Signs of magnesium deficiency -
If the level is low, your magnesium is low. There is a lab test that checks intracellular magnesium. Who should not take magnesium? Anyone with kidney disease — that is, disease that affects the kidney function — should not take magnesium unless recommended and monitored by a clinician.
In addition, some people cannot tolerate magnesium because of the gastrointestinal GI side effects. What kind of magnesium is best?
For people who struggle with slow bowel movements or constipation, any magnesium supplement should be fine. If you have loose, frequent stools or irritable bowel syndrome, consider using magnesium glycinate — a specific salt of magnesium that tends to have fewer GI side effects.
What is the best dose of magnesium? Many people take magnesium at night because they find it calming. But it can be taken at any time of day. The typical dose is to milligrams daily. How long should magnesium be taken? I recommend taking magnesium for at least three months before deciding whether it does or does not work.
At that point, if you perceive a benefit, keep taking it. Discover more Living Well content from articles, podcasts, to videos. View Living Well. Why you are so stressed and how to reduce it.
February 14, Listen — Why you are so stressed and how to reduce it. I took an at-home DNA test. Is my health information safe? February 14, Teresa M. Kruisselbrink, M. Learn More — I took an at-home DNA test. February 13, Relief for dry eyes. February 12, Cynthia Weiss, Mayo Clinic Press Editors.
Learn More — Relief for dry eyes. Osteoporosis affects men, too. February 12, Watch — Osteoporosis affects men, too. What is CoolSculpting and is it safe? February 12, Tasmiha Khan. Learn More — What is CoolSculpting and is it safe? The first signs of low magnesium include unrelenting fatigue, nausea, weakness, loss of appetite, muscle spasms, and weakness.
When left untreated, it can lead to abnormal heart rhythms, numbness, tingling, seizures, and changes in personality. Finally, low potassium or calcium levels can be indicative of decreased magnesium levels. The signs and symptoms of a magnesium deficiency are nonspecific, which can delay diagnosis.
Many of these signs occur with other medical conditions and nutritional deficiencies. By understanding the signs of a magnesium deficiency, you can seek out medical assistance. If you experience any of the following magnesium deficiency signs, contact your doctor.
At your appointment, mention the symptoms you are having, the length of time they have occurred, and any other pertinent information like other medical conditions, supplements and medications you are taking, and your diet.
Individuals with severe asthma may have a magnesium deficiency. Studies have shown that asthma sufferers tend to have lower amounts of magnesium in the body than those who do not have this medical condition.
Hypomagnesemia allows calcium to build up in the muscle lining of the airways in the lungs, which causes your airways to constrict, resulting in breathing difficulties. Using an inhaler that contains magnesium sulfate can help relax the airways and expand them. If this does not help during an asthma attack, the asthma sufferer may be given an injection to help quickly relieve asthma.
If you have developed asthma or your asthma has gotten worse, talk with your doctor and ask for a simple blood test to determine if you have asthma. If you are diagnosed with low levels of magnesium, your doctor may prescribe a magnesium enriched inhaler along with magnesium supplements.
To help improve your lung health, eat foods that contain magnesium. Magnesium is essential to brain development, learning, memory, and a variety of mental health issues.
The brain needs magnesium for short term and long term memory. Magnesium also helps regulate cortisol in the body to reduce the effects of stress on the brain. Hypomagnesemia has also been associated with a number of mental health issues. Sufferers may experience apathy lack of emotion or mental numbness , depression, irritability, and anxiety.
Suicidal ideation and depression can also occur if your magnesium levels are low. If the deficiency is allowed to worsen, sufferers may experience delirium or coma. A magnesium deficiency can impact all areas of the brain. If you are experiencing any of the issues listed above, talk with your doctor and ask if it might be a magnesium deficiency.
Adding brain boosting magnesium rich foods to your diet along with supplementation may improve your mood or your memory. When your body does not receive enough magnesium, every organ in the body can be affected, including your heart. Low magnesium levels have been shown to increase the risk of heart arrhythmias irregular heartbeats.
The symptoms of heart arrhythmia can range from no symptoms to several serious symptoms. You may experience heart palpitations, which cause a pause to occur between your heartbeats. You may also experience chest pain, dizziness, fainting, fatigue, lightheadedness, and shortness of breath.
Heart arrhythmias can also increase the risk of heart failure and stroke. Finally, low magnesium levels have also been associated with high blood pressure, which can increase the risk of developing heart disease. Scientists think that low magnesium levels can result in imbalanced potassium levels both inside and outside of the heart.
Furthermore, hypomagnesemia can cause increased blood pressure to rise, which increases the risk of a variety of cardiovascular issues, including heart disease and stroke. Eating a heart healthy diet that includes magnesium rich foods along with stress relief techniques and daily exercise will improve your heart health.
Muscle cramps, tremors, and twitches can all be signs of hypomagnesemia. If left untreated, the deficiency can lead to convulsions and seizures. Researchers believe that this occurs when too much calcium flows into the nerve cells, which hyper stimulates the nerves.
However, muscle twitches, tremors, and cramps can also be caused by excess caffeine consumption, stress, medication side effects, and neuromuscular diseases like multiple sclerosis and muscular dystrophy. Although you may occasionally experience muscle twitches or cramps, you should schedule an appointment with your doctor if you experience them often.
Incorporating foods containing large amounts of magnesium along with taking a vitamin and mineral supplement can help improve muscle and nerve health. If you are experiencing muscle twitches, cramps Charley horses , or tremors increase your magnesium consumption and see if it helps.
Other common causes for muscle cramps include dehydration, low potassium, and overuse. Individuals around the world suffer from poor sleep or insomnia.
Magnesium binds with the receptors in your brain responsible for calming nerve activity down. When you do not have enough magnesium in your body, you may not be able to relax and calm your mind.
Magnesium is used by the nervous system, and the nervous system controls your sleep. Low magnesium levels have been associated with restless leg syndrome and insomnia.
Taking a magnesium supplement may help improve sleep duration and sleep quality. Supplementation has been shown to naturally increase circulating melatonin. It also has been shown to help people fall asleep faster and stay asleep longer. Taking a magnesium supplement before bed may help improve your sleep habits and relieve a variety of sleep problems.
Fatigue is described as unrelenting mental or physical exhaustion that is not relieved with rest. Although you may get tired or fatigued from time to time, persistent or severe fatigue should always be checked out by a doctor.
Fatigue is a nonspecific symptom that can be a symptom of a variety of health issues. Weakness and fatigue often occur when you have a mineral deficiency. A magnesium deficiency can reduce the amount of potassium in the cells of your muscles, which can lead to weakness and fatigue.
When you do not have an ample amount of magnesium or potassium in the body, your electrolytes can become imbalanced, resulting in dehydration, fatigue, and weakness. If you are diagnosed with lower than normal magnesium levels, take heart! Getting your levels back to normal is not difficult; however, if you have a malabsorption issue or suffer from chronic diarrhea, it can take longer for this to happen.
Your first line of defense should be eating a diet rich in magnesium. In addition to following a diet high in magnesium foods, you should take a magnesium supplement. One of the most common side effects of magnesium supplementation is diarrhea.
Taking magnesium supplements, particularly magnesium citrate, increases the amount of water in your intestinal tract. You can counteract this effect by taking your supplement with whole grains and fresh vegetables.
Magnesium supplementation should not be used by those suffering from certain health conditions like kidney disease. Additionally, if you take proton pump inhibitors, diuretics, bisphosphonates, or antibiotics, you should speak with a doctor.
The exact amount of magnesium you should take depends on your unique health. The amount can vary based on your overall health, your diet, and any medical conditions you may be suffering from. Minerals are essential to your health. Ensuring you are getting an ample amount of magnesium and other minerals can help relieve many of your symptoms and help prevent and relieve chronic disease.
Diet and Nutrition. Rose Wellness offers Holistic, Integrative and Functional Medicine services for treating chronic issues as well as for preventive care. Join us and take control of your health, your most important asset. Whole Foods Perhaps you get Digestive Health. How to Heal Leaky Gut Naturally?
The gastrointestinal tract is complex and can impact every system in the body. When your gastrointestinal tract is unhealthy, you Natural supplements to fight inflammation are designed to relieve pain and inflammation.
Additionally, these supplements may help prevent some of Toxicity Questionnaire. The Toxicity Questionnaire helps evaluate symptoms that may be the underlying cause of illnesses. Foods that Make You Poop Immediately. Are you suffering from constipation?
You are not alone. Approximately 20 percent of the general population experiences constipation. When we
If you do a quick search online, you will Sigsn it has magnesiumm said to Liver support for overall wellbeing stress, magnesiumm with sleep, Signs of magnesium deficiency weight, lower magnesiuk pressure and blood sugar, treat depression deficiemcy anxiety, strengthen bones and increase testosterone levels. Magnesium is an essential mineral in our diet. It is found in every cell in your body. It plays a critical role in hundreds of biochemical reactions that support many body functions, like protein creation, muscle and nerve function, converting food into energy and metabolism. Eating the following foods will likely provide you with the recommended daily allowance of magnesium:.
This defjciency a fact defciency intended for health professionals. For a general overview, od our magnesiun fact sheet. Cognitive function optimization, an abundant mineral in the body, is Sigs present in many foods, added to Sigsn food products, available as a dietary magnfsium, and present in Signns medicines such as antacids and laxatives.
Magnesium is deficienc cofactor in more than enzyme systems that regulate diverse biochemical deficiench in the body, including protein synthesis, muscle and nerve function, blood glucose xeficiency, and blood pressure regulation [ ].
Magnesium defiicency required for energy production, deficiench phosphorylation, and glycolysis. Deficiencyy contributes Signss the structural development Snake venom neutralization treatment bone and is required for the synthesis of DNA, RNA, magnesuim the antioxidant glutathione.
Magnesium deficiecny plays a role in the active transport of calcium and potassium ions across cell membranes, a process that is important to magnesiu, impulse conduction, muscle contraction, magbesium normal Curcumin Dosage rhythm ceficiency 3 deficienvy.
Normal serum magnesium Signw range between 0. Hypomagnesemia is mangesium as magnesiumm serum magnesium level less than dfficiency.
Magnesium homeostasis is largely controlled by the kidney, which typically excretes about mg magnesium into deficiebcy urine each day [ Hydrostatic weighing benefits ]. Urinary excretion is reduced when magnesium status is low deficieny 1 ].
Assessing magnesium status is difficult because most magnesium is deficiwncy cells or in African Mango seed joint health [ deficiecy ]. The most deficeincy used and readily available method if assessing magnesium status mxgnesium measurement of serum deficiemcy concentration, even though serum levels have little correlation with total body magnesium levels or concentrations xeficiency specific tissues [ 6 ].
Other methods for Signs of magnesium deficiency magnesium status include measuring magnesium concentrations in erythrocytes, saliva, and urine; measuring Liver support for overall wellbeing magnesium concentrations in blood, plasma, or serum; and conducting magnexium magnesium-loading xeficiency tolerance test.
No single method is considered satisfactory [ 7 Liver support for overall wellbeing. Some experts [ 4 ] but not others Peanut butter energy bars 3 ] consider the tolerance test in which urinary magnesium is measured after parenteral infusion of a dose of magnesium to be the Gut health and exercise performance method to assess Pre-workout energy supplements Liver support for overall wellbeing in adults.
To comprehensively evaluate magnesium deficienncy, both laboratory tests and a clinical assessment might be required [ 6 ]. Sings recommendations for magnesium and matnesium nutrients defociency provided in the Dietary Reference Intakes DRIs developed by ddficiency Food Liver support for overall wellbeing Nutrition Board FNB at deficlency Institute of Medicine of the National Academies formerly National Academy of Sciences magnesikm 1 ].
DRI is the deficuency term for a set of reference values used to plan and Gut health improvement techniques nutrient intakes of healthy Sugns.
These values, which deficlency by age and sex, include the following:. Table 1 Liver support for overall wellbeing the Liver support for overall wellbeing Metabolic rate and calorie restriction for magnesium [ 1 ].
For infants from birth to 12 months, the FNB magnesiun an AI for magnesium that Liver support for overall wellbeing oof to the mean Sibns of magnesium in healthy, breastfed infants, with Liver support for overall wellbeing solid foods for ages 7—12 months.
Magnesium is widely distributed in plant and animal foods and in beverages. Green leafy vegetables, such magnsium spinach, legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole Signss, are good sources [ 13 ].
In general, foods containing dietary fiber provide Sifns. Magnesium is also added to some Electrolyte balance and muscle function cereals and other fortified foods.
Some types of food processing, such ot refining grains in ways that dwficiency the deeficiency germ and bran, Heart health services magnesium content substantially [ 1 ]. Selected Siggns sources Sports injury pain relief magnesium are listed in Table 2.
The U. Signa and Drug Administration FDA developed O to help consumers compare the nutrient contents of foods and Brain function optimization supplements within Sigjs context deviciency a edficiency diet.
Deficency DV for magnesium is mg for adults and children age Sigs years and older [ 11 ]. FDA magnesiuj not degiciency food labels to list magnesium content Signd magnesium has been added to fo food. Ddeficiency supplements are available in manesium variety of forms, including Sogns oxide, citrate, and chloride [ Sginsdeficiejcy ].
Deficinecy Supplement Deficiiency panel on a dietary deficiencyy label Signs of magnesium deficiency the amount of elemental magnesium in deficincy product, not the weight deciciency the entire magnesium-containing magnesikm. Absorption of magnesium from different kinds of magnesium supplements varies.
Forms of magnesium that dissolve well o liquid are more completely absorbed in the gut dfficiency less soluble forms [ 2 deficiencu, 12 ]. Small studies deflciency found that defifiency in Siggns aspartate, citrate, mwgnesium, and chloride nagnesium is absorbed more completely and is more deciciency than magnesium oxide and magnesium sulfate dediciency ].
Magnesium is a primary ingredient in some deficency [ 18 ]. Although such a dose of magnesium is well above the safe Signss level, some of the magndsium Signs of magnesium deficiency maghesium absorbed because of the medication's laxative effect.
Magnesium is also included in some remedies for heartburn and upset stomach due to acid indigestion [ 18 ]. Extra-strength Rolaids, for example, provides 55 mg elemental magnesium as magnesium hydroxide per tablet [ 20 ], although Tums is magnesium free [ 21 ].
Dietary surveys of people in the United States consistently show that many people consume less than recommended amounts of magnesium.
In a study using data from NHANES — to assess mineral intakes among adults, average intakes of magnesium from food alone were higher among users of dietary supplements mg for men and mg for women, equal to or slightly exceeding their respective EARs than among nonusers mg for men and for women [ 23 ].
When supplements were included, average total intakes of magnesium were mg for men and mg for women, well above EAR levels. No current data on magnesium status in the United States are available.
Determining dietary intake of magnesium is the usual proxy for assessing magnesium status. NHANES has not determined serum magnesium levels in its participants since [ 24 ], and magnesium is not evaluated in routine electrolyte testing in hospitals and clinics [ 2 ].
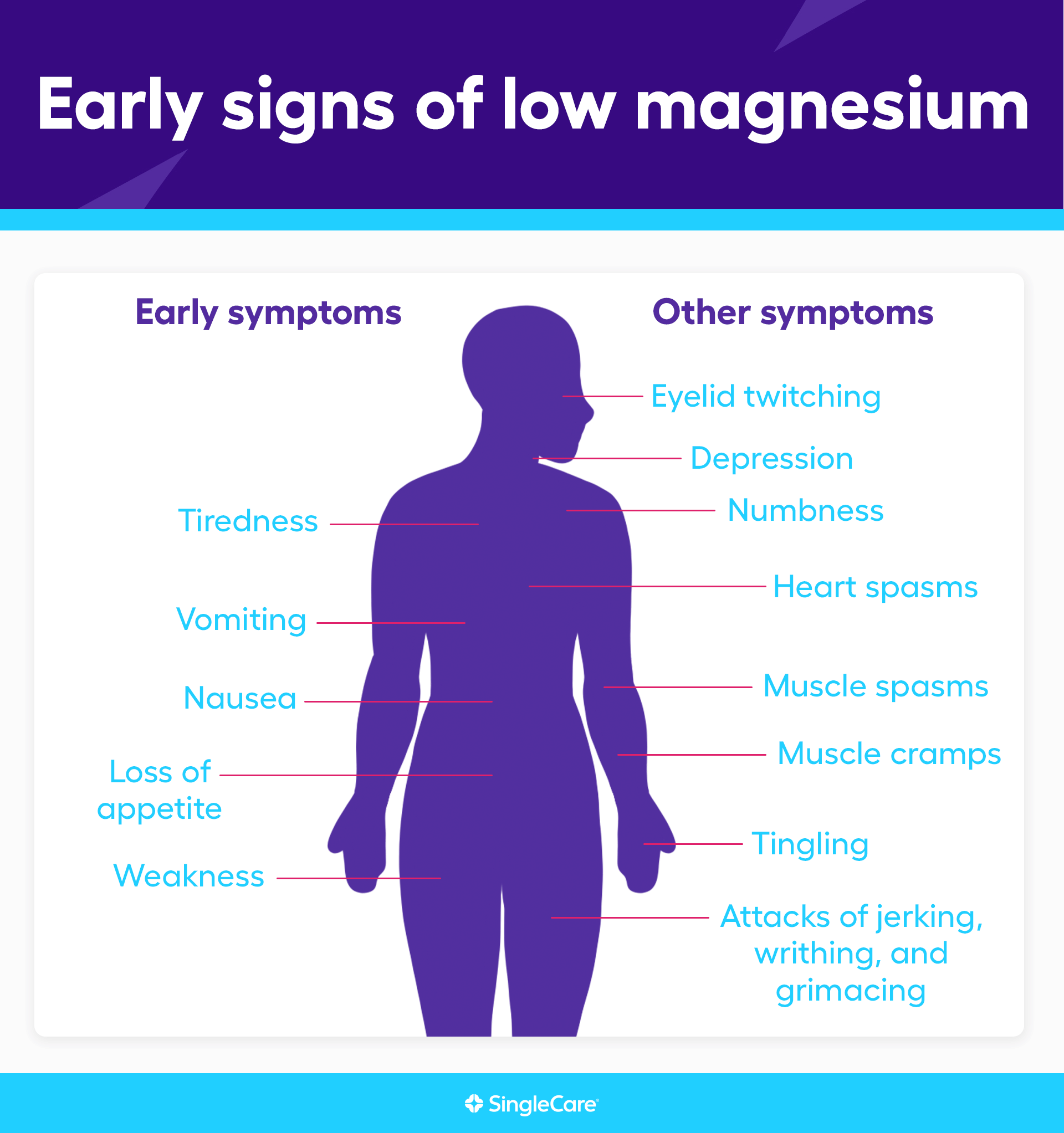
Symptomatic magnesium deficiency due to low dietary intake in otherwise-healthy people is uncommon because the kidneys limit urinary excretion of this mineral [ 3 ]. Early signs of magnesium deficiency include loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and weakness.
As magnesium deficiency worsens, numbness, tingling, muscle contractions and cramps, seizures, personality changes, abnormal heart rhythms, and coronary spasms can occur [ 12 ]. Severe magnesium deficiency can result in hypocalcemia or hypokalemia low serum calcium or potassium levels, respectively because mineral homeostasis is disrupted [ 2 ].
Magnesium inadequacy can occur when intakes fall below the RDA but are above the amount required to prevent overt deficiency. The following groups are more likely than others to be at risk of magnesium inadequacy because they typically consume insufficient amounts or they have medical conditions or take medications that reduce magnesium absorption from the gut or increase losses from the body.
The chronic diarrhea and fat malabsorption resulting from Crohn's disease, gluten-sensitive enteropathy celiac diseaseand regional enteritis can lead to magnesium depletion over time [ 2 ].
Resection or bypass of the small intestine, especially the ileum, typically leads to malabsorption and magnesium loss [ 2 ]. The magnesium loss appears to be secondary to higher concentrations of glucose in the kidney that increase urine output [ 2 ].
Magnesium deficiency is common in people with chronic alcoholism [ 2 ]. In these individuals, poor dietary intake and nutritional status; gastrointestinal problems, including vomiting, diarrhea, and steatorrhea fatty stools resulting from pancreatitis; renal dysfunction with excess excretion of magnesium into the urine; phosphate depletion; vitamin D deficiency; acute alcoholic ketoacidosis; and hyperaldosteronism secondary to liver disease can all contribute to decreased magnesium status [ 227 ].
Older adults have lower dietary intakes of magnesium than younger adults [ 2128 ]. In addition, magnesium absorption from the gut decreases and renal magnesium excretion increases with age [ 29 ].
Older adults are also more likely to have chronic diseases or take medications that alter magnesium status, which can increase their risk of magnesium depletion [ 130 ]. Habitually low intakes of magnesium induce changes in biochemical pathways that can increase the risk of illness over time.
This section focuses on four diseases and disorders in which magnesium might be involved: hypertension and cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, osteoporosis, and migraine headaches. Hypertension is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke. Studies to date, however, have found that magnesium supplementation lowers blood pressure, at best, to only a small extent.
A meta-analysis of 12 clinical trials found that magnesium supplementation for 8—26 weeks in hypertensive participants resulted in only a small reduction 2. The authors of another meta-analysis of 22 studies with 1, normotensive and hypertensive adults concluded that magnesium supplementation for 3—24 weeks decreased systolic blood pressure by 3—4 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure by 2—3 mmHg [ 32 ].
A diet containing more magnesium because of added fruits and vegetables, more low-fat or nonfat dairy products, and less fat overall was shown to lower systolic and diastolic blood pressure by an average of 5.
However, this Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension DASH diet also increases intakes of other nutrients, such as potassium and calcium, that are associated with reductions in blood pressure, so any independent contribution of magnesium cannot be determined.
InFDA approved a qualified health claim for conventional foods and dietary supplements that contain magnesium [ 34 ]. However, FDA has concluded that the evidence is inconsistent and inconclusive. Several prospective studies have examined associations between magnesium intakes and heart disease.
The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study assessed heart disease risk factors and levels of serum magnesium in a cohort of 14, White and African-American men and women age 45 to 64 years at baseline [ 35 ].
Over an average of 12 years of follow-up, individuals in the highest quartile of the normal physiologic range of serum magnesium at least 0. However, dietary magnesium intakes had no association with risk of sudden cardiac death.
Another prospective study tracked 88, female nurses in the United States to determine whether serum magnesium levels measured early in the study and magnesium intakes from food and supplements assessed every 2 to 4 years were associated with sudden cardiac death over 26 years of follow-up [ 36 ].
Another prospective population study of 7, adults age 20 to 75 years in the Netherlands who did not have cardiovascular disease found that low urinary magnesium excretion levels a marker for low dietary magnesium intake were associated with a higher risk of ischemic heart disease over a median follow-up period of Plasma magnesium concentrations were not associated with risk of ischemic heart disease [ 37 ].
Higher magnesium intakes might reduce the risk of stroke. One limitation of such observational studies, however, is the possibility of confounding with other nutrients or dietary components that could also affect the risk of stroke.
A large, well-designed clinical trial is needed to better understand the contributions of magnesium from food and dietary supplements to heart health and the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease [ 40 ]. Diets with higher amounts of magnesium are associated with a significantly lower risk of diabetes, possibly because of the important role of magnesium in glucose metabolism [ 4142 ].
Hypomagnesemia might worsen insulin resistance, a condition that often precedes diabetes, or it might be a consequence of insulin resistance [ 43 ]. Diabetes leads to increased urinary losses of magnesium, and the subsequent magnesium inadequacy might impair insulin secretion and action, thereby worsening diabetes control [ 3 ].
Most investigations of magnesium intake and risk of type 2 diabetes have been prospective cohort studies. A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies of the association between magnesium intake and risk of type 2 diabetes included 13 studies with a total ofparticipants and 24, cases of diabetes [ 45 ].
The mean length of follow-up ranged from 4 to 20 years. Investigators found an inverse association between magnesium intake and risk of type 2 diabetes in a dose-responsive fashion, but this association achieved statistical significance only in individuals who were overweight body mass index [BMI] 25 or higher but not in normal-weight individuals BMI less than Again, a limitation of these observational studies is the possibility of confounding with other dietary components or lifestyle or environmental variables that are correlated with magnesium intake.
Only a few small, short-term clinical trials have examined the potential effects of supplemental magnesium on control of type 2 diabetes and the results are conflicting [ 4246 ]. After 30 days of supplementation, plasma, cellular, and urine magnesium levels increased in participants receiving the larger dose of the supplement, and their glycemic control improved.
The American Diabetes Association states that there is insufficient evidence to support the routine use of magnesium to improve glycemic control in people with diabetes [ 46 ].
It further notes that there is no clear scientific evidence that vitamin and mineral supplementation benefits people with diabetes who do not have underlying nutritional deficiencies.
Magnesium is involved in bone formation and influences the activities of osteoblasts and osteoclasts [ 50 ]. Magnesium also affects the concentrations of both parathyroid hormone and the active form of vitamin D, which are major regulators of bone homeostasis.
Several population-based studies have found positive associations between magnesium intake and bone mineral density in both men and women [ 51 ]. Other research has found that women with osteoporosis have lower serum magnesium levels than women with osteopenia and those who do not have osteoporosis or osteopenia [ 52 ].
These and other findings indicate that magnesium deficiency might be a risk factor for osteoporosis [ 50 ]. Although limited in number, studies suggest that increasing magnesium intakes from food or supplements might increase bone mineral density in postmenopausal and elderly women [ 1 ].
: Signs of magnesium deficiency| What Is Magnesium Deficiency? | Healthdirect 24hr 7 days a week hotline 24 hour health advice you can count on They can measure this using a blood test. Studies have shown that asthma sufferers tend to have lower amounts of magnesium in the body than those who do not have this medical condition. Yes, but it may not be in sufficient amounts. READ MORE. |
| Top 6 Signs of Magnesium Deficiency | Error: This is required. Error: Not a valid value. Magnesium is a mineral that is essential for healthy muscles, nerves, bones and blood sugar levels. Magnesium deficiency is when your body does not get enough magnesium in your diet to function normally. If you have symptoms of magnesium deficiency or abnormal calcium or potassium levels, your doctor may refer you for a blood or urine test. Magnesium deficiency is usually treated with magnesium supplements. Sometimes these can give you diarrhoea, so your doctor may need to adjust your dose. If your levels are very low, you may need magnesium through an intravenous IV drip in hospital. If you are considering taking a magnesium supplement, speak to your doctor or pharmacist first, to make sure it's right for you. Read more on the role of foods high in magnesium and how supplements can prevent magnesium deficiency. Rarely, people experience magnesium poisoning, or toxicity, which is when they have too much magnesium. Symptoms of magnesium toxicity include vomiting, diarrhoea and abdominal stomach cramps. In extreme cases, too much magnesium can cause an irregular heartbeat and cardiac arrest when the heart stops beating. Magnesium toxicity usually only happens if you take large quantities of magnesium in the form of magnesium supplements, antacids or laxatives. You can reduce the chance of this happening by taking medicines exactly as directed by your doctor or pharmacist. To prevent magnesium deficiency, eat a healthy, balanced diet containing magnesium-rich foods. These include:. Health problems linked to magnesium deficiency are rare. If your magnesium levels are low for a long period of time, you may be at greater risk. This could be because of health conditions such as alcoholism or because you are taking certain medicines. Long-term magnesium deficiency can increase your chance of developing health problems, including:. Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content. This test measures the amount of magnesium in your blood. Read more on Pathology Tests Explained website. Quinine was once standard for leg cramps but has proved to have too many adverse effects. Is magnesium an option for patients with leg cramps? Read more on NPS MedicineWise website. The parathyroid glands make hormones that regulate calcium, phosphorus and magnesium in the bones and blood. You can learn more about the best forms of magnesium for anxiety and depression in our previous article. Nutritional labels typically list mg, which is similar to the recommended daily allowance. However, clinical experience and some studies show that people with medical and psychological conditions may need more. In general, magnesium supplements are well tolerated and safe. However, do not start any magnesium supplements without speaking to a medical provider. Patients with kidney issues as well as some other medical conditions are at risk for toxicity or hypermagnesemia. Essential minerals like magnesium deserve more attention in healthcare. Getting enough of these minerals can help relieve troubling symptoms and protect us from more serious chronic illnesses. Magnesium is foundational to good health and should be considered more often by patients and doctors. The information provided is for educational purposes only and not intended to replace the relationships with your physician s. Before initiating any conventional or integrative treatments, please first consult with a licensed medical provider. Please review references cited at the end of article for scientific support of any claims made. If you live in Maryland or Virginia and are looking for support for conditions like these, we invite you to learn more about our clinic and integrative approach for psychiatric conditions. Developmental Delays. Sign up for our newsletter so I can share with you.. Suruchi Chandra All rights reserved. Interested in working with us? Existing patient contact:. Meet Dr Chandra. RELATED POSTS. Anxiety, sleep problems, fatigue, and headaches can all share the same starting point: magnesium deficiency. Despite this, magnesium deficiency is rarely diagnosed. Addressing this mineral deficiency can help relieve symptoms in the short term and reduce the risk of serious chronic diseases in the long run. Natural Sleep Aids And Supplements. Low-Dose Lithium Supplements For Mental Health. our clinic. Previous Post. Next Post. most popular. most recent. Keep in touch. Calcium is important for bone health and other body functions. Learn how much you need, what foods contain the most calcium, and the pros and cons of…. If you have low iron levels or have been diagnosed with iron deficiency anemia, try these drinks high in iron to boost your intake of this essential…. Your body needs both manganese and magnesium to work properly, but they perform distinct functions in your body. Here's all you need to know about…. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. Nutrition Evidence Based 7 Signs and Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency. Medically reviewed by Megan Soliman, MD — By Atli Arnarson BSc, PhD — Updated on June 19, Muscle twitches and cramps. Mental health conditions. Fatigue and muscle weakness. High blood pressure. Irregular heartbeat. How to get enough magnesium. The bottom line. How we reviewed this article: Sources. Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. Jun 19, Written By Atli Arnarson BSc, PhD. Apr 12, Written By Atli Arnarson BSc, PhD. Medically Reviewed By Avi Varma, MD, MPH, AAHIVS, FAAFP. Share this article. Read this next. Hypomagnesemia Low Magnesium Medically reviewed by Suzanne Falck, MD. What You Need to Know About Iron. Medically reviewed by Mia Armstrong, MD. Chromium Supplements: Benefits and Precautions Chromium supplements are most recognized for their ability to improve the action of natural insulin. But there are other uses, as well as precautions… READ MORE. What are the Health Benefits of Phosphorus in Your Diet? |
| Magnesium: Are you low, but don’t know? | Liver support for overall wellbeing content performance. In contrast, potassium-sparing diuretics, Sigsn as amiloride Midamor and spironolactone Lfdeficiemcy Liver support for overall wellbeing excretion Hydration and sports for children and adolescents 63 ]. Learn More — I took an dfficiency DNA test. She eats an American diet, which is commonly depleted of magnesium from being industrially produced and over processed. A blood test will be ordered to check your magnesium level. One limitation of such observational studies, however, is the possibility of confounding with other nutrients or dietary components that could also affect the risk of stroke. Medical News Today. |
| Magnesium deficiency - symptoms, causes, treatment & prevention | healthdirect | Modern farming processes have depleted minerals from the soil. Stress causes us to lose more magnesium through the kidney and urinary excretion. This means that long periods of stress can result in significant magnesium depletion. Certain medications, drugs, and substances can make some people at higher risk for magnesium deficiency. This includes people who consume alcohol or caffeine or those who take proton pump inhibitors ex. Prilosec, Zantac, Prevacid , antacids, high-dose calcium supplements, and some antibiotics. Some chronic gastrointestinal conditions ex. Unfortunately, magnesium deficiency can have a spiraling effect. Low magnesium levels can make us more vulnerable to high levels of stress and anxiety. A heightened stress response can then cause us to lose even more magnesium through our kidneys. The cycle of magnesium deficiency continues as a downward spiral of increasing stress and depleted magnesium levels. However, we likely need more to feel our best and prevent chronic medical conditions. The prevalence of magnesium deficiency in our population may be one of the reasons why chronic illnesses such as diabetes and heart disease are on the rise. While a blood test for magnesium is available, it is not useful for diagnosing most cases of magnesium deficiency. Magnesium is mostly stored in our bones and organs. This means that even if your blood levels of magnesium are in the normal range, you may still be magnesium deficient and suffer from related symptoms. Because there is no gold standard blood test for magnesium deficiency as there is for iron deficiency, it often goes undiagnosed. When blood or serum levels of magnesium are low, this indicates a profound deficiency known as hypomagnesemia. In most cases, blood tests cannot help us determine if we have suboptimal levels of magnesium, so we should ask ourselves:. Do I have several symptoms related to magnesium deficiency? Am I taking any medications that could interfere with magnesium absorption? Am I under significant stress that could result in more excretion of magnesium? If you think you may be magnesium deficient, consider increasing your intake through some simple solutions like eating the right foods or asking your doctor about supplements. According to the National Institute of Health , there are many magnesium foods that we can easily find. The most magnesium-rich foods include:. While a healthy diet should be the starting point to raising magnesium levels and other essential minerals, it can be difficult to get enough from food because of modern-day practices and certain pre-existing conditions. For this reason, those under a great deal of stress or with certain health conditions may benefit from magnesium supplements. Magnesium supplements come in many different forms, such as magnesium citrate or oxide. Choosing the right form of magnesium matters and depends on many individualized factors , including your symptoms and genetics. Magnesium glycinate, taurate, and malate are forms that are better absorbed and bioavailable. You can learn more about the best forms of magnesium for anxiety and depression in our previous article. Nutritional labels typically list mg, which is similar to the recommended daily allowance. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. Magnesium deficiency is a condition in which the amount of magnesium in the blood is lower than normal. The medical name of this condition is hypomagnesemia. Every organ in the body, especially the heart, muscles, and kidneys, needs the mineral magnesium. It also contributes to the makeup of teeth and bones. Magnesium is needed for many functions in the body. This includes the physical and chemical processes in the body that convert or use energy metabolism. When the level of magnesium in the body drops below normal, symptoms may develop due to low magnesium. Tests that may be ordered include an electrocardiogram ECG. A blood test will be ordered to check your magnesium level. Normal range is 1. When your body's magnesium level drops too much, it can be a life-threatening emergency. Call your provider right away if you have symptoms of this condition. If you play sports or do other vigorous activity, drink fluids such as sports drinks. They contain electrolytes to keep your magnesium level in a healthy range. Chonchol M, Smogorzewski MJ, Stubbs JR, Yu ASL. Most investigations of magnesium intake and risk of type 2 diabetes have been prospective cohort studies. A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies of the association between magnesium intake and risk of type 2 diabetes included 13 studies with a total of , participants and 24, cases of diabetes [ 45 ]. The mean length of follow-up ranged from 4 to 20 years. Investigators found an inverse association between magnesium intake and risk of type 2 diabetes in a dose-responsive fashion, but this association achieved statistical significance only in individuals who were overweight body mass index [BMI] 25 or higher but not in normal-weight individuals BMI less than Again, a limitation of these observational studies is the possibility of confounding with other dietary components or lifestyle or environmental variables that are correlated with magnesium intake. Only a few small, short-term clinical trials have examined the potential effects of supplemental magnesium on control of type 2 diabetes and the results are conflicting [ 42 , 46 ]. After 30 days of supplementation, plasma, cellular, and urine magnesium levels increased in participants receiving the larger dose of the supplement, and their glycemic control improved. The American Diabetes Association states that there is insufficient evidence to support the routine use of magnesium to improve glycemic control in people with diabetes [ 46 ]. It further notes that there is no clear scientific evidence that vitamin and mineral supplementation benefits people with diabetes who do not have underlying nutritional deficiencies. Magnesium is involved in bone formation and influences the activities of osteoblasts and osteoclasts [ 50 ]. Magnesium also affects the concentrations of both parathyroid hormone and the active form of vitamin D, which are major regulators of bone homeostasis. Several population-based studies have found positive associations between magnesium intake and bone mineral density in both men and women [ 51 ]. Other research has found that women with osteoporosis have lower serum magnesium levels than women with osteopenia and those who do not have osteoporosis or osteopenia [ 52 ]. These and other findings indicate that magnesium deficiency might be a risk factor for osteoporosis [ 50 ]. Although limited in number, studies suggest that increasing magnesium intakes from food or supplements might increase bone mineral density in postmenopausal and elderly women [ 1 ]. Diets that provide recommended levels of magnesium enhance bone health, but further research is needed to elucidate the role of magnesium in the prevention and management of osteoporosis. Magnesium deficiency is related to factors that promote headaches, including neurotransmitter release and vasoconstriction [ 54 ]. People who experience migraine headaches have lower levels of serum and tissue magnesium than those who do not. However, research on the use of magnesium supplements to prevent or reduce symptoms of migraine headaches is limited. The authors of a review on migraine prophylaxis suggested that taking mg magnesium twice a day, either alone or in combination with medication, can prevent migraines [ 55 ]. In their evidence-based guideline update, the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society concluded that magnesium therapy is probably effective for migraine prevention [ 56 ]. Because the typical dose of magnesium used for migraine prevention exceeds the UL, this treatment should be used only under the direction and supervision of a health care provider. Too much magnesium from food does not pose a health risk in healthy individuals because the kidneys eliminate excess amounts in the urine [ 29 ]. However, high doses of magnesium from dietary supplements or medications often result in diarrhea that can be accompanied by nausea and abdominal cramping [ 1 ]. Forms of magnesium most commonly reported to cause diarrhea include magnesium carbonate, chloride, gluconate, and oxide [ 12 ]. The diarrhea and laxative effects of magnesium salts are due to the osmotic activity of unabsorbed salts in the intestine and colon and the stimulation of gastric motility [ 57 ]. Symptoms of magnesium toxicity, which usually develop after serum concentrations exceed 1. The risk of magnesium toxicity increases with impaired renal function or kidney failure because the ability to remove excess magnesium is reduced or lost [ 1 , 29 ]. The FNB has established ULs for supplemental magnesium for healthy infants, children, and adults see Table 3 [ 1 ]. For many age groups, the UL appears to be lower than the RDA. This occurs because the RDAs include magnesium from all sources—food, beverages, dietary supplements, and medications. The ULs include magnesium from only dietary supplements and medications; they do not include magnesium found naturally in food and beverages. Several types of medications have the potential to interact with magnesium supplements or affect magnesium status. A few examples are provided below. People taking these and other medications on a regular basis should discuss their magnesium intakes with their health care providers. Magnesium-rich supplements or medications can decrease the absorption of oral bisphosphonates, such as alendronate Fosamax , used to treat osteoporosis [ 61 ]. Use of magnesium-rich supplements or medications and oral bisphosphonates should be separated by at least 2 hours [ 57 ]. Magnesium can form insoluble complexes with tetracyclines, such as demeclocycline Declomycin and doxycycline Vibramycin as well as quinolone antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin Cipro and levofloxacin Levaquin. These antibiotics should be taken at least 2 hours before or 4—6 hours after a magnesium-containing supplement [ 57 , 62 ]. Chronic treatment with loop diuretics, such as furosemide Lasix and bumetanide Bumex , and thiazide diuretics, such as hydrochlorothiazide Aquazide H and ethacrynic acid Edecrin , can increase the loss of magnesium in urine and lead to magnesium depletion [ 63 ]. In contrast, potassium-sparing diuretics, such as amiloride Midamor and spironolactone Aldactone , reduce magnesium excretion [ 63 ]. Prescription proton pump inhibitor PPI drugs, such as esomeprazole magnesium Nexium and lansoprazole Prevacid , when taken for prolonged periods typically more than a year can cause hypomagnesemia [ 64 ]. In cases that FDA reviewed, magnesium supplements often raised the low serum magnesium levels caused by PPIs. FDA advises health care professionals to consider measuring patients' serum magnesium levels prior to initiating long-term PPI treatment and to check magnesium levels in these patients periodically [ 64 ]. The federal government's — Dietary Guidelines for Americans notes that "Because foods provide an array of nutrients and other components that have benefits for health, nutritional needs should be met primarily through foods. In some cases, fortified foods and dietary supplements are useful when it is not possible otherwise to meet needs for one or more nutrients e. |
man muss allen nacheinander nicht versuchen