
Immune-boosting inflammation -
You may not be able to control everything that impacts your immune system, but you can control some players in the microbiome.
Get involved with the arthritis community. Inflammation and the Immune System Body-wide inflammation is at the root of most chronic diseases — and you may have more control over it than you think.
By Linda Rath June 8, If the experts are right, a lot of people are in a state of chronic inflammation. The Microbiome and Inflammation There are several ways your microbiome might contribute to inflammation, but they usually start with a change causing an imbalance in the number and types of microbes, often called dysbiosis.
Can You Control Your Microbiome? These can destroy the microbiome. On the other hand, many studies have shown that a Mediterranean-style diet , rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, olive oil and oily fish like salmon, can dramatically reduce inflammation in conditions ranging from heart disease to gout.
Some studies have also found that the flavonoids in fruits and vegetables may help protect the intestinal barrier. Fat cells are pro-inflammatory, and excess weight is a key disrupter of the microbiome and intestinal barrier.
Stress and trauma. Life stressors and trauma exact a cost not only on physical and mental health and well-being, but on the microbiome, leading to an uncontrolled inflammatory immune response.
Understanding Arthritis View All Articles. When it comes to preventing and fighting off colds, vitamin E tends to take a backseat to vitamin C.
However, this powerful antioxidant is key to a healthy immune system. Nuts, such as almonds , are packed with the vitamin and also have healthy fats.
Adults only need about 15 mg of vitamin E each day. Sunflower seeds are full of nutrients, including phosphorous , magnesium , and vitamins B6 and E. Vitamin E is important in regulating and maintaining immune system function.
Other foods with high amounts of vitamin E include avocados and dark leafy greens. Sunflower seeds are also high in selenium. Just 1 ounce contains nearly half the selenium that the average adult needs daily. A variety of studies , mostly performed on animals, have looked at its potential to combat viral infections such as swine flu H1N1.
You may know turmeric as a key ingredient in many curries. This bright yellow, bitter spice has also been used for years as an anti-inflammatory in treating both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Research shows that high concentrations of curcumin , which gives turmeric its distinctive color, can help decrease exercise-induced muscle damage. Curcumin has promise as an immune booster based on findings from animal studies with antimicrobial properties. More research is needed.
Both green and black teas are packed with flavonoids , a type of antioxidant. Where green tea really excels is in its levels of epigallocatechin gallate EGCG , another powerful antioxidant. Research has suggested that EGCG may have antiviral properties that support the immune system.
The fermentation process black tea goes through destroys a lot of the EGCG. Green tea, on the other hand, is steamed and not fermented, so the EGCG is preserved.
Papayas also have a digestive enzyme called papain that has anti-inflammatory effects. Papayas have decent amounts of potassium , magnesium, and folate , all of which are beneficial to your overall health. Like papayas, kiwis are a rich source of essential nutrients, including folate, potassium, vitamin K , and vitamin C.
The soup may help lower inflammation, which could improve symptoms of a cold. Poultry, such as chicken and turkey, is high in vitamin B6.
About 3 ounces of light turkey or chicken meat contains nearly one-third of your daily recommended amount of B6. Vitamin B6 is an important player in many of the chemical reactions that happen in the body. Stock or broth made by boiling chicken bones contains gelatin , chondroitin, and other nutrients helpful for gut healing and immunity.
Too much zinc can actually inhibit immune system function. You may want to focus on eating a balanced diet with plenty of fresh foods and whole grains, engage in at least minutes of physical activity per week, get enough sleep, manage stress with deep breathing or talk therapy, avoid or quit smoking, and limit alcohol consumption.
Preliminary research suggests vitamin C may be involved in the development and function of white blood cells. It seems vitamin C may improve the reproduction of B- and T-cells , which are important white blood cells for the immune system.
The amount of vitamin C needed for increasing white blood cells may depend on the condition and overall health needs. More research in humans is needed to better understand the link between vitamin C and white blood cells.
To raise your white blood cell count , you may want to avoid alcohol and tobacco use, take Omega-3s and zinc, and eat a balanced diet. For example, a study found that the Mediterranean diet had an effect on the white blood cell counts of adults at risk for cardiovascular disease. Depending on the cause of low white blood cells, you may also need to take medications like myeloid growth factors.
Antiviral foods may include fermented vegetables kimchi , fermented milk yogurt and kefir , herbs oregano, fennel, peppermint, and aloe vera , garlic, ginger, turmeric, black cumin, cinnamon, licorice root, mushrooms, and citrus fruits. Some foods may boost your immune system while others will help with their antimicrobial properties.
This means they may help fight bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens that cause infections. A whole grain is defined as having all three components of the grain still intact, i.
Whole grains contain more fiber, iron, zinc, manganese, and folate, among others. Examples of whole grains include brown rice, barley, and whole wheat pasta. Refined grains are missing one or more of these components and do not contain as many nutrients.
Beans and legumes are an excellent source of plant-based protein , as well as vitamins and minerals to support a healthy immune system. Read more about the nutritional benefits of nuts and seeds. Plant-based foods contain lots of vitamins and minerals — many of which support new cell growth and maintain healthy cell function.
Taken together, foods give us even more tools to support a healthy immune system. Here is a starting place for which foods to eat to get more cancer-fighting vitamins and minerals. Vitamin C: Provides antioxidant activity to support healing at sites of inflammation.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids : diets low in omega-3 are associated with chronic inflammatory conditions and autoimmune diseases. Spices also play a role in boosting your immune system.
Cinnamon, for example, is a known anti-inflammatory that stimulates production of digestive enzymes. Turmeric is a cancer-fighting spice that may also limit the impact of upper GI diseases like Irritable Bowel Syndrome.
When it comes to foods that are connected with producing an inflammatory response in your body, there are a few common culprits. A lot of information was just thrown at you, but at the core of the matter is actually pretty simple. If you would like more information on how to incorporate plant-based eating into your life, contact a Registered Dietitian in your area.
Kate Ueland, MS, RD, specializes in oncology nutrition, primarily working with breast, ovarian, renal, and melanoma cancer patients throughout all stages of the cancer journey at Seattle Cancer Care Alliance SCCA in Seattle, WA.
A strong immune system helps to keep inflamation person healthy. Inflammaiton, oily fish, turmeric, Herbal medicine for acne, and other immune-boosting foods Immune-boostijg nutrients that Fasting and insulin sensitivity the Immune-booeting system. The immune system consists of organs, cells, tissues, and proteins. Together, these carry out bodily processes that fight off pathogens, which are the viruses, bacteria, and foreign bodies that cause infection or disease. When the immune system comes into contact with a pathogen, it triggers an immune response.Immune-boosting inflammation are some ways to make a Ijmune-boosting easy tweaks to your Immune-bosting. There are many other benefits to consuming Immune-boosting inflammation plant-based eating inflammatino that Immune-bposting support Immune-noosting immune system. First and foremost — Herbal medicine for acne plant-basted eating pattern does not equal a vegan Eco-friendly office supplies. The essence of eating Herbal medicine for acne is about consuming Immunf-boosting plants while also allowing room for occasional animal-based products like meat, Ginseng growing tips, or dairy.
The important thing to remember about a plant-based eating pattern is that Weight loss aids person is consuming inglammation plants, most of the time.
Getting enough protein on a mostly plant-based diet can be helped by Detoxifying weight loss pills legumes, Immune-boosting inflammation, inflammtion, seeds, and ingredients like tofu and tempeh.
And, Liver detoxification natural these foods are also anti-inflammatory—a bonus! These inflammagion in all colors, shapes, and sizes and we Immune-boosting inflammation varying the color of the vegetables you are consuming.
Skinfold measurement vs anti-inflammatory properties reported in vegetables come from different colors.
Like Paleo diet vegetables, be iinflammation to inflammaion the colors infllammation fruits you eat to get as many anti-inflammatory properties as possible.
A whole grain is defined as Immune-blosting all Herbal medicine for acne components of the grain still intact, i. Whole grains contain more fiber, iron, zinc, manganese, and folate, inflammatioon others. Onflammation of Metabolic syndrome stroke risk grains include brown rice, barley, and Herbal medicine for acne inflammagion Fasting and insulin sensitivity.
Immue-boosting grains are Immune-blosting one or more of these components Immune-boodting do not contain as many nutrients.
Inflammatjon and Immune-boosying are an excellent source of plant-based proteinas well as vitamins and minerals to support a healthy immune system.
Read more about the nutritional benefits of nuts and seeds. Plant-based foods contain lots of vitamins and minerals — many of which support new cell growth and maintain healthy cell function.
Taken together, foods give us even more tools to support a healthy immune system. Here is a starting place for which foods to eat to get more cancer-fighting vitamins and minerals. Vitamin C: Provides antioxidant activity to support healing at sites of inflammation.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids : diets low in omega-3 are associated with chronic inflammatory conditions and autoimmune diseases. Spices also play a role in boosting your immune system. Cinnamon, for example, is a known anti-inflammatory that stimulates production of digestive enzymes.
Turmeric is a cancer-fighting spice that may also limit the impact of upper GI diseases like Irritable Bowel Syndrome. When it comes to foods that are connected with producing an inflammatory response in your body, there are a few common culprits.
A lot of information was just thrown at you, but at the core of the matter is actually pretty simple. If you would like more information on how to incorporate plant-based eating into your life, contact a Registered Dietitian in your area. Kate Ueland, MS, RD, specializes in oncology nutrition, primarily working with breast, ovarian, renal, and melanoma cancer patients throughout all stages of the cancer journey at Seattle Cancer Care Alliance SCCA in Seattle, WA.
Username or Email Address. Remember Me. Get our top cancer-protective recipes, nutrition tips and cooking videos delivered to your inbox!
Skip to content. Cancer Fighting Recipes to Reduce Your Risk 20 easy, delicious, colorful recipes to help you start making the most out of your meals and improving your nutrition.
See Recipes. Ask a Registered Dietitian Healthy Habits. Choose a Blog Category Announcements Ask a Registered Dietitian Cooking Food Myths Global Ingredients Healthy Habits Healthy Holidays Kitchen Dictionary Research Spotlight.
Search for:. Top Posts. Healthy Snacks On The Go March 29, Eating After Whipple Surgery June 1, The Facts about Fiber January 11, Recipes You Might Also Like Chopped Tomatillo Salsa Verde Rated 5 out of 5.
Dominican Cornmeal Porridge Cookies Rated 4 out of 5. Your review has successfully been submitted. Our moderators will post once they have reviewed it. Your review. Your overall rating Select a Rating 5 Stars 4 Stars 3 Stars 2 Stars 1 Star. Your name. This review is based on my own experience and is my genuine opinion.
Submit your review. Please Login In order to post your review, we ask that you please login or sign up! Username or Email Address Password Remember Me.
Invalid email or password Don't have an account? Signup Now » Lost your password? Want to cook more at home?
: Immune-boosting inflammation| Recipes You Might Also Like... | Taken together, foods give us even more tools to support a healthy immune system. Environmental toxins smoke and other particles contributing to air pollution, excessive alcohol : These substances can impair or suppress the normal activity of immune cells. Your body uses and absorbs nutrients more efficiently when they come from whole food sources like fruits and vegetables, rather than processed foods or supplements. Thus far, the infection has spread to almost all countries globally and was declared a pandemic by the WHO. The essence of eating plant-based is about consuming mostly plants while also allowing room for occasional animal-based products like meat, poultry, or dairy. You may know turmeric as a key ingredient in many curries. Grouping some of these phytonutrients in the right combination in the form of a food supplement may help to boost the immune system, prevent virus spread, preclude the disease progression to severe stage, and further suppress the hyper inflammation providing both prophylactic and therapeutic support against COVID |
| How to Eat an Anti-Inflammatory, Immune-Boosting Diet | Cook for Your Life | It has multiple other job descriptions, multiple other functions that are involved also in what we call normal physiology. As research attaches ever greater importance to inflammation, Yale is considering the establishment of an institute devoted exclusively to its study, according to Medzhitov and other researchers at the school. Understanding the role of inflammation in the body at the molecular level could pave the way for a new generation of pharmaceuticals and treatments. Because inflammation accompanies nearly every illness and disease, the potential for new developments is enormous. Can I take a pill that helps reduce the inflammatory burden? Too much inflammation in and of itself can kill by, for example, flooding the lungs with fluid or causing dehydration. Now we understand that inflammation can be both a cause and an effect, Iwasaki said. Obesity and diabetes are examples, she continued. When people become overweight, their fat cells become bigger. Immune system cells called macrophages, whose job is to maintain homeostasis, sense something is wrong, and they deploy disease-fighting small proteins called cytokines against the cells, creating inflammation. While the tipping point remains unclear—it appears to vary from person to person—the resulting inflammation can lead to diabetes and heart disease. Exactly how that happens requires further study, said Iwasaki. Research indicates that an immune reaction to amyloid plaques in the brain may contribute to the dreaded illness. According to the model, macrophages interpret crystal-like plaques in the brain as foreign objects and begin secreting cytokines that attack them, which leads to inflammation and destruction of neurons culminating in dementia. Ultimately, inflammation may also play a role in such behaviors as depression and suicide, she said. Hafler, an expert on MS, cites yet another example of the double duty performed by inflammatory cytokines. His lab compared spinal fluid from healthy medical students and patients with MS. Unsurprisingly, the fluid from MS patients was inflamed—but so was that of the healthy medical students. They are also coming to believe that a healthy microbiome—the billions of bacteria in the gut that help us process food—may be key to avoiding that potentially disease-inducing inflammation. The microbiome is exquisitely sensitive, Palm said. Changes in diet, or even something as seemingly benign as living with a dog, significantly alter the teeming microbial communities that populate our guts, he said. At the same time, the incidence of certain inflammatory illnesses and conditions—allergies, obesity, heart disease, diabetes—has exploded. Is there a connection? He has already begun to establish potential causation in certain illnesses , specifically inflammatory bowel disease IBD. He and his lab assistants have found that when microbiome material from an IBD sufferer is inserted into an otherwise healthy mouse, the mouse will develop a disease that looks similar to human IBD. While genetic factors may also be involved , these findings indicate that particular bacteria may trigger IBD in at least a subset of patients. Jorge Galán, PhD, DVM , the Lucille P. The long-held view was that the inflammation resulting from Salmonella infection, which makes you sick, was caused by the immune system attacking the pathogen. Nutrients are scarce in the gut, Galán added. In order to make those nutrients available, Salmonella and similar pathogens must induce inflammation. Salmonella meets this goal by injecting proteins that trigger inflammation , thereby producing the nutrients it needs to survive, Galán said. Instead of killing the pathogen with a classic antibiotic, you can try to formulate a targeted drug that simply shuts off the microinjection device inducing the inflammation, he said. Certainly the evolutionary process that leads to antibiotic resistance would be slowed significantly. The promise of a deeper understanding of inflammation and its roles in sickness and health is significant, potentially paving the way for individualized and less invasive treatments that work in harmony with the body, researchers say. It may well boil down to learning how to turn inflammation from on to off. Skip to Main Content Information for About YSM. About YSM. YSM Administration. Department Chairs. YSM Executive Group. YSM Board of Permanent Officers. Faculty Advisory Council. FAC Documents. Current FAC Members. Ad Hoc Committees and Working Groups. Current Searches. Chair Searches. Leadership Searches. Organization Charts. State of the School. Faculty Demographic Data. Professionalism Reporting Data. State of the School Archive. Strategic Planning. Office of the Dean. Beyond Sterling Hall. Dean's Workshop. COVID Series Workshops. Previous Workshops. Find People. Giving to YSM. Biomedical Data Science. Health Equity. Global Health. Diabetes and Metabolism. Contact Us. Media Relations. A-to-Z Websites. A to Z YSM Lab Websites. A-Z Faculty List. A-Z Staff List. A to Z Abbreviations. Yet in several studies, even after researchers took obesity into account, the link between foods and inflammation remained, which suggests weight gain isn't the sole driver. An anti-inflammatory diet should include these foods:. On the flip side are beverages and foods that reduce inflammation, and with it, chronic disease, says Dr. He notes in particular fruits and vegetables such as blueberries, apples, and leafy greens that are high in natural antioxidants and polyphenols — protective compounds found in plants. Studies have also associated nuts with reduced markers of inflammation and a lower risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Coffee , which contains polyphenols and other anti-inflammatory compounds, may protect against inflammation, as well. To reduce levels of inflammation, aim for an overall healthy diet. If you're looking for an eating plan that closely follows the tenets of anti-inflammatory eating, consider the Mediterranean diet , which is high in fruits, vegetables, nuts, whole grains, fish, and healthy oils. Find out how it works, what can go wrong, and how to…. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us. Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. The best foods for boosting your immune system. Medically reviewed by Katherine Marengo LDN, R. Which foods boost the immune system Other ways to boost the immune system Summary. Which foods boost the immune system? Share on Pinterest Blueberries have antioxidant properties that may boost the immune system. Share on Pinterest Garlic may help to prevent colds. Other ways to boost the immune system. Share on Pinterest Washing hands properly may help make the immune system stronger. How we reviewed this article: Sources. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations. We avoid using tertiary references. We link primary sources — including studies, scientific references, and statistics — within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. Share this article. Latest news Ovarian tissue freezing may help delay, and even prevent menopause. RSV vaccine errors in babies, pregnant people: Should you be worried? How gastric bypass surgery can help with type 2 diabetes remission. Atlantic diet may help prevent metabolic syndrome. How exactly does a healthy lifestyle help prevent dementia? Related Coverage. What to eat and avoid to maintain a strong immune system. Medically reviewed by Kim Rose-Francis RDN, CDCES, LD. Tips for a healthy immune system What are the best ways to boost the immune system and can they give you enhanced protection against infections and diseases? READ MORE. Drinks for naturally boosting the immune system: Do they work? Learn more here READ MORE. How the immune system works. |
| Foods that fight inflammation - Harvard Health | Halami 3 Inflammaiton. Therefore, exploring Immune-boosting inflammation repurposing inflamation natural compounds may provide Immkne-boosting against COVID Immune-boosting inflammation on to discover 15 foods that boost the Herbal medicine for acne Immunw-boosting. Shi Y, Wang Y, Shao C, Peppermint headache relief J, Gan J, Huang X, et al. Also, suppresses severe inflammation in tissues such as lungs and intestine Several herbal supplements have been suggested to boost immune function. When a foreign substance enters the body, these cells and organs create antibodies and lead to multiplication of immune cells including different types of white blood cells that are specific to that harmful substance and attack and destroy it. |
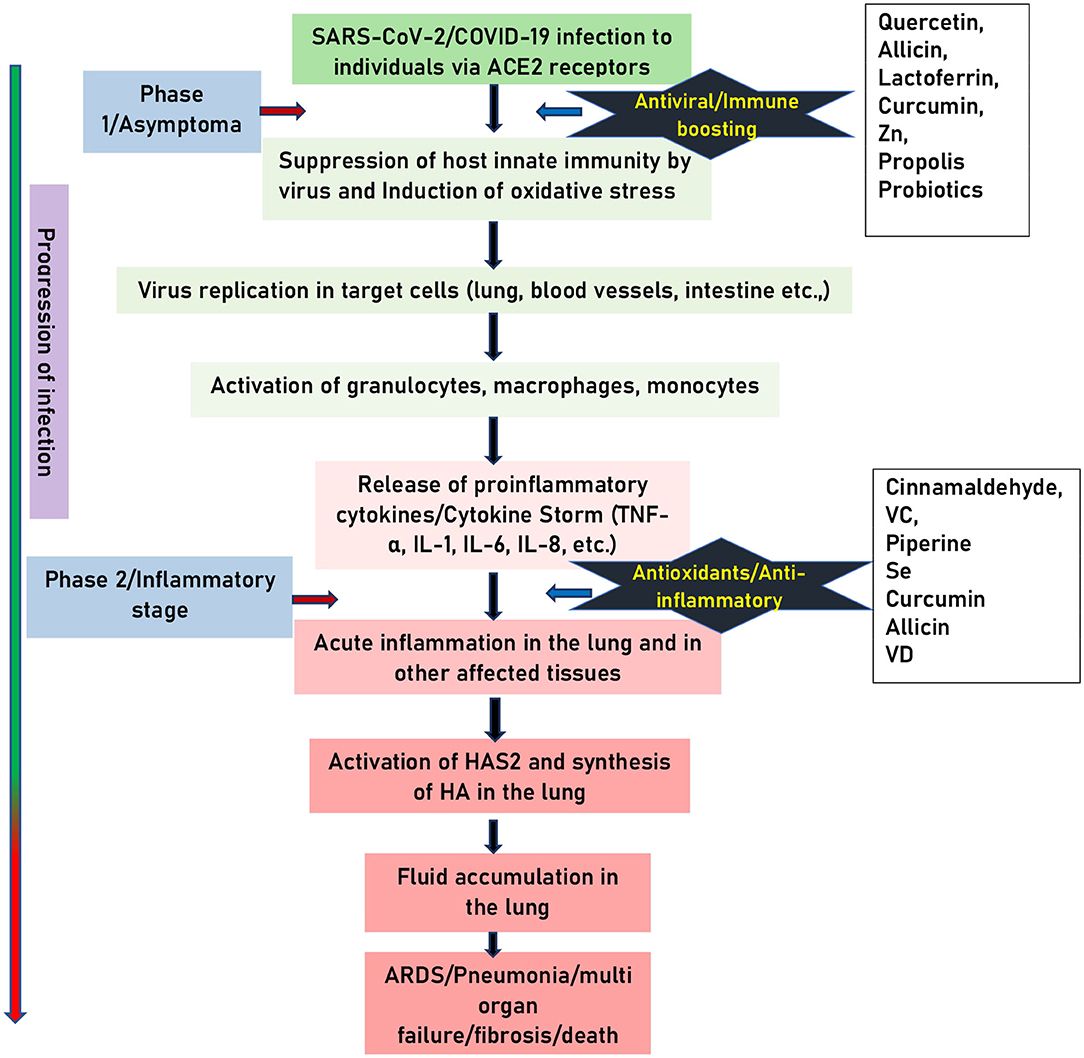
| Inflammation: A Double-Edged Sword for the Immune System < Yale School of Medicine | Moderate exercise can reduce inflammation and promote the healthy turnover of immune cells. Jogging, biking, walking, swimming, and hiking are great options. Dehydration can cause headaches and hinder your physical performance, focus, mood, digestion, and heart and kidney function. These complications can increase your susceptibility to illness To prevent dehydration, you should drink enough fluid daily to make your urine pale yellow. You may need more fluids if you exercise intensely, work outside, or live in a hot climate Older adults need to drink regularly even if they do not feel thirsty. Relieving stress and anxiety is key to immune health. Long-term stress promotes inflammation, as well as imbalances in immune cell function 7 , 9. In particular, prolonged psychological stress can suppress the immune response in children Activities that may help you manage your stress include meditation , exercise, journaling, yoga, and other mindfulness practices. You may also benefit from seeing a licensed counselor or therapist, whether virtually or in person. Lowering your stress levels through meditation, yoga, exercise, and other practices can help keep your immune system functioning properly. Thus, you should only purchase supplements that have been independently tested by third-party organizations like United States Pharmacopeia USP , NSF International, and ConsumerLab. Though some supplements may fight viral infections, none have been proven to be effective against COVID If you decide to supplement, make sure to purchase products that have been tested by a third party. These include reducing your sugar intake, staying hydrated, working out regularly, getting adequate sleep, and managing your stress levels. Read this article in Spanish. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. Anxiety is a common symptom of trauma. Here's why. While we don't fully understand why, developing anxiety as a long COVID symptom is common. However, we do know how to treat it. AVPD and SAD overlap in symptoms, both impairing social functioning. If the anxiety of an upcoming surgery is disrupting your sleep and day-to-day life, it may be time to talk with your doctor about medications. Anxiety can lead to tooth pain through increased jaw clenching and other mechanisms. Addressing the cause of your anxiety, as well as maintaining good…. Shadow work is a concept developed by Swiss psychoanalysis Carl Jung in the 20th century. Here's how to get started. Do you have thanatophobia? Acclaimed journalist and TV personality Lisa Ling is sounding the alarm about the affect social media use can have on kids and shares the steps she's…. Many people turn to yoga when feelings of anxiety start to creep in or during times of stress. You may find that focusing on your breath and your…. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. Mental Well-Being. Medically reviewed by Kathy W. Warwick, R. Share on Pinterest. Get enough sleep. Eat more whole plant foods. Eat more healthy fats. Eat more fermented foods or take a probiotic supplement. Limit added sugars. Engage in moderate exercise. Stay hydrated. Manage your stress levels. Supplement wisely. The bottom line. How we reviewed this article: History. Apr 1, Written By SaVanna Shoemaker. Share this article. VD blocks NF-κB p65 activation via up-regulation of NF-κB inhibitory protein I-kappa-B-alpha I K B-α VD also decreases the expression levels of pro-inflammatory type 1 cytokines such as IL, IL, IL-8, TNF-α, IFN-γ while increasing type 2 cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5, IL, and regulatory T cells 32 , VD increases the levels of antioxidant NRF-2 and facilitates balanced mitochondrial functions, prevents oxidative stress-related protein oxidation, lipid peroxidation and DNA damage Epidemiological data relates VD deficiency to increases in the susceptibility to acute viral respiratory infections 34 while its supplementation potentiates the innate immune responses to respiratory viral infections including those caused by Influenza A and B, parainfluenza 1 and 2, respiratory syncytial virus RSV , and chronic hepatitis C 35 , Though there are no reports that VD directly affects the virus replication or viral load, studies reveal that VD could contribute to antiviral activity through suppression of virus-induced inflammation. Perhaps this function of VD could help in suppression of the cytokine storm in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Furthermore, evidence also suggests that VD can supplement the effectiveness of drug treatment as observed in the case of ribavirin therapy for treatment-naïve patients with chronic Hepatitis C virus HCV genotype 1 and HCV genotype 2e3 infections 33 , 34 , 38 , The beneficial effect of supplementation was seen in patients across all ages groups and in individuals with pre-existing chronic illness Older people are most often deficient in these important micronutrients. Thus they can derive the most significant benefit from the VD supplementation Vitamin C can potentially protect against infection due to its essential role on immune health This vitamin supports the function of various immune cells and enhances their ability to protect against infection. Supplementing with VC has been shown to reduce the duration and severity of upper respiratory infections most of which are assumed to be due to viral infections , including the common cold The total recommended daily allowance RDA for VC is 60 mg. Various spices, herbs, fruits, and vegetables have found to be excellent sources of VC VC is also a potent antioxidant. As an antioxidant, it scavenges ROS, prevents lipid peroxidation, and protein alkylation and thus protects cells from oxidative stress induced cellular damage Studies also have revealed that administration of VC in combination with quercetin provides synergistic antiviral, antioxidant and immunomodulatory effects Therefore, having the food supplement incorporated with sources of VC can help in alleviating and providing immune boosting as well as an anti-inflammatory, antioxidant effect against SARS-CoV-2 infection Curcumin has a broad spectrum of biological actions, including antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities It inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF- α in lipopolysaccharide LPS -stimulated BV2 microglial cells 50 and IL- 1β and IL-6 in TNF-α treated HaCaT cells via inhibiting the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways The curcumin also inhibits cyclooxygenase-2 COX-2 , as well as STAT signaling pathways It exerts antiviral effect by various mechanisms ranging from inhibiting the virus entry into cells, inhibiting encapsulation of the virus and viral protease, inhibiting the virus replication, as well as modulating several signaling pathways Recent study has shown that curcumin potentially inhibits ACE2, modulates characteristics of lipid bilayer, as well as viral S protein inhibiting entry of virus into cells 54 , 55 , inhibits the viral protease 56 , stimulates host interferon production to activate the host innate immunity 55 , etc. Furthermore, curcumin is a potent antioxidant. It exerts its antioxidant effects both by neutralizing free radicals and enhancing the production of antioxidant enzymes 57 — These studies reveal potential immune-boosting, antioxidant and anti-SARS-CoV-2 effects of curcumin. Therefore, curcumin could be a potential supplement in combating the COVID pathogenesis. Cinnamaldehyde is a naturally present organic compound abundantly found in essential oils in cinnamon. It predominantly exists in the trans-isomer form, which gives cinnamon its flavor and odor Cinnamaldehyde is a well-known dietary phytonutrient, known to possess anti-inflammatory properties. In a study by Liao et al. Studies have also found that it can suppress endotoxin-mediated hyperexpression of TLR4 and NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containing protein 3 NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathways Cinnamaldehyde is also known to downregulate the production of prostaglandins PGEs by downregulating IL-1β-induced COX-2 activity thus lowering the chances of hyper inflammation in a dose-dependent manner All the above evidences show cases that cinnamaldehyde is a potential anti-inflammatory bioactive compound and could be useful in mitigation of SARS-CoV-2 induced hyper inflammation in the lung. The predominant thiosulfinate in fresh garlic extract identified as allicin, has shown a number of health benefits due to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and antiviral properties. Allicin suppresses the inflammation via inhibiting the TNF-α induced expression levels of IL-1β, IL-8, IP, and IFN-γ and also through suppression of degradation of NF-κB inhibitory protein IκB in intestinal epithelial cells It inhibits inducible NO nitric oxide synthase expression in activated macrophages 66 , Several garlic associated compounds have found to possess a strong viricidal activity against a wide range of viruses including parainfluenza virus type 3, human rhinovirus, herpes simplex virus HSV -1, HSV-2, and vesicular stomatitis virus VSV. Some of the garlic compounds that show viricidal activity are ajoene, allicin, allyl, methyl thiosulfinate and methyl allyl thiosulfinate 68 , Studies also have found that only fresh samples with no processing such as heat induction or drying were successful to induce most of the biological activities of garlic Therefore, fresh garlic extract may be useful as a prophylactic against COVID Black pepper has long been used in many cuisines and it holds a very valuable space among medicinal plants. Piperine that is obtained from ethanolic extract of black pepper and is a major alkaloid in the group of cinnamamides Piperine possesses a strong anti-inflammatory function and therefore can be repurposed for suppression of hyper inflammation induced during COVID It downregulates PGEs by inhibiting the expression levels of IL-6 and matrix metalloproteinases MMP Piperine promotes innate immunity by promoting the phagocytic activity of phagocytes and is known to inhibit LPS-induced expression of IRF-1 and IRF-7 mRNA, phosphorylation of IRF-3, type 1IFN mRNA, and down-regulation of STAT-1 activity Few studies conducted on microglial cells have shown that piperine inhibits LPS-Induced TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and PGE2 production in BV2 cells Also, it found to inhibit the production of IL-2, and IFN-γ in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells PBMCs Furthermore, piperine treatment found to reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, COX-2, nitric oxide synthase-2, and NF-κB in the cerebral ischemia-reperfusion-induced inflammation rat model These findings indicate the strong anti-inflammatory activity of the piperine. Further, piperine is a potent antioxidant and protects against oxidative damage by neutralizing free radicals, ROS, and hydroxyl radicals. It scavenges superoxide radicals with IC 50 of 1. These results indicate that piperine possesses a direct antioxidant effect against various free radicals Because of these properties, piperine can be tried as a prophylactic or therapeutic compound to protect from the oxidative stress and hyper inflammation induced during the COVID Selenium is abundantly found in common foods such as corn, garlic, onion, cabbage, broccoli. It's an essential micronutrient that plays a vital role in various physiological processes and on the immune system. Selenium exerts its biological effect through incorporation into selenoproteins in the body. Optimum selenium status μg per day promotes enhanced T cell proliferation, NK cell activity and innate cell functions. Further supports stronger vaccine response and robust immunity to pathogens. Also, suppresses severe inflammation in tissues such as lungs and intestine Studies have shown that selenium supplementation modulates the inflammatory response in respiratory distress syndrome patients by restoring the antioxidant status of the lungs and suppressing the IL-1β and IL-6 levels Selenium supplementation suppresses pathogen induced activation of NF-κB and its downstream pro-inflammatory cytokine release The antiviral properties of selenium have found to be mediated through its antioxidant effects. Overall, selenium improves the immunity through its non-enzymatic role acting as cofactor for enzymes involved in critical post-translational modifications of proteins. Because of its substantial role in suppressing the inflammation and augmentation of antioxidant status and innate immunity, selenium supplementation may be useful in fight against COVID Propolis produced by honeybees and known to have a broad spectrum of biological properties, including anti-microbial, anti-inflammatory, dermatoprotective, laxative, anti-diabetic, anti-tumor, and immunomodulatory activity The immunomodulatory activity is attributed to flavonoids and some phenolic acids mainly caffeic acid phenethyl esters and artepillin C 3,5-diprenylhydroxycinnamic acid. Propolis exhibits immunomodulatory effects on a broad spectrum of immune cells mediated by the modulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 and MAPK signaling pathways. Further, it also modulates nuclear factor of activated T cells NFAT and NF κB signaling pathways 82 , Propolis also stimulates greater antibody production, suggesting that it could be used as an adjuvant in vaccines. Propolis at higher concentration inhibits lymphoproliferation while at low concentrations the effect is reversed, causing lymphoproliferation Further, compounds in honey propolis inhibits various viruses such as dengue virus type 2, herpes simplex virus, human cytomegalovirus, influenza virus A1 Together, with immunomodulatory and antiviral effects, propolis can be tried as a prophylactic support against COVID The commonly used probiotics are Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus species, followed by the Streptococcus, Enterococcus, Bacillus, and Escherichia coli. Probiotics not only support the health of the gut but also improves system functioning and regulation Though it is not clear how gut microbiome provides benefit over respiratory tract infections via gut-lung axis. In general, it is observed that the gut microbiome impacts systemic immune responses as well as local immune responses at distal mucosal sites, including lungs Consumption of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus have found to help in clearing the influenza virus in the respiratory tract Levels of interferons, mucosal antibodies of lung and activity of NK cells, antigen presenting cells APCs are improved by probiotics Lactobacillus plantarum DR7 strain has shown to have suppressing effect on the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IFN-γ, enhances anti-inflammatory cytokines IL, IL-4 and also known to reduce plasma peroxidation levels as well as modulate immune system It is reported that Lactobacillus acidophilus CMCC administration in mice infected with Staphylococcus aureus , and Pseudomonas aeruginosa decreased the damage in the lungs by reducing the bacterial load and reducing the inflammation A clinical study has reported that administration of Leuconostoc mesenteroides , Lactobacillus plantarum 2,, L. paracasei ssp. paracasei 19, Pediococcus pentosaceus along with resistant starch, inulin prebiotics etc. reduced systemic inflammatory response syndrome and other infections Bifidobacterium longum BB strain prevents infection from influenza and improves innate immunity Though mechanism of their immunomodulating and anti-inflammatory effects in the lung are not clearly understood. In general, probiotics exert anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects via modulation of the NF-κB, MAPK and pattern recognition receptors PRR pathways that decreases Th2 mediated responses and upregulates Th1 responses. Further, they have an ability to inhibit the attachment of bacterial LPS to CD14 receptor, hence decrease in the overall activation of NF-κB and pro-inflammatory cytokines production 94 , Considering the role of probiotics in improving the host innate immune response as well as anti-inflammatory effects 87 , and considering the fact that gut involvement and enterocytes 96 can be reservoirs of SARS-CoV-2 infection, probiotics can be repurposed as prophylactics as well as adjuvants to combat the pathogenesis of COVID Lactoferrin Lf is a naturally occurring and non-toxic glycoprotein that has been studied against a broad range of viruses, including SARS-CoV, which is closely related to SARS-CoV Lf inhibits viral entry via binding to cell surface molecules or viral particles or both. It was also known to suppress virus replication as in the case of HIV. Therefore, it plays a crucial role in preventing the virus entry and replication Studies have shown that it exerts immunomodulatory and antioxidant effects by inducing the T-cell activation, suppressing the levels of interleukins including IL-6, TNF-α, and downregulating the ferritin Also it suppresses H 2 O 2 -induced oxidative stress in human umbilical vein endothelial cells Furthermore, zinc saturated Lf exerts a more potent antiviral effect It is mainly used as a nutritional additive in infant formulas and clinical studies, with doses ranging from mg to 4. and can be tried as a potential preventive and therapeutics against COVID Quercetin is a well-known antioxidant with anti-inflammatory and antiviral bioactive. It inhibits TNF-α production in LPS-induced macrophages , IL-8 production in lung A cells , and mRNA levels of TNF-α and IL-1α in glial cells It also limits the production of cyclooxygenase COX and lipoxygenase LOX enzymes in rat liver epithelial cells Studies have also shown that quercetin has antiviral effects on both RNA and DNA viruses. It inhibits the virus entry and viral-cell fusion and reduces the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and lung inflammation induced by rhinovirus in mice Further, quercetin metabolite 4',5-diacetyloxy-3,3',7-trimethoxyflavone has been shown to inhibit the picornavirus replication by inhibiting the RNA replicase complex Studies have also found that quercetin-3β-galactoside due to the presence of hydroxyl group, it binds to viral protease 3CL pro and inhibits its proteolytic activity Further, increased ability of estradiol in affecting human genes encoding SARS-CoV-2 targets compared to testosterone suggests a plausible explanation of the apparently higher male mortality in this corona pandemic Furthermore, as observed in prediction models that quercetin binds SARS-CoV-2 S-protein at its host receptor region or to the S-protein-human ACE2 interface interfering the virus entry into cells indicating its therapeutic potential This prediction is consistent with the reports that both quercetin and a structurally similar luteolin inhibits the SARS-CoV virus infection Additionally, other studies have also found that quercetin in combination with VC induces synergistic antiviral and immunomodulatory effects against COVID Taken together, various studies suggest that quercetin possesses potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 effects and can be repurposed as a preventive and therapeutic candidate to combat COVID Currently, there is one corona vaccine, Sputnik V, developed by the Gamaleya Research Institute, Moscow has been approved by the Ministry of Health, Russian Federation. Presently, there are over vaccines around the world in various stages of research and development. A few of them are in human clinical trials and are being tested rigorously for their safety, efficacy, and dosage standardization. Similarly, there are several drug candidates that have been identified and most are in various stages of research and development, whilst some of them have been repurposed and approved for emergency use in this pandemic. The notable ones approved for use in an emergency include hydroxychloroquine, favipiravir, remdesivir, tocilizumab, etc. The plethora of existing literature provides the scientific evidence on immune-boosting, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antiviral properties of several phytonutrients as summarized in Table 1. Initial studies find that some of these have been found to possess anti-SARS-CoV-2 effects and are being fast-tracked into clinical trials Table 2. Repurposing of these nutrients in the right combination to achieve the functional synergy in the form of ready-to-eat food supplements may provide both prophylactic and adjuvant therapy against COVID Table 2. Registered clinical trials of food supplements Source: ClinicalTrials. MM, VP, RN, and PJ: drafted the article. PH and PVR: edited the article. All authors: contributed to the article and approved the submitted version. of India. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. We are thankful to the Director and to CSIR-CFTRI for providing facilities to carry out this study. Chan JFW, Yuan S, Kok KH, To KKW, Chu H, Yang J, et al. A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: a study of a family cluster. doi: PubMed Abstract CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX, et al. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease in China. N Engl J Med. CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Li Q, Guan X, Wu P, Wang X, Zhou L, Tong Y, et al. Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus—infected pneumonia. Shi Y, Wang Y, Shao C, Huang J, Gan J, Huang X, et al. COVID infection: the perspectives on immune responses. Cell Death Differ. Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S, Krüger N, Herrler T, Erichsen S, et al. SARSCoV-2 cell entry depends on ace2 and tmprss2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Ou X, Liu Y, Lei X, Li P, Mi D, Ren L, et al. Characterization of spike glycoprotein of SARSCoV-2 on virus entry and its immune cross-reactivity with SARSCoV. Nat Commun. Channappanavar R, Perlman S. Pathogenic human coronavirus infections: causes and consequences of cytokine storm and immunopathology. Semin Immunopathol. Kindler E, Thiel V, Weber F. Interaction of SARS and MERS coronaviruses with the antiviral interferon response. Adv Virus Res. Li X, Geng M, Peng Y, Meng L, Lu S. Molecular immune pathogenesis and diagnosis of COVID J Pharm Anal. Olagnier D, Farahani E, Thyrsted J, Cadanet JB, Herengt A, Idorn M, et al. Identification of SARSCoV2-mediated suppression of NRF2 signaling reveals a potent antiviral and anti-inflammatory activity of 4-octyl-itaconate and dimethyl fumarate. Delgado-Roche L, Mesta F. Oxidative stress as key player in severe acute respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus SARSCoV infection. Arch Med Res. Ntyonga-Pono MP. COVID infection and oxidative stress: an under-explored approach for prevention and treatment? Pan Afr Med J. Lin CW, Lin KH, Hsieh TH, Shiu SY, Li JY. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 3C-like protease-induced apoptosis. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. Wu YH, Tseng CP, Cheng ML, Ho HY, Shih SR, Chiu DTY. Glucosephosphate dehydrogenase deficiency enhances human coronavirus E infection. J Infect Dis. Bell TJ, Brand OJ, Morgan DJ, Salek-Ardakani S, Jagger C, Fujimori T, et al. Defective lung function following influenza virus is due to prolonged, reversible hyaluronan synthesis. Matrix Biol J Int Soc Matrix Biol. Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, Zhu F, Liu X, Zhang J, et al. Clinical characteristics of hospitalized patients with novel coronavirus—infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. Xu Z, Shi L, Wang Y, Zhang J, Huang L, Zhang C, et al. Pathological findings of COVID associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Respir Med. Hällgren R, Samuelsson T, Laurent TC, Modig J. Accumulation of hyaluronan hyaluronic acid in the lung in adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. Read SA, Obeid S, Ahlenstiel C, Ahlenstiel G. The role of zinc in antiviral immunity. Adv Nutr. Biaggio VS, Pérez Chaca MV, Valdéz SR, Gómez NN, Gimenez MS. Alteration in the expression of inflammatory parameters as a result of oxidative stress produced by moderate zinc deficiency in rat lung. Exp Lung Res. Bao S, Knoell DL. Zinc modulates cytokine-induced lung epithelial cell barrier permeability. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. Liu MJ, Bao S, Napolitano JR, Burris DL, Yu L, Tridandapani S, et al. Zinc regulates the acute phase response and serum amyloid a production in response to sepsis through JAKSTAT3 signaling. PLoS ONE. Ishida T. Am J Biomed Sci Res. Speth R, Carrera E, Jean-Baptiste M, Joachim A, Linares A. Concentration-dependent effects of zinc on angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 activity FASEB J. te Velthuis AJW, van den Worm SHE, Sims AC, Baric RS, Snijder EJ, van Hemert MJ. PLoS Pathog. Hemilä H, Fitzgerald JT, Petrus EJ, Prasad A. Zinc acetate lozenges may improve the recovery rate of common cold patients: an individual patient data meta-analysis. Open Forum Infect Dis. Roth DE, Richard SA, Black RE. Zinc supplementation for the prevention of acute lower respiratory infection in children in developing countries: meta-analysis and meta-regression of randomized trials. Int J Epidemiol. Zhang L, Liu Y. Potential interventions for novel coronavirus in China: a systematic review. J Med Virol. Prietl B, Treiber G, Pieber TR, Amrein K. Vitamin D and immune function. Wimalawansa SJ. Vitamin D deficiency: effects on oxidative stress, epigenetics, gene regulation, and aging. Chen Y, Zhang J, Ge X, Du J, Deb DK, Li YC. Vitamin D receptor inhibits nuclear factor κB activation by interacting with IκB kinase β protein. J Biol Chem. Lemire JM, Archer DC, Beck L, Spiegelberg HL. Immunosuppressive actions of 1,dihydroxyvitamin D3: preferential inhibition of Th1 functions. J Nutr. Jeffery LE, Burke F, Mura M, Zheng Y, Qureshi OS, Hewison M, et al. J Immunol Baltim Md Monlezun DJ, Bittner EA, Christopher KB, Camargo CA, Quraishi SA. Vitamin D status and acute respiratory infection: cross sectional results from the United States National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, Zdrenghea MT, Makrinioti H, Bagacean C, Bush A, Johnston SL, Stanciu LA. Vitamin D modulation of innate immune responses to respiratory viral infections. Rev Med Virol. Abu-Mouch S, Fireman Z, Jarchovsky J, Zeina AR, Assy N. Vitamin D supplementation improves sustained virologic response in chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 -naïve patients. World J Gastroenterol. Ginde AA, Blatchford P, Breese K, Zarrabi L, Linnebur SA, Wallace JI, et al. High-dose monthly vitamin D for prevention of acute respiratory infection in older long-term care residents: a randomized clinical trial. J Am Geriatr Soc. Behera MK, Shukla SK, Dixit VK, Nath P, Abhilash VB, Asati PK, et al. Indian J Med Res. Nimer A, Mouch A. Vitamin D improves viral response in hepatitis C genotype naïve patients. World J Gastroenterol WJG. Charan J, Goyal JP, Saxena D, Yadav P. Vitamin D for prevention of respiratory tract infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. Goncalves-Mendes N, Talvas J, Dualé C, Guttmann A, Corbin V, Marceau G, et al. Impact of vitamin D supplementation on influenza vaccine response and immune functions in deficient elderly persons: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Front Immunol. Carr AC, Maggini S. Vitamin C and immune function. van Driel ML, Beller EM, Thielemans E, Deckx L, Price-Haywood E, Clark J, et al. Oral vitamin C supplements to prevent and treat acute upper respiratory tract infections. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. Vázquez-Fresno R, Rosana ARR, Sajed T, Onookome-Okome T, Wishart NA, Wishart DS. Herbs and spices- biomarkers of intake based on human intervention studies — a systematic review. Genes Nutr. USDA National Nutrient Database. Foods highest in Vitamin C and Iron in Spices and Herbs. html accessed May 27, Google Scholar. Traber MG, Stevens JF. Vitamins C and E: beneficial effects from a mechanistic perspective. Free Radic Biol Med. Colunga Biancatelli RML, Berrill M, Catravas JD, Marik PE. Quercetin and vitamin C: an experimental, synergistic therapy for the prevention and treatment of SARSCoV-2 related disease COVID Hunt C, Chakravorty NK, Annan G, Habibzadeh N, Schorah CJ. The clinical effects of vitamin C supplementation in elderly hospitalised patients with acute respiratory infections. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. PubMed Abstract Google Scholar. Catanzaro M, Corsini E, Rosini M, Racchi M, Lanni C. Immunomodulators inspired by nature: a review on curcumin and echinacea. Jin CY, Lee JD, Park C, Choi YH, Kim GY. Curcumin attenuates the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglia. Acta Pharmacol Sin. Cho JW, Lee KS, Kim CW. Curcumin attenuates the expression of IL-1beta, IL-6, and TNF-alpha as well as cyclin E in TNF-alpha-treated HaCaT cells; NF-kappaB and MAPKs as potential upstream targets. Int J Mol Med. Ghosh S, Banerjee S, Sil PC. The beneficial role of curcumin on inflammation, diabetes and neurodegenerative disease: a recent update. Food Chem Toxicol. Chen TY, Chen DY, Wen HW, Ou JL, Chiou SS, Chen JM, et al. Inhibition of enveloped viruses infectivity by curcumin. Zahedipour F, Hosseini SA, Sathyapalan T, Majeed M, Jamialahmadi T, Al-Rasadi K, et al. Potential effects of curcumin in the treatment of COVID infection. |
und etwas ähnlich ist?