line Defining sudo Rules Expand section " Defining sudo Rules" Collapse section " Defining sudo Rules" About External Users About sudo Options Format Defining sudo Rules in the Web UI Defining sudo Rules in the Command Line Suspending and Removing sudo Rules Configuring Hosts to Use IdM sudo Policies Expand section " Configuring Hosts to Use IdM sudo Policies" Collapse section " Configuring Hosts to Use IdM sudo Policies" Applying the sudo Policies to Hosts Using SSSD Applying the sudo Policies to Hosts Using LDAP Policy: Configuring Host-Based Access Control Expand section " Policy: Configuring Host-Based Access Control" Collapse section " Policy: Configuring Host-Based Access Control" About Host-Based Access Control Creating Host-Based Access Control Entries for Services and Service Groups Expand section " Creating Host-Based Access Control Entries for Services and Service Groups" Collapse section " Creating Host-Based Access Control Entries for Services and Service Groups" Adding HBAC Services Expand section " Adding HBAC Services" Collapse section " Adding HBAC Services" Adding HBAC Services in the Web UI Adding Services in the Command Line Adding Service Groups Expand section " Adding Service Groups" Collapse section " Adding Service Groups" Adding Service Groups in the Web UI Adding Service Groups in the Command Line Defining Host-Based Access Control Rules Expand section " Defining Host-Based Access Control Rules" Collapse section " Defining Host-Based Access Control Rules" Setting Host-Based Access Control Rules in the Web UI Setting Host-Based Access Control Rules in the Command Line Testing Host-Based Access Control Rules Expand section " Testing Host-Based Access Control Rules" Collapse section " Testing Host-Based Access Control Rules" The Limits of Host-Based Access Control Configuration Test Scenarios for Host-Based Access Control CLI-Based Testing Host-Based Access Control Rules in the UI Policy: Group Policy Object Access Control Expand section " |
| Select Your Language | Read more. March 14, What is teaming? Teaming or LACP NOTE: every clients speed can only be as high as the single link speed of one of the members. That means, if the interfaces I use in the bond have 1 Gigabit, every client will only have a maximum speed of 1 Gigabit. The advantage of teaming is, that it can handle multiple connections with 1 Gigabit. How many connections depends on the amount of your network cards. I'm using 2 network cards for this team on my server. That means I can handle 2 Gigabit connections at full rate on my server provided the rest of the hardware can deliver that speed. There also exists 'Bonding' in the Linux world. They both do the same in theory but for a detailed comparison check out this article about teaming in RHEL7. To create a teaming-interface, we will first have to remove all the interface configurations we've done on the soon to be sla. Push logs and data into elasticsearch - Part 2 Mikrotik Logs. August 16, Prerequesites: You'll need a working Elasticsearch Cluster with Logstash and Kibana. Start by getting the Log Data you want to structure parsed correctly. That means a message that the remote logging will send to Logstash will look like this: firewall,info forward: in:lan out:wan, src-mac aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff, proto UDP, The following is my example which might not fit your needs. may jun? FreeIPA - Integrating your DHCPD dynamic Updates into IPA. January 25, I recently went over my network configuration and noticed that the dhcp-leases were not pushed into the IPA-DNS yet. So I thought, why not do it now. The setup is very similar to setting it up on a single bind instance not managed by IPA I've already written a guide about this here. December November October September August July June May April March February January. List overview Download. ipsilon issues. Ipsilon, AWS and SAML2. Howard Johnson. Tuesday, 27 June Tue, 27 Jun '17 a. In Ipsilon, we recently OK, about a year ago added an authorisation stack. This allows us to control, Ipsilon-side, which users are permitted to log into which service providers. Our authorisation plugin functions are currently fairly limited, basically using user group membership to control which service providers a user has access to. One of the things we'd like to support is using FreeIPA's HBAC rules rather than user attributes directly. In my opinion, this makes it much more obvious what's going on and fits in better with FreeIPA's architecture. There're a few options that have come up in discussions around this on ipsilon and sssd: 1 Treat each service provider as a new service in FreeIPA. SSSD will then permit or deny the check based on the HBAC rules. This moves the HBAC check to the FreeIPA server, where the logic already exists. This requires Ipsilon to have access to the FreeIPA API and the appropriate login credentials. Moving the HBAC checks into FreeIPA itself has load implications for the IPA servers. This lets SSSD deal with connections to FreeIPA, including authentication and failover, which it's already doing. Some mechanism would be needed for Ipsilon to pass the "destination host" to SSSD for use in the HBAC check rather than the local IPA hostname. All of these options assume that there's an HBAC rule to permit the user to log in to the Ipsilon server itself via the "ipsilon" service, which we require now. Considering I'm writing this mail, it'll come as no surprise that I'm most interested in option 4. SSSD only fetches HBAC rules from FreeIPA that affect the local host unless the legacy src host option is enabled , so there'd need to be an option to enable fetching all rules instead. |
Video
Vogtle Part 2: Murphy’s Law
Ich wollte mit Ihnen reden, mir ist, was, in dieser Frage zu sagen.
Ich habe etwas versäumt?
ähnlich gibt es etwas?